 LA GLYCOLYSE
LA GLYCOLYSE
LA GLYCOLYSE. Introduction-généralites. Définition. La glycolyse est aussi appelée voir d'Emben meyerhoff. Elle dégrade le glucose en pyruvate elle est à.
 La glycolyse
La glycolyse
La glycolyse est la voie du catabolisme oxydatif anaérobie du glucose en pyruvate. Tous les enzymes catalysant cette voie sont cytosoliques. 2. INTERET. Le
 La glycolyse
La glycolyse
Devenir du Pyruvate. VIII.Entrée des autres glucides dans la séquence glycolytique. IX. Pathologie liées a la glycolyse. Page 16
 PATHOLOGIE DES ENZYMES DE LA GLYCOLYSE I
PATHOLOGIE DES ENZYMES DE LA GLYCOLYSE I
Glycolyse erythrocytaire - andmies hemolytiques - erythroenzymopathies - d~ficit en pyruvate kinase - d(~ficit en G6PD. Summary. Since Carson et aL [8]
 Caractérisation dun rôle inédit de la glycolyse: contrôle du senseur
Caractérisation dun rôle inédit de la glycolyse: contrôle du senseur
9 mars 2015 lactis et S. cerevisiae. Mots-clés : glucose glycolyse
 Caracterisation dun role inedit de la glycolyse
Caracterisation dun role inedit de la glycolyse
cerevisiae nous avons utilisé à la fois des mutants glycolytiques et l'inhibition chimique de la glycolyse pour rompre le flux glycolytique. Ces résultats
 Caractérisation dun rôle inédit de la glycolyse: contrôle du senseur
Caractérisation dun rôle inédit de la glycolyse: contrôle du senseur
9 mars 2015 cerevisiae nous avons utilisé à la fois des mutants glycolytiques et l'inhibition chimique de la glycolyse pour rompre le flux glycolytique.
 RECYCLAGE DU POLY (ETHYLENE TEREPHTALATE) PAR
RECYCLAGE DU POLY (ETHYLENE TEREPHTALATE) PAR
Nous étudions la dépolymérisation du poly (éthylène téréphtalate) par glycolyse en phase homo gène en utilisant le naphtalène comme solvant avec dif férents
 Le métabolisme des Glucides : La glycolyse
Le métabolisme des Glucides : La glycolyse
Plusieurs voies métaboliques sont alors empruntées par le glucose dont la glycolyse. Le métabolisme est subdivisé en deux : catabolisme et anabolisme. II.
 LA GLYCOLYSE
LA GLYCOLYSE
(voir toute la glycolyse en détail dans la page suivante). Etape 1 : Consomme 1 ATP et fait entrer le glucose dans la cellule : étape limitante = de
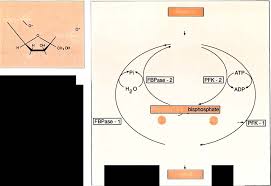
 Le fructose-2 6-bisphosphate chez les mammifères
Le fructose-2 6-bisphosphate chez les mammifères
glycolyse et la néoglucogenèse hépatiques. qué non seulement dans le contrôle de la glycolyse mais aussi ... effectivement le flux glycolytique.
 Activité 1 : La glycolyse première étape de dégradation du glucose
Activité 1 : La glycolyse première étape de dégradation du glucose
3) au vu des données sur le bilan chimique de la glycolyse (doc. 4). Quarante années de recherches en biochimie ont permis d'élucider la glycolyse voie
 La glycolyse: transcription de la vidéo
La glycolyse: transcription de la vidéo
Partons à l'échelle cellulaire et regardons les différentes voies du catabolisme cellulaire. Vous les avez ici en jaune. Vous voyez que la glycolyse se
 Caracterisation dun role inedit de la glycolyse
Caracterisation dun role inedit de la glycolyse
Le glucose est métabolisé par les cellules vivantes grâce à la glycolyse pour générer de l'ATP et de la biomasse. Le fructose est un autre hexose qui est
 Effets de la vitesse de glycolyse post mortem du muscle de dinde
Effets de la vitesse de glycolyse post mortem du muscle de dinde
24 nov. 2008 4.1 Les enzymes glycolytiques et la qualité de la viande PSE . ... d'accélération de la glycolyse musculaire post mortem qui accélèrerait la ...
 Études Sur la Glycolyse Hépatique
Études Sur la Glycolyse Hépatique
possiderait un mecanisme glycolytique propre. En effet alors qu'il forme facilement de l'acide lactique aux depens de !'acide phosphoglycerique ou de I'acide
 Caractérisation dun rôle inédit de la glycolyse: contrôle du senseur
Caractérisation dun rôle inédit de la glycolyse: contrôle du senseur
9 mars 2015 Le métabolisme du glucose par la glycolyse et sa régulation chez les ... cancéreuses les cellules produisent de l'ATP par la glycolyse
 COURS DE METABOLISME LA GLYCOLYSE : VOIE DEM BDEN-M
COURS DE METABOLISME LA GLYCOLYSE : VOIE DEM BDEN-M
3 - LES ETAPES DE LA GLYCOLYSE. A - ETAPES ENZYM ATIQUES DE LA PREM IERE PHASE. 3.1 - Phosphorylation du glucose par l'ATP. 3.2 - Transformation de G-6-P en
 doc François
doc François
La glycolyse est une étape de dégradation des molécules de glucose au cours de laquelle une molécule de glucose produit deux molécules de pyruvate (molécule
 Glycolysis - California State University Northridge
Glycolysis - California State University Northridge
Glycolysis The Glycolytic pathway describes the oxidation of glucose to pyruvate with the generation of ATP and NADH It is also called as the Embden-Meyerhof Pathway Glycolysis is a universal pathway; present in all organisms: from yeast to mammals In eukaryotes glycolysis takes place in the cytosol
 Glycolysis The Glycolytic Pathway The Reactions of Glycolysis
Glycolysis The Glycolytic Pathway The Reactions of Glycolysis
(Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas Pathway) Glycolysis convertsone C6 unit (glucose) totwo C3 units(pyruvate) of lower energy in a process that harnesses thereleased free energy to synthesize ATP from ADP and Pi Overall reaction - Glucose + 2NAD + 2ATP + i2P?2NADH + 2pyruvate + 2ATP + 2O + 2H + 4H
 Glycolysis: The Initial Steps: Energy Input - Purdue University
Glycolysis: The Initial Steps: Energy Input - Purdue University
Title: http://www northland cc mn us/b PDF Author: Chris' Laptop Created Date: 4/3/2003 9:14:53 PM
 Searches related to glycolyse PDF
Searches related to glycolyse PDF
Glycolysis is a set of reactions that converts glucose to pyruvate or lactate This is the first metabolic pathway to be elucidated and hence is considered as a paradigm of metabolic pathways Glycolysis is also called Embden-Meyerhoff pathway The complete set of reactions occurs in the cytoplasm of virtually every animal cell
Overview
This article is about glycolysis, the first step in the breakdown of glucose to extract energy for cellular metabolism. It explains that glycolysis consists of an energy-requiring phase followed by an energy-releasing phase and has ten steps. The article also provides information on how phosphofructokinase regulates glycolysis and what happens to N...
Glycolysis
The first step in the breakdown of glucose to extract energy for cellular metabolism, glycolysis consists of an energy-requiring phase followed by an energy-releasing phase. It is found in most organisms and is the first stage of cellular respiration.
Simplified Pathway
Glycolysis takes place in cytosol and can be divided into two main phases, the energy-requiring phase and the energy-releasing phase. It converts one six-carbon molecule of glucose into two three-carbon molecules of pyruvate with net products being 2 ATP and 2 NADH.
Energy Requiring Phase
A simplified version that highlights key steps without tracing every single atom involved in glycolysis's 10 steps process which starts with transferring a phosphate group from ATP to glucose making glucose 6 phosphate.
What is the chemical equation for glycolysis?
The Glycolytic Pathway (Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas Pathway) Glycolysis converts one C6 unit (glucose) to two C3 units (pyruvate) of lower energy in a process that harnesses the released free energy to synthesize ATP from ADP and Pi. Overall reaction - Glucose + 2NAD+ + 2ATP + 2P. i ? 2NADH + 2pyruvate + 2ATP + 2H2O + 4H.
What are the two phases of glycolysis?
Glycolysis consists of two phases. In the first phase, glucose is broken down to two molecules of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate in a series of five reactions. In the second phase, another series of five reactions convert these two molecules of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate into two molecules of pyruvate.
What happens at the end of glycolysis?
At the end of glycolysis, we’re left with two ext {ATP} ATP, two ext {NADH} NADH, and two pyruvate molecules. If oxygen is available, the pyruvate can be broken down (oxidized) all the way to carbon dioxide in cellular respiration, making many molecules of ext {ATP} ATP.
Does phosphofructokinase speed up or slow down glycolysis?
Phosphofructokinase speeds up or slows down glycolysis in response to the energy needs of the cell. Overall, glycolysis converts one six-carbon molecule of glucose into two three-carbon molecules of pyruvate.
[PDF] métabolisme énergétique musculaire
[PDF] faille decrochante
[PDF] métabolisme musculaire définition
[PDF] rendement musculaire definition
[PDF] failles transformantes définition
[PDF] une faille transformante est une limite
[PDF] a travers l exemple de la fermentation montrer que le métabolisme
[PDF] tp métabolisme des levures
[PDF] métabolisme calcul
[PDF] métabolisme de base pdf
[PDF] métabolisme rapide
[PDF] failles normales
[PDF] biochimie métabolique résumé
[PDF] biochimie métabolique ppt