 Addressing Modes Introduction
Addressing Modes Introduction
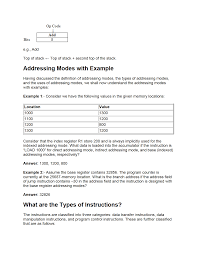
○Examples. »COM : Complement Accumulator. ▫Operand in AC is implied in the Explain different types of Addressing modes in 8085 and. 8086 micro processor.
 Addressing Modes of 8086
Addressing Modes of 8086
Thus addressing modes describe the types of operands and the way they are accessed For example the arithmetic
 Data Types and Addressing Modes 29
Data Types and Addressing Modes 29
A byte is eight bits a word is 2 bytes (16 bits)
 Addressing Modes Notes PDF
Addressing Modes Notes PDF
Implicit: The opcode itself specifies the addressing mode used. •. Explicit: The mode field is used in the instruction format to specify the type of addressing
 8085 Addressing Modes & Interrupts
8085 Addressing Modes & Interrupts
• Vector interrupt − In this type of interrupt the interrupt address is known to the processor. For example: RST7.5
 Addressing Modes
Addressing Modes
Each of the instruction contains operations and operands. • Operation specifies the type of action to be performed. • For example: ADD SUB
 Lecture 4: Addressing modes
Lecture 4: Addressing modes
g An instruction in the MC68000 contains two types of information n The type g Example n The contents of A3 are copied onto A0. INSTRUCTION. MOVEA.L A3A0.
 8086 Addressing Modes
8086 Addressing Modes
Program Memory addressing Modes: This mode involves program memory addresses during various operations. Example: JMP AX in this instruction
 Addressing Modes
Addressing Modes
• Available addressing modes depend on the address size used. ∗ 16-bit modes Example 3: Address and data size override mov EAX[EBX*ESI+2] ==> 66
 Addressing Modes
Addressing Modes
itself specify the operands implicitly. It is also called as implicit addressing mode. Examples-. • The instruction “Complement Accumulator” is an implied mode
 Addressing Modes
Addressing Modes
?Zero address instruction in stack are implied mode ?Example : LD ADR. ADR = Address part ... Explain different types of Addressing modes in 8085 and.
 Addressing Modes and Formats Computer Organization and
Addressing Modes and Formats Computer Organization and
Instruction Sets: Addressing Modes and. Formats Different types of addresses involve tradeoffs ... Example Intel direct address instructions.
 4. Addressing modes
4. Addressing modes
Efficient access to data of various sizes is so important that modern machines (32 bit machines) provide access to byte (8 bits) half-word (16 bits)
 1. Instruction Formats One address. Two address. Zero address
1. Instruction Formats One address. Two address. Zero address
2. Addressing modes with numeric examples. 3. Program control. Status bit conditions. Conditional branch instructions. 4. Program interrupts. 5. Types of
 Data Types and Addressing Modes 29
Data Types and Addressing Modes 29
The fundamental data types of the Intel Architecture are bytes words
 Addressing Modes
Addressing Modes
two classes of comparison codes? — G L
 Addressing Modes
Addressing Modes
Examples. » Sum of 1-d array. » Sum of a column in a 2-d array. • Recursion. ? Examples Pentium offers several addressing modes to access.
 1. Addressing Modes
1. Addressing Modes
Addressing modes. Example. Instruction. Meaning. When used. Register. Add R4R3 A type of architecture that is based on a single computing unit.
 MSP430 addressing modes
MSP430 addressing modes
@Rn. Register indirect. The operand is in memory at the address held in Rn. 11. -. s n ? 0 2
 Addressing Modes - Carleton University
Addressing Modes - Carleton University
• Addressing modes • Simple addressing modes ? Register addressing mode ? Immediate addressing mode • Memory addressing modes ? 16-bit and 32-bit addressing » Operand and address size override prefixes ? Direct addressing ? Indirect addressing ? Based addressing ? Indexed addressing ? Based-indexed addressing • Examples
 Addressing Modes: Definition Types & Examples - Studycom
Addressing Modes: Definition Types & Examples - Studycom
The most used addressing modes are presented below; a left arrow meansassignment and M stands for memory We use an array notation formemory because we can view the memory as an array of bytes (or half-words or words whichever you prefer but the signi?cance of the notationmust be very clear) Register
 Addressing Modes Introduction
Addressing Modes Introduction
Application of Addressing Modes The 8085 has the following 5 different types of addressing 1 Immediate Addressing 2 Direct Addressing 3 Register Addressing 4 Register Indirect Addressing 5 Implied Addressing
 Searches related to types of addressing modes with examples pdf PDF
Searches related to types of addressing modes with examples pdf PDF
addressing modes Assembly Language Addressing Modes • Memory is accessed by calculating its effective address using the distance (or offset) of the data from the beginning of a segment (usually the data segment) • Memory Addressing modes: Direct Register Indirect Based or Indexed Base-indexed Base-indexed with displacement
Immediate
With immediate addressingmode, the actual data to be used as the operand is included in the instruction itself. Let's say we want to store operand 1 into a register and then add operand 2. With immediate addressing mode, the data values 1 and 2 would be part of the instruction itself as shown below. This would be a relatively fast option since ther...
Direct Addressing
When using direct addressing mode, the address of the operand is specified in the instruction. The processor will retrieve the data directly from the address specified in the instruction. In this figure, the example shows how the instruction tells the processor where to get the data from in memory. The variable addr_of_2is a pointer to the effectiv...
What are the different types of addressing modes?
Let's take a look at the different types of addressing modes, one at a time now. 1. Immediate With immediate addressing mode, the actual data to be used as the operand is included in the instruction itself. Let's say we want to store operand 1 into a register and then add operand 2.
What is direct addressing mode?
Direct Addressing Mode- The address field of the instruction contains the effective address of the operand. Only one reference to memory is required to fetch the operand. It is also called as absolute addressing mode. ADD X will increment the value stored in the accumulator by the value stored at memory location X. 5. Indirect Addressing Mode-
What is register addressing mode?
Register addressing mode indicates the operand data is stored in the register itself, so the instruction contains the address of the register. The data would be retrieved from the register. Here's how this would work: Figure 3. Register Retrieving data from the register is fast and the instructions are shorter because no memory is involved.
What is memory addressing mode?
The addressing mode specifies a rule for interpreting or modifying the address field of the instruction before the operand is actually executed. The 8086 memory addressing modes provide flexible access to memory, allowing you to easily access variables, arrays, records, pointers, and other complex data types.
Addressing Modes
Er. Anshu Singh
Assistant Professor
Computer Science & Engineering Department
University of Lucknow
Lucknow
Branch: BCA
Semester: 3
Subject: Computer Architecture
Disclaimer: The e-content is exclusively meant for academic purposes and for enhancing teaching and learning. Any other use for economic/commercial purpose is strictly prohibited. The users of the content shall not distribute, disseminate or share it with anyone else and its use is restricted to advancement of individual knowledge. The information provided in this e-content is developed from authentic references, to the best of my knowledge.Addressing Modes-
The different ways of specifying the location of an operand in an instruction are called as addressing modes.1. Implied / Implicit Addressing Mode
2. Stack addressing mode
3. Immediate Addressing Mode
4. Direct Addressing Mode
5. Indirect Addressing Mode
6. Register Direct Addressing Mode
7. Register Indirect Addressing Mode
8. Relative Addressing Mode
9. Indexed Addressing Mode
10. Base Register Addressing Mode
11. Auto-Increment Addressing Mode
12. Auto-Decrement Addressing Mode
Implied Addressing Mode-In this addressing mode, the definition of the instruction itself specify the operands implicitly. It is also called as implicit addressing mode.Examples-
In a stack organized computer, Zero Address Instructions are implied mode instructions. (since operands are always implied to be present on the top of the stack) Stack Addressing Mode-In this addressing mode, the operand is contained at the top of the stack.Example- ADD
This instruction simply pops out two symbols contained at the top of the stack.The addition of those two operands is performed.
The result so obtained after addition is pushed again at the top of the stack. Immediate Addressing Mode- In this addressing mode, the operand is specified in theinstruction explicitly. Instead of address field, an operand field is present that contains the operand.
Examples-
ADD 10 will increment the value stored in the accumulator by 10. MOV R #20 initializes register R to a constant value 20. Direct Addressing Mode- In this addressing mode, the address field of the instruction contains the effective address of the operand. Only one reference to memory is required to fetch the operand. It is also called as absolute addressing mode. AMemory
Example-
ADD X will increment the value stored in the accumulator by the value stored at memory location X.AC ін
Indirect Addressing Mode- In this addressing mode, the address field of the instruction specifies the address of memory location that contains the effective address of the operand. Two references to memory are required to fetch the operand. 100200
Example-
ADD X will increment the value stored in the accumulator by the value stored at memory location specified by X.AC ін
operand opcode A EA operand opcode A 200operand opcode 100 Register Direct Addressing Mode- In this addressing mode, the operand is contained in a
register set. The address field of the instruction refers to a CPU register that contains the operand.
No reference to memory is required to fetch the operand. RRegister set
Example-
ADD R will increment the value stored in the accumulator by the content of register R.AC ін
This addressing mode is similar to direct addressing mode. The only difference is address field of the instruction refers to a CPU register instead of main memory. Register Indirect Addressing Mode- In this addressing mode, the address field of the instruction refers to a CPU register that contains the effective address of the operand. Only one reference to memory is required to fetch the operand. R EARegister Set Memory
Example-
ADD R will increment the value stored in the accumulator by the content of memory location specified in register R.AC ін
This addressing mode is similar to indirect addressing mode. The only difference is address field of the instruction refers to a CPU register. operand opcode R EA operand opcode RReferences:
4. Linda Null, Julia Lobur- The Essentials of Computer Organization and
Architecture, 2014, 4th Edition.
quotesdbs_dbs10.pdfusesText_16[PDF] types of adjectives in french
[PDF] types of advance directives
[PDF] types of advertising pdf
[PDF] types of air pollution pdf
[PDF] types of alcohol you shouldn't mix
[PDF] types of alkalinity of water
[PDF] types of analysis in pspice
[PDF] types of antibodies
[PDF] types of ants in east texas
[PDF] types of ants in houston texas
[PDF] types of ants in north texas
[PDF] types of ants in south texas
[PDF] types of api
[PDF] types of application software
