FONCTION LOGARITHME NEPERIEN
FONCTION LOGARITHME NEPERIEN
On la note lna . La fonction logarithme népérien notée ln
 FONCTION LOGARITHME NÉPÉRIEN
FONCTION LOGARITHME NÉPÉRIEN
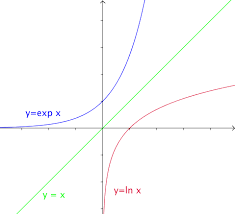
. 1. 2 exp ln. Page 4. 4. Yvan Monka – Académie de Strasbourg – www.maths-et-tiques.fr. - Les courbes représentatives des fonctions et sont
 FONCTION LOGARITHME NEPERIEN (Partie 2)
FONCTION LOGARITHME NEPERIEN (Partie 2)
Démonstration : Nous admettons que la fonction logarithme népérien est dérivable sur 0;+∞⎤⎦⎡⎣ . Posons f (x) = eln x . Alors f '(x) = (ln x)'eln x
 FONCTION LOGARITHME NÉPÉRIEN
FONCTION LOGARITHME NÉPÉRIEN
On la note ln . ○ La fonction logarithme népérien notée
 FONCTION LOGARITHME NÉPÉRIEN
FONCTION LOGARITHME NÉPÉRIEN
Les mathématiciens de l'époque établissent alors des tables de logarithmes de plus en plus précises. L'intérêt d'établir ces tables logarithmiques est de
 FONCTION LOGARITHME NEPERIEN (Partie 1)
FONCTION LOGARITHME NEPERIEN (Partie 1)
La fonction logarithme népérien notée ln
 La fonction logarithme népérien
La fonction logarithme népérien
3 déc. 2014 Conclusion : la fonction ln est dérivable sur ]0; +∞[ et (ln x)′ = 1 x . 3.2 Limite en 0 et en l'infini. Théorème 6 : On a les limites ...
 TP 1 - Découverte de R
TP 1 - Découverte de R
# logarithme népérien c(12
 FONCTION LOGARITHME NEPERIEN
FONCTION LOGARITHME NEPERIEN
On la note lna . La fonction logarithme népérien notée ln
 FONCTION LOGARITHME NEPERIEN
FONCTION LOGARITHME NEPERIEN
- Les courbes représentatives des fonctions exp et ln sont symétriques par rapport à la droite d'équation y = x. - Dans le domaine scientifique on utilise la.
 LOGARITHME NEPERIEN
LOGARITHME NEPERIEN
.. x ? IR+. * y = ln x. ? y ? IR e y. = x traduit le fait que les fonctions exponentielle et logarithme népérien sont réciproques l'une ...
 FONCTION LOGARITHME NEPERIEN (Partie 2)
FONCTION LOGARITHME NEPERIEN (Partie 2)
Démonstration : Nous admettons que la fonction logarithme népérien est dérivable sur 0;+????? . Posons f (x) = eln x . Alors f '(x) = (ln x)'eln x
 FONCTION LOGARITHME NÉPÉRIEN (Partie 2)
FONCTION LOGARITHME NÉPÉRIEN (Partie 2)
Démonstration : Pour tout réel >0 (ln ) = > 0. Page 2. 2. Yvan Monka – Académie de Strasbourg – www.maths-et-tiques.fr. 3) Convexité. Propriété : La
 FONCTION LOGARITHME NÉPÉRIEN
FONCTION LOGARITHME NÉPÉRIEN
FONCTION LOGARITHME NÉPÉRIEN. Tout le cours en vidéo : https://youtu.be/VJns0RfVWGg. En 1614 un mathématicien écossais
 FONCTION LOGARITHME NEPERIEN (Partie 1)
FONCTION LOGARITHME NEPERIEN (Partie 1)
La fonction logarithme népérien notée ln
 La fonction logarithme népérien
La fonction logarithme népérien
3 déc. 2014 On dit que la fonction ln est la fonction réciproque de la fonction exponentielle. Remarque : Cette fonction existe bien car la fonction ...
 Chapitre V : Logarithme népérien
Chapitre V : Logarithme népérien
LEÇON 05: FONCTION LOGARITHME NEPERIEN. A. SITUATION D'APPRENTISSAGE. Le médico-scolaire de ta commune organise une campagne de dépistage de la fièvre
 FONCTION LOGARITHME NÉPÉRIEN (Partie 1)
FONCTION LOGARITHME NÉPÉRIEN (Partie 1)
Donc : ln( × ) = ln + ln . Page 3. 3. Yvan Monka – Académie de Strasbourg – www.maths-et-tiques.fr. Remarque : Cette formule permet de transformer un
 Terminale S - Fonction logarithme népérien
Terminale S - Fonction logarithme népérien
1) Définition de la fonction logarithme népérien. Soit un nombre réel strictement positif. On appelle logarithme népérien.
FONCTION LOGARITHME NÉPÉRIEN
- Chapitre 2/2 Tout le cours en vidéo : https://youtu.be/VJns0RfVWGg Partie 1 : Étude de la fonction logarithme népérien1) Continuité et dérivabilité
Vidéo https://youtu.be/3KLX-ScJmcI
Propriété : La fonction logarithme népérien est continue sur0;+∞
Propriété : La fonction logarithme népérien est dérivable sur0;+∞
et ln(���)Démonstration au programme :
Vidéo https://youtu.be/wmysrEq4XIg
Rappel : /���
En posant : ���
=ln(���), on a : /��� =(ln(���))′���Or /���
=1.Donc : (ln(���))′���
=1Soit : (ln(���))′=
Méthode : Calculer une dérivée contenant des logarithmesVidéo https://youtu.be/yiQ4Z5FdFQ8
Dériver la fonction ��� définie sur
0;+∞
par : ��� ln(���) 2Correction
ln(���)Avec : ���
ln(���) =2× 1×ln(���)
=1 2××ln(���)×���-
ln(���) ×12ln(���)-
ln(���) ln(���)×(2-ln 22) Variations
Propriété : La fonction logarithme népérien est strictement croissante sur0;+∞
Démonstration :
Pour tout réel ���>0,
ln(���) >03) Convexité
Propriété : La fonction logarithme népérien est concave sur0;+∞
Démonstration :
Pour tout réel ���>0,
ln(���) ln(���) Donc la fonction logarithme népérien est concave.4) Limites aux bornes
Propriétés : lim
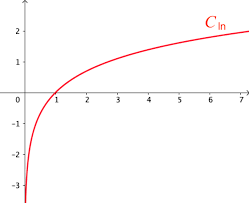
ln(���)=-∞ et lim ln(���)=+∞ On dresse le tableau de variations de la fonction logarithme népérien :0 +∞
ln(���) ln(���)5) Tangentes en 1 et en ���
Rappel : Une équation de la tangente à la courbe de ��� au point d'abscisse ��� est de la forme :
Dans le cas de la fonction logarithme népérien, l'équation est de la forme : 1 +ln(���). Au point d'abscisse 1, l'équation de la tangente est ���= 1 1 ���-1 +ln(1) soit : ���=���-1. Au point d'abscisse ���, l'équation de la tangente est ���= 1 +ln(���) soit : 1 36) Courbe représentative
Valeurs particulières : ln(1)=0, ln(���)=1
Partie 2 : Croissance comparée des fonctions logarithme et puissancesPropriétés (croissances comparées) :
a) lim ln(���) =0 et pour tout entier naturel non nul ���, lim ln(���) =0 b) lim ���ln(���)=0 et pour tout entier naturel ���, lim 0 ln(���)=0 Démonstration du b. dans les cas où ���=1 (au programme) :Vidéo https://youtu.be/LxgQBYTaRaw
En posant ���=ln(���), on a : ���=���
1 Or, si ��� tend vers 0, alors ���=ln(���) tend vers -∞.Donc : lim
���ln(���)=lim1→2/
1 ×���=0 par croissance comparée de la fonction exponentielle et des fonctions puissances. Remarque : Les fonctions puissances imposent leur limite devant la fonction logarithme népérien. 4 Méthode : Déterminer une limite par croissance comparéeVidéo https://youtu.be/lA3W_j4p-c8
Vidéo https://youtu.be/OYcsChr8src
���)lim ���-ln(���)���)lim ln(���) ���-1 ���)lim 1 +1)ln(���)Correction
a) Il s'agit d'une forme indéterminée de type "".Levons l'indétermination :
���-ln(���)=������1- ln(���) EPar croissance comparée : lim
ln(���) =0,Donc : lim
1- ln(���) =1.Et donc, comme limite d'un produit : lim
���F1- ln(���)G=+∞
Soit : lim
���-ln(���)=+∞. b) Il s'agit d'une forme indéterminée de type "".Levons l'indétermination :
ln(���) ���-1 #2+ 1- H lim ln =0,parcroissancecomparée. lim 1- 1 =1Donc, comme limite d'un quotient : lim
ln(���) 1- 1 0 1 =0Soit : lim
ln(���) ���-1 =0. 1 +1)ln(���) 1 ln(���)+ln(���) R lim ln =0,parcroissancecomparée lim lnDonc, comme limite d'une somme : lim
ln +ln(���)=-∞ Et donc, comme limite d'un quotient (inverse) : lim 1 2 ln(���)+ln(���) =0 5Soit : lim
1 2 +1)ln(���) =0Partie 3 : Études de fonctions
1) Cas de fonctions contenant la fonction ���⟼ln(���)
Méthode : Étudier les variations d'une fonction contenant des logarithmesVidéo https://youtu.be/iT9C0BiOK4Y
a) Déterminer les variations de la fonction ��� définie sur0;+∞
par =3-���+2ln(���) b) Étudier la convexité de la fonction ���.Correction
=-1+ 22-���
Comme ���>0, ���
est du signe de 2-���. La dérivée ���′ est donc positive sur 0;2 et négative sur2;+∞
On dresse le tableau de variations :
2 =3-2+2ln(2)=1+2ln(2) -1���-2-���
×1 -���-2+��� -2 <0 On en déduit que la fonction ��� est concave sur0;+∞
Méthode : Étudier la position relative de la courbe de la fonction logarithme et de la droite d'équation ���=���Vidéo https://youtu.be/0hQnOs_hcss
Étudier la position relative de la courbe de la fonction logarithme et de la droite d'équation0 2 +∞
+ 0 -1+2ln(2)
6Correction
On considère la fonction ��� définie sur
0;+∞
par ��� =���-ln(���). =1- 1 ���-1Comme ���>0, ���
est du signe de ���-1. La dérivée ���′ est donc négative sur 0;1 et positive sur1;+∞
On dresse ainsi le tableau de variations :
1 =1-ln(1)=1On en déduit que pour tout ��� de
0;+∞
, on a ��� =���-ln(���)≥1>0 soit ���>ln(���). La fonction logarithme est située en dessous de la droite d'équation ���=���.2) Cas de fonctions contenant la fonction composée ���⟼ln(���
Fonction Dérivée
ln(���)Démonstration :
On pose : ���
=ln(���), donc : ln(���) 1Donc :
ln(��� , selon la dérivée d'une fonction composée. 1 Méthode : Dériver des fonctions du type ln(���)Vidéo https://youtu.be/-zrhBc9xdRs
Dériver la fonction ��� définie sur
0;2 par ��� =ln2���-���
Correction
=ln2���-���
=ln(���0 1 +∞
- 0 + 1 7Avec : ���
=2���-��� =2-2���2-2���
2���-���
Méthode : Étudier une fonction du type ln(���)Vidéo https://youtu.be/s9vyHsZoV-4
Vidéo https://youtu.be/3eI4-JRKYVo
Vidéo https://youtu.be/CyOC-E7MnUw
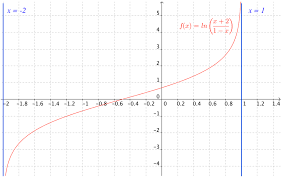
On considère la fonction ��� définie sur
-2;1 par : =ln��� ���+21-���
E a) Calculer les limites de ��� aux bornes de son ensemble de définition et en déduire leséquations des asymptotes à la courbe.
b) Déterminer le sens de variations de la fonction ���. c) Tracer la courbe représentative de ���.Correction
a) lim #→2* X lim #→2* ���+2=0 lim #→2*1-���=3
Donc, comme limite d'un quotient : lim
#→2* ���+21-���
=0 Et donc, comme limite d'une fonction composée : lim #→2* ln��� ���+21-���
E=-∞
En effet, si ���→-2, on a : ���=
���+21-���
→0 et donc : lim1→-
ln(���)=-∞. lim R lim ���+2=3 lim1-���=0
,car���<1Donc, comme limite d'un quotient : lim
���+21-���
Et donc, comme limite d'une fonction composée : lim ln��� ���+21-���
E=+∞
En effet, si ���→1, on a : ���=
���+21-���
→+∞ et donc : lim1→./
ln(���)=+∞. La courbe de fonction ��� admet deux asymptotes verticales d'équations : ���=-2 et ���=1. 8 b) ��� =lnF ���+21-���
G=ln(���
), avec ��� ���+21-���
1×1-���
-(���+2)×(-1)1-���
1-���+���+2
1-���
31-���
Donc :
3 +2#La fonction ��� est strictement positive sur
-2;1 et 0 !1" >0.Donc ���
>0. On présente le sens de variations de ��� dans le tableau : c) ��� -2 1quotesdbs_dbs23.pdfusesText_29[PDF] LE LOGOTYPE
[PDF] La loi normale
[PDF] Le lotissement Réglementation - Cours de Génie Civil
[PDF] Mécanismes et macro- économie monétaires
[PDF] Bien demarrer avec Flash - Site Web ? vocation éducationnel de l
[PDF] COURS DE MAINTENANCE
[PDF] La brochure 2017-2018 - Cours Municipaux d Adultes - Parisfr
[PDF] Management de l 'innovation
[PDF] Les sept principes du management de la chaîne logistique
[PDF] MRH COURS 1 Fichier - Moodle
[PDF] Management du risque
[PDF] Programme MSG CPGE ECT - cachemediaeducationgouvfr
[PDF] Management de la santé - IAE Pau-Bayonne
[PDF] Guide de Formation [COURS DE MAQUILLAGE] - Espace