16. DEVELOPMENT CONTROLS AND REGULATIONS
16. DEVELOPMENT CONTROLS AND REGULATIONS
shall be applicable to the area falling within the limits of planning area of the Chandigarh Master Plan 2031 Manimajra
 MASTER PLAN REPORT MASTER PLAN REPORT
MASTER PLAN REPORT MASTER PLAN REPORT
To integrate the planning and development of S.A.S. Nagar with Chandigarh and the adjourning towns. • To provide a variety and range of housing types for the
 11. OPEN SPACES AND LANDSCAPING OF CHANDIGARH
11. OPEN SPACES AND LANDSCAPING OF CHANDIGARH
Source : Google map - Location of The Rock Garden. Chandigarh Master Plan – 2031. The Rock Garden was not a part of the original Plan as conceived by. Le
 14 CHANDIGARH VILLAGES
14 CHANDIGARH VILLAGES
The Development Plan for the 16 kms belt around the Master Plan brought under the Punjab New Capital (Periphery) Control Act.
 Chandigarh Master Plan – 2031
Chandigarh Master Plan – 2031
Sr. No. Title. Page Number. 5.1. Population growth. 40. 5.2. Rural – Urban Composition. 41. 5.3. Density. 41. 5.4. Sex ratio. 46. 5.5. Literacy rate.
 3 MASTER PLAN AREA
3 MASTER PLAN AREA
The 44 sq km periphery area of Chandigarh is regulated by the. Punjab New Periphery Control Act 1952 with the exception of the abadi deh of the villages
 New Chandigarh Master Plan
New Chandigarh Master Plan
Road Width in New Chandigarh Master Plan. SECTOR ROAD. Road. Proposed Road Name PLANNING AND. PROPOSED REVISED LAND USE PLAN. NEW CHANDIGARH. 2008 TO 2031.
 13. LAND USE
13. LAND USE
From the perspective of the Chandigarh Master Plan 2031 as a whole given the fait accompli of land acquisition
 City Development Plan Chandigarh
City Development Plan Chandigarh
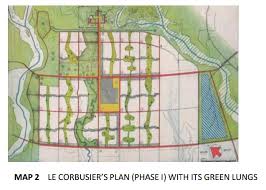
Le Corbusier conceived the master plan of Chandigarh as analogous to human body with a clearly defined head (the Capitol Complex
 City of Chandigarh
City of Chandigarh
?The master plan of the city has a rectangular shape with a grid iron pattern for the fast traffic roads. ?Vertical and high rise buildings were ruled out
 4 PHYSICAL SETTING AND PLANNING CONCEPTS
4 PHYSICAL SETTING AND PLANNING CONCEPTS
Chandigarh Master Plan – 2031. 4.1 LOCATION EXTENT AND PHYSIOGRAPHY Groundwater contour map for shallow aquifers indicates that the.
 City Development Plan Chandigarh
City Development Plan Chandigarh
Consultations are mandatory in the preparation and finalization of master plan by Chandigarh Administration and Municipal Corporation. The Engineering
 Untold Story of Chandigarh Master Plan
Untold Story of Chandigarh Master Plan
11-Jul-2013 development because: ? It defines system of urban government. ? Establishes systems of Urban Planning & Regulation of land development.
 14 CHANDIGARH VILLAGES
14 CHANDIGARH VILLAGES
The Development Plan for the 16 kms belt around the Master Plan brought under the Punjab New Capital (Periphery) Control Chandigarh Master Plan – 2031.
 10 PHYSICAL INFRASTRUCTURE Chandigarhs sectoral grid has a
10 PHYSICAL INFRASTRUCTURE Chandigarhs sectoral grid has a
Chandigarh Master Plan – 2031. MAP M1 –. PREMONSOON storm water drainage master plan to alleviate the problems of flooding.
 13. LAND USE
13. LAND USE
Chandigarh Master Plan – 2031. Considering the development already taken up within the area comprising of the periphery the same is now proposed to be.
 PREAMBLE
PREAMBLE
Chandigarh Master Plan – 2031. In March 1948 the then Government of Punjab in consultation with the Government of India approved the site for the new
 11. OPEN SPACES AND LANDSCAPING OF CHANDIGARH
11. OPEN SPACES AND LANDSCAPING OF CHANDIGARH
Chandigarh Master Plan – 2031. 11. OPEN SPACES AND LANDSCAPING OF CHANDIGARH. 11. 1 INTRODUCTION. Chandigarh is known all over the world as an outstanding
 6. HOUSING IN CHANDIGARH
6. HOUSING IN CHANDIGARH
Chandigarh Master Plan – 2031. 51 government housing ranged from 37.5 sq. yds. to allocated for private residential plots in the original master plan.
 CHANDIGARH MASTER PLAN 2031 - Chandigarh Administration
CHANDIGARH MASTER PLAN 2031 - Chandigarh Administration
Chandigarh Master Plan 2031 Master Plan Area(Size: 358 KB Format: PDF Language: English); Physical Setting and Planning Concept(Size: 372 KB
 [PDF] [PDF] [PDF] Planning & Architecture - Urban Planning
[PDF] [PDF] [PDF] Planning & Architecture - Urban Planning
build a new capital city called Chandigarh about 240 Kms north of New Delhi on a gently sloping The Master plan was developed by Le Corbusier who also
 [PDF] 13 LAND USE - Urban Planning
[PDF] 13 LAND USE - Urban Planning
13 LAND USE Chandigarh Master Plan – 2031 controlled rural belt around it to nourish it Although the city has largely developed as per the original plan
 [PDF] City Development Plan Chandigarh
[PDF] City Development Plan Chandigarh
Le Corbusier conceived the master plan of Chandigarh as analogous to human body with a clearly defined head (the Capitol Complex Sector 1)
 Chandigarh Master Plan 2031 - Map Summary & Free Download!
Chandigarh Master Plan 2031 - Map Summary & Free Download!
Chandigarh Master Plan 2031 provides a useful base for regulating development and building activity in the entire UT of Chandigarh Thus the reference area for
 [PDF] City of Chandigarh
[PDF] City of Chandigarh
LE CORBUSIER'S MASTER PLAN: ?The master plan of the city has a rectangular shape with a grid iron pattern for the fast traffic roads
 New Chandigarh (2008-2031) Revenue Master Plan - PUDA
New Chandigarh (2008-2031) Revenue Master Plan - PUDA
PDF icon New Chandigarh (2008-2031) Revenue Master Plan (English) 2 17 MB E-SERVICES E-Auctions · E-CLU Portal · E-Tendering · E-Water Sewerage Bill
 (PDF) CHANDIGARH MASTER PLAN Doorva Upadhyay
(PDF) CHANDIGARH MASTER PLAN Doorva Upadhyay
The city today is valued universally for being the first realization of Le Corbusier's urban percepts and the site of his most elaborate architectural creation
 [PDF] CHANDIGARH Urban Planning Concepts
[PDF] CHANDIGARH Urban Planning Concepts
CHANDIGARH Urban Planning Concepts Picture of LE CORBUSIER with the Master Plan of Chandigarh A Comparative Study with Residential Development QT8
 City Development Plan - Municipal Corporation Chandigarh
City Development Plan - Municipal Corporation Chandigarh
City Development Plan City Development Plan 20 1 MB Last modified date : 30-05-2018 Last Update: 09/05/2023 - 17:25 Contact us
What is Chandigarh master plan concept?
Le Corbusier conceived the master plan of Chandigarh as analogous to human body, with a clearly defined head (the Capitol Complex, Sector 1), heart (the City Centre Sector-17), lungs ( the leisure valley, innumerable open spaces and sector greens), the intellect (the cultural and educational institutions), theWho is the master plan of Chandigarh?
The master plan of Chandigarh was prepared by Le Corbusier, transformed from an earlier plan by the American planner Albert Mayer. Le Corbusier designed an iconic city, fulfilling not just a utopian agenda, but reflecting concepts of 'modernism' movement that arose in Europe but took root here too.How many people are in Chandigarh master plan?
Le Corbusier's Master Plan
Phase-I consisting of 30 low density sector spread over an area of 9000 acres (Sector 1 to 30) for 1,50,000 people whereas Phase-II consisting of 17 considerably high density Sectors ( Sectors 31 to 47) spread over an area of 6000 acres for a population of 3,50,000.- Number 1 in the country in terms of Human Development Index. Chandigarh has been rated as the “Wealthiest Town” of India. In terms of family wealth, it was rated as the sixth most prosperous city. Good Governance- A compact, efficient Administration having Quick Decision making system.
Jit Kumar Gupta,
Chief Town Planner
Sahara Prime City Ltd,
Area Office , Chandigarh
Untold Story
of ChandigarhMaster Plan
Urban Planning and Legal Framework
In this era of rapid and massive urbanization:
¾urban land development and
¾urban development process
emerged critical areas of major concerns to all governments. Planning and Management of urban settlements have major implications on:¾economic development,
¾social change,
¾Environmental sustainability,
¾operational efficiency of any society and
¾Welfare of the community
At the root of such development / administration are -human beings and their basic requirements of living, working, cobs and travel - land / its allocation / planning and management involving -- Sub-division and --- Use of Land Land-use planning emerges most powerful element in the process of urban development.Urban Planning and Legal Framework
yAll civilized societies have roots in a defined system of rules /regulations yPlanned growth and development also requires a well defined regime of law to support . yPlanning legislation has profound implications for urban development because:¾It defines system of urban government.
¾Establishes systems of Urban Planning & Regulation of land development. ¾Delimits the role and power of Urban Planners & Managers. ¾Defines basic procedure for Plan Preparation, Approval and making them Operational. yLaw never a neutral instrument. yLaw has vital implications for society- and cities for their functioning and development. yBehind every law lies political and policy issues and not merely technical agenda. yIndian legal framework for planning is primarily colonial.yLegal System not rational to cope with emerging problems of India because of inadequacies of planning practices/planning systems of colonial law.
Urban Planning and Legal Framework
yWith urbanizations picking up number of laws have been enacted to control, regulate & promote planned urban development.
yUrban development being state subject - states enacted large number of laws. yMost of the laws are subject specific yEach law has its¾Objectives
¾Basic framework in terms of what is permitted and prohibited¾Management system and
¾Operational system
yAccordingly there is:¾Multiplicity of laws.
¾Multiplicity of agencies created under law
¾Multiplicity of rules and regulations framed.
yIndian laws are characterized by high degree of bureaucratization with bureaucrats ruling the system.
yNeed to relook at legal framework to make it rational and closer to ground realities. yUrban legal scenario underwent critical change due to the enactment of 74th CAA, 1992 yGave constitutional recognition to Urban Local Bodies yChanged federal structure of the country from 2 to 3 tier y Recognized subjects of yUrban planning, yTown planning & yLand use planning yDistrict planning yMetropolitan planning yProvided for empowering the local authorities to take up the onus of yplanning, ydevelopment and ymanagement of urban areas yProvided for setting up yDistrict Planning Committees at District level yMetropolitan Area Planning Committee for Metropolitan Area yfor preparing District Plans and Metropolitan Area Plans.74th Constitutional Amendment Act, 1992
METHODOLGY FOR MASTER PLAN
The various stages of preparation of Master Plan include:1. Identification and notification of Local Planning Area and Planning Agency
2. Preparation of Existing Land Use Plan
· 3. Assessment and analysis of Local Planning Area in terms of· Regional Setting
· Historical Evolution
· Demographic Studies
· Socio-Economic Studies
Housing
Slums & Poverty
Trade and commerce
Industries
· Traffic & Transportation
· Physical Infrastructure (Water Supply, Sewerage, Solid Waste Management, · Social Infrastructure (Educational, Medical, Recreational, Miscellaneous)Environment , Heritage and Tourism
· Growth Pattern
· Land use
· Available studies and report
· Ongoing and Proposed Projects
METHODOLGY FOR MASTER PLAN
4. Involving Stakeholders through:
y· Meeting with experts y· Think Tank meetings y· NGOs/ Private agencies/ Public Agencies/state Departments y· Public Representatives, y5. Identifying Gaps , Issues and Problems through: y· Comparison with available norms and standards y· Spatial Distribution , Quantitative and Qualitative y6. Carrying out S.W.O.T analysis based upon yȈ Studies made and analysis carried on yȈ City Assessment yȈ Identified problems and gaps yȈ Identifying major socio-economic driversMETHODOLGY FOR MASTER PLAN
y7. Working out City requirements- for next 20 Years based on: y· Population Projections ,Norms and Standard , Broad Land use Requirements. y8. Defining Conceptual Framework through: y· Defining Vision for future growth and development y· Identifying broad objectives y· Laying down mission statements for critical areas y9. Preparation of alternatives--Concept Plans y10. Evolving Draft Master Plan Ȃ Involving Proposed Land Use Plan /Traffic & Transportation Plan along with Development Control Regulations (D.C.R) y· Based on existing land use plan , critical areas, growth divers, areas to be preserved and conserved and promoted, heritage y· Studies and assessment made --- Gaps and problems identified y· Future population growth---- Future infrastructure requirements/ Available land for development y 11. Notifying Draft Master Plan for Inviting Public Objections/ Suggestions--- ConsideringPublic Objections/Suggestions
y12 Finalising Master Plan- Issuing Public notice including Phasing and Investment Plan y12. Evolving Zonal Plans based on Proposed Land UseChandigarh in Historical Perspective
y1947- Capital City of Lahore lost to Pakistan in partition of India y1948- Punjab Government approves the setting up of a new capital y1948- Site for new capital city selected in consultation with Govt of India y1949- First Team- Albert Mayer- hired to plan the city y1949- First Master Plan prepared, Details of superblocks finalised y1950- Death of Mathew Nowiski in a plane crash and hiring of Second team led by Le Corbusier y1951- Second Master Plan evolved y1952- Capital of Punjab, Periphery Control Act, 1952 put in placeȄ8 Kms of periphery notified y1962-Army cantonment, Air Force Station and HMT established in periphery y1962 ȂPeriphery extended from 8 kms to 16 Kms/Periphery controlled area plan put in place y1966Ȃ Re-organisation of Punjab- Chandigarh made UT with 114 skms area- City 70 kms+ 44kms of periphery ( Punj-1021 skm, Haryana-295 skm out of periphery total area of 1360 skms yPost 1966- Mohali (5500 acs)and Panchkula (5000 acs)created by Punjab/ Haryana in periphery y1975- High Powered Co-ordination Committee constituted by GOI under Sec MOUD y1977-Formulation of Chandigarh Urban Complex Plan Involving CHD, Mohali, Panchkula -330 skm y1984- Chandigarh Interstate Regional Plan -2001 prepared-TCPO-2431 skm-pop-25 lakh y1999- Preparation of Chandigarh Interstate Metropolitan Regional Plan for 50 kms radi. y2008- Notification of GMADA Regional Plan 2056- with area of 1021 skm yPost 2008- Haryana added 1550 Acs to Panchkula development y2009 December- Expert Committee Constituted for Draft Master Plan for Chandigarh- 2031LEGAL FRAMEWORK OF CHANDIGARH
Two laws defining the legal framework of Chandigarh -For City-The Capital of Punjab( Development and Regulation )Act, 1952 -For Periphery Ȃ The Punjab New Capital (Periphery) Control Act, 1952 -- The Punjab Capital (Development and Regulation)Building Rules,1952The Capital of Punjab( Development and
Regulation )Act, 1952:
yStatement of Objects and Reasons: yThe construction of the New Capital of Punjab at Chandigarh is in progress. yIt is considered necessary to vest the State Government with legal authority to regulate the sale of building sites and to promulgate building rules on the lines of Municipal Bye-laws so long as a properly constituted local body does not take over the administration of the city. yThe Capital of Punjab (Development and Regulation) Bill, 1952, seeks to carry out the above objects and to repeal the Capital of Punjab (Development and Regulation) Act, 1952, which is a President's Act and is due to expire in April, 1953.The Capital of Punjab(Development &
Regulation)Act, 1952
yIt extends to the City of Chandigarh which shall comprise the area of the site of the Capital of Punjab as notified by the Government and to such areas as may be notified from time to time. yChandigarh" means the areas to which this Act extends; yLaw Provides for; yS 3- Power of Government to Transfer of Land and Buildings yS4ȄPower to issue directions in respect of erection of buildings---architectural features, number of residential units, regulating use of sites , maintaining heights and position of walls, fences and hedges;r estricting use of site for purpose other than building yS5ȄBar to erect buildings in contravention of building rules yS6- Power to require proper maintenance of site and buildings yS7Ȃ Levy of fee or tax for amenities yS8ȄPower to resume and forfeiture of sites for breach of conditions of transfer yS11-Preservation and planting trees-issue Tree Preservation Order yS12ȄContol of AdvertisementsȂ issue Advertisement Control OrderLEGAL FRAMEWORK OF CHANDIGARH-The Capital of
Punjab(Development & Regulation)Act, 1952
yS17-Registration of Architects, engineers and plumbers etcȂ competency to certify any plan or completion of building and engage in plumbing work unless registered and licensed by the Chief Administrator as per qualification prescribed in the first schedule yTHE FIRST SCHEDULE y1. Fellow / Associate of Royal Institute of British Architects or an equivalent registration in any other foreign country. y2. Member / Associate member of the Institution of Engineers (India) y3. Member / Associate member of the Institution of Civil Engineers (England) or an equivalent registration in any other country. y4. Fellow /Associate of the Indian Institute of Architects y5. B.Sc. in Engineering of any Engineering University in India or abroad or Diploma in C.E. Roorkee. y6. Diploma from J.J. School of Arts Bombay. y7. Diploma from School of Architecture, Delhi Polytechnic. y8. Diploma, degree or certificate from any other institution recognised by the Indian Institute of Architects or Institution of Engineers (India).LEGAL FRAMEWORK for area outside CHANDIGARH-
The Punjab New Capital(Periphery) Control Act, 1952 yObjects and Reasons ; yPunjab government is constructing a new capital named Chandigarh. y The Master Plan providing for the future extension of the capital which will extend over a much greater area than the area acquired so far the construction of the first phase of capital. yTo ensure healthy and planned development of the new city it is necessary to prevent growth of slums and ramshackle construction on the land lying on the periphery of the new city. y To achieve this object it is necessary to have legal authority to regulate the use of the said land for the purposes other than the purpose for which it is used at present yPROVISIONS; yS3- Declaration of Controlled Area yS4- Publication of plans for the Controlled Area yS5-Restrictions in controlled Area yS6-Application for permission and grant/refusal of permission yS7- Appeal, S8- Compensation, S9- Arbitration for compensation yS10- Savings, S11-Prohibtion of use of land,, S12- Offences and penalties, S15-ExemptionsFIRST MASTER PLAN OF CHANDIGARH
SECOND MASTER PLAN OF CHANDIGARH
CHANDIGARH PERIPHERY - BEFORE 1966
Chandigarh Periphery-After 1966
Preparing Chandigarh Master Plan- 2031
1 - Punjab &Haryana High Court in CWP 4252 of 2008 Ȃ
Gurbax Singh Gill vs Union of India & others directs : yi)Preparation of the Master Plan for the remaining Periphery area in Act,1952 as also the 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendments; yii) Preparation of Regional Plan for the tri-city of Chandigarh/Mohali/Panchkula for guiding future growth in the periphery; yiii) Preventing any further implementation of ad-hoc projects in the periphery till the formulation of Master Plan.2 -Constitution of the 11 members Expert Committee in December
2009 and expanded on May28, 2010 vide order no 684
-- for preparation of Draft Master Plan of UT Chandigarh keeping in mind and adhering to: y--Decisions of Co-ordination Committee headed by Ministry of Urban Development, GOI y--Directions /orders of the High Court of the Punjab & Haryana High Court in the CWP 4252 OF 2008- Gurbax Singh Shergill vs Union Of India & othersCONSTITUTION OF EXPERT COMMITTEE
Preparing Chandigarh Master Plan- 2031
y3. Expert Committee discussed the strategy/methodology and course of action for preparing the draft master plan y4. Plan preparation involved study of historical documents , ongoing policies and projects of the administration including: y-Mass Rapid Transport Plan y--Shifting of whole-sale markets y--Slum Rehabilitation y--Demand for Higher Floor Area Ratio y--Re -densification of Phase-1 y-Heritage Plan y--Change of landuse of Industrial Plots etcPreparing Chandigarh Master Plan- 2031
y5. Committee met more than 80 times, visited various sites in city/periphery and interacted with various stakeholders including: y--Traders y--Industrialists y--Resident welfare organizations y--Municipal Councilors y-- Representatives of Educational institutions y-State Departments y-- NGOs y--Village Panchayats For feedback on the city, its problems, expectations and their vision for future ChandigarhPreparing Chandigarh Master Plan- 2031
y6. Expert Committee was also briefed by Administrator ( Governor of Punjab) and Advisor to Administrator besidesChief Administrator.
y Expert Committee appoached the various departments of Chandigarh Administration to share their problems, vision and proposals for meeting the immediate and future needs of the city related to their operational areas. y7 Meetings held with representatives of y--- Government of India y--State Governments of Punjab and Haryana y8. Presentation made by RITES regarding Comprehensive Mobility Plan for Chandigarh Urban Complex and improving transport infrastructure in the cityPreparing Chandigarh Master Plan- 2031
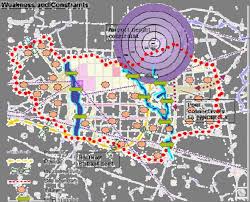
y9 Expert Committee deliberated and considered major issues including: y-Preservation of original concept / basic character of city y--preserving environment, ecology and heritage y--Protecting Sukhna Wildlife Sanctuary/Lake catchment area y--Growth and development of Villages-within / outside grid y--Informal residential/commercial development y--Development of Mohali and Panchkula y--Urban design/architectural controls y-Completing the Capitol complex y--Promoting Pedestrianisation/cycling including rationalisation of traffic y--Revitalizing City Centre/ sub-city centres y--High rise development planned in the north of capitol in Punjab y--Promoting environment, ecology, forest cover y--Improving economy, eco-tourism and mixed land use, infrastructure yRegional issues -- solid waste management/drainage/sanitation/water supply y-Preparing Chandigarh Master Plan- 2031
y- Demographical profile of the city- existing and future y--Holding capacity of city based on existing and future development y-- Promoting Rain water harvesting y--Tapping solar energy to make Chandigarh Solar city y- Promoting zero drainage of storm water from large institutions y-- Providing additional housing and institutional area y--Limitation of city area/ traffic congestion/ large urbanisation in periphery y10. Draft Master Plan- 2031 prepared y11. Draft Master Plan notified by Chandigarh Administration on July 11,2013 for inviting public objections and suggestions y12 In all 171 Suggestions/ objections were received and documentedPreparing Chandigarh Master Plan- 2031
objections/ suggestions received/ give recommendations within one month by giving public hearing for the objections received y14 Board comprised of 8 members, headed by Chairman Chandigarh Housing Board with Municipal Commissioner, Secretary IT, Chief Architect, Chief Engineer, Former Mayor, K S Sidhu(retd) IAS, Chief Planner TCPO/ his representative y15 Board invited 116 applicants for hearing . 101 appeared. Based on study / hearing carried out Board finalised the report/ recommendations and submitted to Chandigarh Administration y16. Chief Architect, Chandigarh Administration finalised the Master Plan in consultation with Chief administrator /Advisor and submitted to Administrator on September 6,2014 y17 Final Master Plan 2031 is still pending for notification.CHANDIGARH POPULATION - EXISITING AND PROJECTED
PHASE I , II & III OF CHANDIGARH
LE CORBUSIER LETTER - 1957
VACANT POCKETS AND AGRICULTURAL AREA
PERSPECTIVE PLAN CHANDIGARH
CHANDIGARH MASTER PLAN -2031
LAND USE DISTRIBUTION -
EXISITING AND PROPOSED
ySince Chandigarh has no legal framework for preparing Master Plan- the Master Plan-2031 may not stand testimony of law yConsidering existing development and population scenario, it is vital that Chandigarh should be transformed from a Designed City to a Planned city yChandigarh now deserves a legally supported and legally framed Comprehensive Development Plan and Regional Plan to rationalize it future growth and development yA Comprehensive Planning ,Development and Management Legal framework in the form of a State of Art law needs to be immediately put in place for Chandigarh to replace the existing laws. yComprehensive law must provide for integrated planning and development of city and periphery. ySince Periphery has lost relevance, Periphery Control Act should be replaced by a Central Regional Planning law on the pattern followed for NCR to prepare and implement Regional Plan forChandigarh Capital Inter-State Regional Plan.
yInter-state Co-ordination Committee constituted by Government of India should be replaced by the Regional Planning Board comprising of partner states of Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh , Chandigarh,GOI and others yChandigarh needs a dedicated Professional Authority to replace bureaucratic structure to regulate its future Growth and development on professional lines. yRole of Municipal Corporation Chandigarh would needs redefinition, considering provisions of 74th ConstitutionalAmendment Act,1992 and specialized planning,
development and management requirements of the cityTHANKS
FOR YOUR
PATIENCE
AND TIME
quotesdbs_dbs14.pdfusesText_20[PDF] master's programs in paris
[PDF] mastering bitcoin pdf
[PDF] mastering bootstrap 4 second edition free download
[PDF] mastering bootstrap 4 github
[PDF] mastering data analysis in excel pdf
[PDF] mastering html
[PDF] mastering object oriented php pdf
[PDF] mastering sql queries pdf
[PDF] mastering the zodiac pdf
[PDF] masters in international business curriculum
[PDF] masters in international dispute settlement
[PDF] mata bus schedule 40
[PDF] mata bus schedule memphis tn
[PDF] material para enseñar español a extranjeros adultos