IN THIS ISSUE
IN THIS ISSUE
Chicago's O'Hare Airport used VHB Tapes in construction. Metal cladding at the world's tallest hotel the Burj Al Arab in Dubai
 The making of an Icon
The making of an Icon
The Burj Al Arab was a career-defining project for those involved in its creation. To celebrate the. 50th anniversary of Atkins in the Middle East region
 BURJ AL ARAB UPGRADES COMPLIMENTARY PREMIUM WI-FI
BURJ AL ARAB UPGRADES COMPLIMENTARY PREMIUM WI-FI
Menezes. In all over 900 APs were deployed across the hotel
 Sky-high Risk - The Impact of Increasing Tall Tower Construction in
Sky-high Risk - The Impact of Increasing Tall Tower Construction in
The region remained largely unchanged during the 1980s and 1990s with only the. Burj Al Arab (UAE)
 Designing a Landmark for the United Arab Emirates Designing a
Designing a Landmark for the United Arab Emirates Designing a
Functionally Burj Al Arab is part of the Jumeirah Beach Resort and is sited The building height is 321 m
 Burj al arab construction process
Burj al arab construction process
Burj al arab construction time. Burj al arab cost to build. Island making the worlds largest atrium. It needed to be a building that would become ...
 Freestyle Membrane Architecture
Freestyle Membrane Architecture
The Burj Al Arab luxury hotel juts out of the Arabian Sea near. Jumeirah/Dubai. Resting on an artificial island it stands at 321 meters (1
 Reflecting on the Inauguration of the Burj Khalifa Dubai 2010 3
Reflecting on the Inauguration of the Burj Khalifa Dubai 2010 3
The international public relations and media perception of Dubai – starting with the Burj. Al Arab in 1994 – created the link between this quiet desert city
 final
final
Burj Al Arab Construction. Slide Share. Retrieved from
 To Study the Science behind the Construction and Techniques of
To Study the Science behind the Construction and Techniques of
04-Apr-2017 The Burj al-Arab is a luxury hotel located in Dubai United Arab Emirates. It is the fourth tallest hotel in the world.The.
 The making of an Icon
The making of an Icon
The Burj Al Arab was a career-defining project for those involved in its creation. To celebrate the. 50th anniversary of Atkins in the Middle East region
 Case Study- BURJ-AL-ARAB Dubai
Case Study- BURJ-AL-ARAB Dubai
Chief Architect: The primary architect who designed the building Tom Wright of Atkins. • Chief Contractor: WS Atkins Partners Overseas. • Construction
 Burj Al Arab Construction
Burj Al Arab Construction
The burj al arab island. • Steel Works. • Concept architect. Amazing facts about burj al arab. Materials used in construction. Island construction process.
 Burj Al Arab
Burj Al Arab
The Burj Al Arab (Tower of the Arabs) is a luxury hotel located in Dubai. United Arab Emirates. Construction of Burj Al Arab began in 1994.
 Skin friction concept
Skin friction concept
24-Jul-2013 Due to this principle the construction of Burj Al Arab in. Dubai was possible. Its foundation consists of 250 steel.
 IN THIS ISSUE
IN THIS ISSUE
Chicago's O'Hare Airport used VHB Tapes in construction. Metal cladding at the world's tallest hotel the Burj Al Arab in Dubai
 BURJ AL ARAB UPGRADES COMPLIMENTARY PREMIUM WI-FI
BURJ AL ARAB UPGRADES COMPLIMENTARY PREMIUM WI-FI
Menezes. In all over 900 APs were deployed across the hotel
 Designing a Landmark for the United Arab Emirates Designing a
Designing a Landmark for the United Arab Emirates Designing a
Burj Al Arab is an extraordinary. Modern Steel Construction / August 2000. Building Team. Architecture Engineering
 Brief on the Construction Planning of the Burj Dubai Project Dubai
Brief on the Construction Planning of the Burj Dubai Project Dubai
Ahmad Abdelrazaq is Vice President and Executive Director of the Highrise Building and Structural Engineering Divisions at Samsung Corporation. Since joining
 [PDF] Case Study- BURJ-AL-ARAB Dubai
[PDF] Case Study- BURJ-AL-ARAB Dubai
Initial core test-Drilling done 180mts down and no solid rock was formed but architect was defiant about the design and construction ? Then reinforced
 [PDF] Creating the Burj Al Arab Dubai - By Tom Wright RIBA - Squarespace
[PDF] Creating the Burj Al Arab Dubai - By Tom Wright RIBA - Squarespace
Creating the Burj Al Arab Dubai In 1993 Atkins was commissioned to design and construction manage the Jumeirah Burj Al Arab from sketch to reality
 [PDF] Burj Al Arab Construction - WEC CIVILIANS
[PDF] Burj Al Arab Construction - WEC CIVILIANS
Burj al Arab building is made of 12000ton of structural steelworks •Total steel works are phased into Exoskeleton rear leg Horizontals Diagonals Rear
 Construction of Burj Al Arab PDF Deep Foundation - Scribd
Construction of Burj Al Arab PDF Deep Foundation - Scribd
DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION OF BURJ AL ARAB ??? ????? Presented by Muhamed Munjee In General • The tallest and most luxurious hotel on earth with
 (PDF) Evaluation of the Hotel Burj Al Arab Promoting a study Project
(PDF) Evaluation of the Hotel Burj Al Arab Promoting a study Project
Resumen This work was done with the aim of promoting the use of certain materials that are previously seen in the undergraduate study of civil engineering
 burj al-arab torre caja madrid - Academiaedu
burj al-arab torre caja madrid - Academiaedu
The purpose of this paper is to provide structural and architectural technological solutions applied in the construction of high-rise buildings
 The Construction of Burj Al-Arab - PDFCOFFEECOM
The Construction of Burj Al-Arab - PDFCOFFEECOM
Construction of Burj Al Arab began in 1994 and was completed in 1999 It was built n the shape of the Arab dhow a type of Arabian vessel Two 'wings' spread in
 (PDF) Burj Al Arab PDF - DOKUMENTIPS
(PDF) Burj Al Arab PDF - DOKUMENTIPS
8182019 Burj Al Arab PDF 111 Burj Al-Arab UAE Structural Steel Construction For A Mega Project By Dato' A K Nathan Managing Director Shin Eversendai Sdn
 Construction of Burj Al Arab Dubai - RTF Rethinking The Future
Construction of Burj Al Arab Dubai - RTF Rethinking The Future
23 fév 2023 · Burj Al Arab Dubai was developed between 1994 and 1999 It was built in the shape of the Arab dhow a kind of Arabian vessel Two wings
Case Study- BURJ-AL-ARAB, Dubai
BY:Chetna Shaktawat
Deeksha Joshi
Sakshi Gandhi
Prodipta Chatterjee
ͻUnited Arab Emirates - Dubai
ͻPrivate Island (280 m Offshore)
LOCATION
BURJ AL-ARAB
ͻBuilding Name: Burj-Al-Arab Hotel.
ͻOther/Former Names: Arab Sail.
ͻChief Architect: The primary architect who designed the building Tom Wright of Atkins. ͻChief Contractor: WS Atkins Partners Overseas.ͻConstruction Contractor: Murray & Roberts.
ͻConstruction : 1993 - 1999.
ͻFloors : 60.
ͻFloor Area : 111,500 m2 (1,200,000 sq ft)
BURJ AL-ARAB
Architect's Background
ͻTom Wright (formerly Tom Wills-Wright) - The architect and designer of the Burj al Arab in Dubai, UAE. ͻTom Wright lived in Dubai during the design and construction of the project, working as the project Design Director for Atkins , one of the world഻s leading multi discipline design consultancies. ͻTom Wright is British, born in Croydon a suburb ofLondon on 18th September 1957.
ͻEducated at the Royal Russell School and then KingstonPolytechnic school of Architecture.
ͻWright became a member of the Royal institute of British Architects in 1983 and has been in practice ever since. The felt pen illustration was an early development sketch of the hotel drawn by Wright .BURJ AL-ARAB
Introduction
Sail͞.
used exclusively as a hotel. transformation and to mimic the sail of a boat.Burj Al Arab - the world's third tallest hotel.
BURJ AL-ARAB
Concept
Dubai) was to design, not just a hotel, but also a signature building; one that would announce, "Welcome to Dubai". that would immediately conjure up images of the city. tall building are founded on rock. The Burj al Arab is supported on 250, 1.5M diameter columns that go 45 meters under the sea. As there is only sand to hold the building up the columns rely on friction.BURJ AL-ARAB
Concept -
Orientation and Circulation
ͻThe orientation of the building minimizes the
heat gain during the summer seasons.ͻThe south elevation has the most exposed
surface area. As a result, it has the maximum capacity for heat absorption. ͻFor people, there is access to the hotel through the roof via a helicopter. At the main entrance there is a grand stairway, an escalator and elevators. ͻFor air, the revolving door located at the main entrance acts as a locking mechanism to prevent a phenomenon known as the stack effect, which occurs when the hot air rises and the cool air falls in a tall building. systems/1-drawings-diagramsBURJ AL-ARAB
Environmental Approach
Wind Effects Dubai's
ͻGeographic location subjects the hotel to severe weather conditions including strong winds and occasional violent thunderstorms.ͻDue to the structure's proximity to its adjacent hotel resort, wind tunnel testing was considered to
ensure a safe design. ͻwind speed of 45 meters per second, under the recommendations of Dubai Municipality, was adopted for the design.Seismic Impact Dubai
ͻItself is not located in an earthquake intensive zone. However, southern Iran which is only 100 miles
away to the north is subjected to moderate earthquake risk and in turn which could create tremors inDubai if a seismic event were to occur in Iran.
ͻTo reinforce the structure from any potential swaying, two tuned mass dampers, weighing about 2 tonnes each, limit vibrations in the tubular steel mast that projects 60 m above the building.BURJ AL-ARAB
Environmental Approach
BURJ AL-ARAB
VORTEX SHEDDING
response under wind loads skeleton. Wind blowing away sharp edges can cause destruction.RESPONSE
Architect was against and forced the engineer
to re-think. variable places - when wind blows, 5 ton weight will swing and damp down the vibrations to safety limits (refer image for locations highlighted in red)BURJ AL-ARAB Environmental Approach
concrete and blended with structural steel. reinforced concrete tower inhabiting hotel rooms and lobbies. atrium in the world standing about 180m height. storeys) with 10,000 Sqmt floor area, 60,000 Sqmt of concrete and 9,000 ton of reinforced steel. prefabricated concrete which forms the base of the V-shape and the trusses are connected to it.BURJ AL-ARAB
Typical Floor Plan
on the inside as well as outside.BURJ AL-ARAB
CONCEPT AND DESIGN
concept was -sail rising from water-people close to sea. of waves. Testing were done to ensure island was safe-3 weeks of testing came up with positive results. and less than 3 yrs to construct the building. waves. shape solid blocks designed to reduce the impact of waves. blocks beforeIsland Construction
to support boundary rocks side of sheet piles displace seawater and form island (fill layers partially complete in figure) protect itfrom the waves sea bedbelow to stabilize structure coffer dam insertedBURJ AL-ARAB
Concrete blocks worked like sponge
turn around in itself and hence force is dissipated and hence battle for secure island is won. was ready in Nov 1995.BURJ AL-ARAB
THE CHALLENGE
to Support the mega structure-270 miles off coast, 320 mtr in height on man-made island (6mts from Arabian Sea) resistant to earthquake (falling under range of major fault line) and wind that blows 90 miles per hour. built before. Location on a reclaimed land was added challenge.TESTS AND RESULTS
no solid rock was formed but architect was defiant about the design and construction. into sand with concept of skin -friction were designed. between sand and surface of piles. When friction between them is equal to impact, situation is handled.BURJ AL-ARAB Foundation
This stopped the building from sinking.
times as long as tiring hotel to support. earthquakes.BURJ AL-ARAB
BURJ AL-ARAB
CONSTRUCTION SITE PICTURES
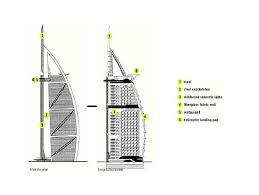
Materials and Structure
1. Core
2. Exoskeleton frame
3. Facade
4. Skyview Restaurant
5. Helipad
BURJ AL-ARAB
CoreBURJ AL-ARAB
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3l2LhpyJfkg connecting the two cores with cross bracings of fabricated box section,imparting stability
-The v shape form of prefabricated concrete is hold in place with cross brace frame and a gigantic steel structure known
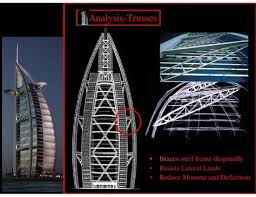
as exoskeleton.BURJ AL-ARAB Exoskeleton Frame
Exoskeleton is made of two legs on each side of
the structure.These Legs are built up H-Sections connected by lattice braced members.
Diagonal are huge tubular triangular trusses
tied to two legs to the central core.The diagonal trusses can contract and expand up to5 cm in 24 hours.
Horizontals-connects rear leg to core wall
-The exoskeleton bows are provided with tuned mass damper at 11 critical points with 5 ton weight which swings to damp down the vibrations caused by vortex shedding, http://www.gerb.com/ http://www.gerb.com/Facade
BURJ AL-ARAB
-Fabric wall stretched between horizontal beams -stretch woven double skinned teflon coated woven glass fibre screen. -Glazed curtain wall with aluminium cladding -Steel structure claded with 6mm composite aluminium panelsBURJ AL-ARAB
Skyview Restaurant
Sky view restaurant:survives wind 160 km/hour aluminium, glass, steel frame Box girders 27 m projected each side,200m above sea series of steel brackets cast into the core 10 girders radiates outSkyview Restaurant
BURJ AL-ARAB
Helipad
BURJ AL-ARAB
-Made of steel trusses and 20mm thick plates -Two props circular steel pipes 1m in diameter -Forms inverted V-shape inclined at 30 degree angle. -Tied back to the central core by 40 metre long spine trussHelipad
BURJ AL-ARAB
Load Analysis
BURJ AL-ARAB
Total dead load : 2850,000,000 lbs
Total live load : 86,160,000 lbs
Total load on foundation : 150,000 lbs/SF
Maximum horizontal wind load : 2,366,000 lbs
Lateral Loads
the two sides of the V (in green). (in red). which acts similar to a diaphragm. a square building because of the streamlined V and curved fabric atrium wall (in blue). powerpoint/Load Tracing
BURJ AL-ARAB
VERTICAL LOADS
from the top to the bottom of the structure using several different aspects. loading is through the large spine. This is the most direct way for the vertical loads to reach the ground. through the curved edge. structure also helps in deflecting the horizontal loads.Multiframe
BURJ AL-ARAB
Multiframe 2D Model of Building section Axial Load DiagramMultiframe
BURJ AL-ARAB
Bending moment diagram Shear force diagram Deflection diagramBibliography
BURJ AL-ARAB
calculationsArab#scribd.
BURJ AL-ARAB
THANK YOU
quotesdbs_dbs14.pdfusesText_20[PDF] malay customs and traditions in singapore
[PDF] malayalam assignment format
[PDF] malaysia food import statistics
[PDF] malaysian case law library
[PDF] male cabaret show sydney
[PDF] maleic anhydride
[PDF] maleic anhydride production
[PDF] mall address in canada toronto
[PDF] malloc algorithm
[PDF] malloc implementation
[PDF] maltodextrin
[PDF] man printf
[PDF] manage apple ids business
[PDF] manage bookings