 1. Protonate 2. Add 3. Deprotonate 1. Protonate 2. Add 3. Deprotonate
1. Protonate 2. Add 3. Deprotonate 1. Protonate 2. Add 3. Deprotonate
Some Practice Problems for the Carbonyls Test 3. Draw the Products and Acetal/ketal formation: Hemicetal/hemiketal formation: 1. Protonate 2. Add ...
 PRACTICE PROBLEMS – UNIT 19
PRACTICE PROBLEMS – UNIT 19
How can the reaction be shifted toward the carbonyl starting material? 19C. Predict the products of imine enamine
 Answers to Practice Sets - Organic Chemistry II Table of Contents
Answers to Practice Sets - Organic Chemistry II Table of Contents
Test 1 PS#3: Alcohol-related Mechanisms Problems. 11. Test 1 PS#4: Alcohol-Related in acetal/ketal formation: 1. Protonate 2. Add alcohol 3. Deprotonate.
 Untitled
Untitled
PRACTICE PROBLEMS - UNIT 19. 19A.1 Provide systematic names for aldehydes and ketones. 19A Draw the mechanism of imine enamine and acetal formation. 2
 CHM 202 Practice Problems – CH 19 1. Provide a stepwise
CHM 202 Practice Problems – CH 19 1. Provide a stepwise
Provide a stepwise mechanism for the following reaction. Show all acetal. Page 2. 2. Give the chemical steps required for the following syntheses: a). CCl. O.
 Untitled
Untitled
Acetal formation involves the acid-catalyzed nucleophilic addition of Practice Problem 9.5. 9.9 Nucleophilic Addition of Grignard Reagents: Alcohol Formation.
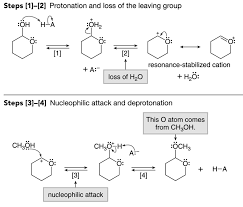 Addition of Alcohols—Acetal Formation
Addition of Alcohols—Acetal Formation
The mechanism for acetal formation is similar to the formation of a hydrate To solve this problem we can use a protecting group to block the more.
 Organic Chemistry
Organic Chemistry
same compound and a cyclic acetal is formed. • Practice drawing the mechanism of acetal formation with. SkillBuilder 19.2. Copyright © 2017 John Wiley & Sons
 of 49 “Syllabus‐Like” Document for Organic Chemistry 2 (Chem
of 49 “Syllabus‐Like” Document for Organic Chemistry 2 (Chem
Oct 13 2017 All C‐C forming reactions are extremely handy and are most easily incorporated into synthesis problems ... Incomplete mechanism for Acetal ...
 19.1 Ketones and Aldehydes
19.1 Ketones and Aldehydes
• Practice drawing the mechanism of acetal formation with. SkillBuilder 19.2 We need to convert an ester to 1˚ alcohol which requires LAH
 1. Protonate 2. Add 3. Deprotonate 1. Protonate 2. Add 3. Deprotonate
1. Protonate 2. Add 3. Deprotonate 1. Protonate 2. Add 3. Deprotonate
Some Practice Problems for the Carbonyls Test 3 Hemiacetal/hemiketal to carbonyl second phase of acetal/ketal hydrolysis ... (an addition reaction).
 PRACTICE PROBLEMS – UNIT 19
PRACTICE PROBLEMS – UNIT 19
How can the reaction be shifted toward the carbonyl starting material? 19C. Predict the products of imine enamine
 Answers to Practice Sets - Organic Chemistry II Table of Contents
Answers to Practice Sets - Organic Chemistry II Table of Contents
Test 1 PS#3: Alcohol-related Mechanisms Problems Test 3 PS2: Retrosynthesis + Synthesis Design Practice ... second stage in acetal/ketal formation:.
 Organic Chemistry II Spring 2022 Week 13
Organic Chemistry II Spring 2022 Week 13
In these sessions I will provide practice problems and be available for -Acetal Hydrolysis usually requires acidic conditions (acid catalysis).
 3150 Ch 19 handout Klein ald_ketone.cdx
3150 Ch 19 handout Klein ald_ketone.cdx
formation of C=O can be a driving force for a reaction formation of acetal adds ___ equivalents of alcohol ... Acetal Mechanism Practice Problems.
 Untitled
Untitled
PRACTICE PROBLEMS - UNIT 19. 19A.1 Provide systematic names for aldehydes and ketones Draw the mechanism of imine enamine and acetal formation.
 Organic Chemistry II_Week 12
Organic Chemistry II_Week 12
In these sessions I will provide practice problems and be available for specific -Acetal Hydrolysis usually requires acidic conditions (acid catalysis).
 Aldehydes and Ketones
Aldehydes and Ketones
The reaction above is an example of acid‡catalyzed acetal formation in which the prod- this problem
 Objectives Organic Chemistry 360
Objectives Organic Chemistry 360
Alcohols (reversible hemiactal and acetal formation including cyclic hemiacetals and acetals; and the reverse reactions involving acetal hydrolysis).
 Addition of Alcohols—Acetal Formation
Addition of Alcohols—Acetal Formation
Like gem-diol formation the synthesis of acetals is reversible
[PDF] acetamide reaction with naoh
[PDF] acetamide with naoh
[PDF] acetic acid bacteria in fermented foods and beverages
[PDF] acetic acid bacteria in wine
[PDF] acetic acid production biology discussion
[PDF] acetic acid production by fermentation pdf
[PDF] acetic anhydride and water balanced equation
[PDF] acetic anhydride boiling point under vacuum
[PDF] acetic anhydride density ml
[PDF] acetic anhydride hazards and disposal
[PDF] acetic anhydride hydrolysis mechanism
[PDF] acetic anhydride melting point range
[PDF] acetic anhydride msds pubchem
[PDF] acetic anhydride nmr chegg
