 Advanced R Cheat Sheet
Advanced R Cheat Sheet
R base types - the internal C-level types that underlie the above OO systems RStudio® is a trademark of RStudio Inc. • CC BY Arianne Colton
 R Markdown Cheat Sheet
R Markdown Cheat Sheet
The above is metadata saved in a YAML header. The RStudio template writes the YAML header for you output: html_document html file
 R and R Studio Reference Guides and Cheat Sheet Compilation
R and R Studio Reference Guides and Cheat Sheet Compilation
7 to 8 • Base R Cheat Sheet
 Base R - Cheat Sheet
Base R - Cheat Sheet
Use projects in RStudio to set the working directory to the folder you are working in. Vectors. Creating Vectors c(2 4
 data-wrangling-cheatsheet.pdf
data-wrangling-cheatsheet.pdf
RStudio® is a trademark of RStudio Inc. • CC BY RStudio • info@rstudio.com • 844 Logic in R - ?Comparison
 Base R
Base R
Base R. Cheat Sheet. RStudio® is a trademark of RStudio Inc. • CC BY Mhairi McNeill • mhairihmcneill@gmail.com. Learn more at web page or vignette • package
 paulvanderlaken.com
paulvanderlaken.com
Base R. Cheat Sheet. RStudio® is a trademark of RStudio Inc. • CC BY Mhairi McNeill • mhairihmcneill@gmail.com. Learn more at web page or vignette • package
 R color cheatsheet
R color cheatsheet
This color cheatsheet will help! R uses hexadecimal to represent colors. Hexadecimal is a base-16 number system used to describe color. Red green
 Colors in R
Colors in R
Colors in R. 1. This wonderful R colors cheat-sheet was created by. Dr. Ying Wei. Department of Biostatistics. Columbia University https://yingweistat.com/. It
 base R cheat-sheet
base R cheat-sheet
Base R. Cheat Sheet. RStudio® is a trademark of RStudio Inc. • CC BY Mhairi McNeill Read and write an R data file
 Base R - Cheat Sheet
Base R - Cheat Sheet
Base R. Cheat Sheet. Getting Help. Accessing the help files ?mean. Get help of a particular function. Use projects in RStudio to set the working.
 Base R
Base R
Base R. Cheat Sheet. RStudio® is a trademark of RStudio Inc. • CC BY Mhairi McNeill Read and write an R data file
 paulvanderlaken.com
paulvanderlaken.com
Base R. Cheat Sheet. RStudio® is a trademark of RStudio Inc. • CC BY Mhairi McNeill • mhairihmcneill@gmail.com. Learn more at web page or vignette
 data-wrangling-cheatsheet.pdf
data-wrangling-cheatsheet.pdf
Cheat Sheet. RStudio® is a trademark of RStudio Inc. • CC BY RStudio • info@rstudio.com • 844-448-1212 Tidy Data - A foundation for wrangling in R.
 Base R Cheat Sheet
Base R Cheat Sheet
Base R. Cheat Sheet. RStudio® is a trademark of RStudio Inc. • CC BY Mhairi McNeill Read and write an R data file
 Advanced R Cheat Sheet
Advanced R Cheat Sheet
Advanced R. Cheat Sheet. Environment Basics. RStudio® is a trademark of RStudio Inc. • CC BY Arianne Colton
 Base R Cheat Sheet
Base R Cheat Sheet
Ki?n th?c c? b?n v? R. Cheat Sheet. RStudio® is a trademark of RStudio Inc. • CC BY RStudio • info@rstudio.com • 844-448-1212 • rstudio.com.
 Base R
Base R
Base R. Cheat Sheet. RStudio® is a trademark of RStudio Inc. • CC BY Mhairi McNeill • mhairihmcneill@gmail.com. Learn more at web page or vignette
 R Markdown Cheat Sheet
R Markdown Cheat Sheet
R Markdown Cheat Sheet learn more at rmarkdown.rstudio.com rmarkdown 0.2.50 Updated: 8/14. 1. Workflow R Markdown is a format for writing reproducible
 Base R Programming - unicefr
Base R Programming - unicefr
Base R Cheat Sheet Getting HelpVectors Creating Vectors c(2 4 6) 2 4 6 2:6 2 3 4 5 6 For Loop Programming While Loop for (variable in sequence) { Do something } Accessing the help ?les ?mean Get help of a particular function help search('weighted mean') Search the help ?les for a word or phrase seq(2 3 by=0 5) 2 0 2 5 3 0
 R Reference Card - The Comprehensive R Archive Network
R Reference Card - The Comprehensive R Archive Network
log(x base)computes the logarithm of x with base base scale(x)if x is a matrix centers and reduces the data; to center only use the option center=FALSE to reduce only scale=FALSE (by default
 Cheat Sheet for R and RStudio - University of California
Cheat Sheet for R and RStudio - University of California
Open R-Studio In the interpreter (lower left-hand box of RStudio) type library(foreign) and hitEnter This will install the package that reads your csv?les In the box on the upper-right hand corner of RStudio click on the tab that says“Workspace” Then click on “Import Dataset>From Text File ” Find your csvdataset and openit
 Searches related to base r cheat sheet rstudio filetype:pdf
Searches related to base r cheat sheet rstudio filetype:pdf
Data Visualization with ggplot2 : : CHEAT SHEET ggplot2 is based on the grammar of graphics the idea that you can build every graph from the same components: a data set a coordinate system and geoms—visual marks that represent data points Basics GRAPHICAL PRIMITIVES a + geom_blank() (Useful for expanding limits)
What is a backtick in RStudio?
- Note: the backtick (`), lets you refer to functions or variables that have otherwise reserved or illegal names. Simplifying vs. Preserving Subsetting RStudio® is a trademark of RStudio, Inc. • CC BY Arianne Colton, Sean Chen • data.scientist.info@gmail.com • 844-448-1212 • rstudio.com Updated: 2/16
How to list all variables in the environment in RStudio?
- List all variables in the environment. rm(x)Remove x from the environment. rm(list = ls())Remove all variables from the environment. You can use the environment panel in RStudio to browse variables in your environment.
What are the different types of data in R?
- Converting between common data types in R. Can always go from a higher value in the table to a lower value. Boolean values (TRUE or FALSE). Integers or ?oating point numbers. Character strings. Generally preferred to factors. Character strings with preset levels. Needed for some statistical models. Natural log. Exponential. Largest element. Sum.
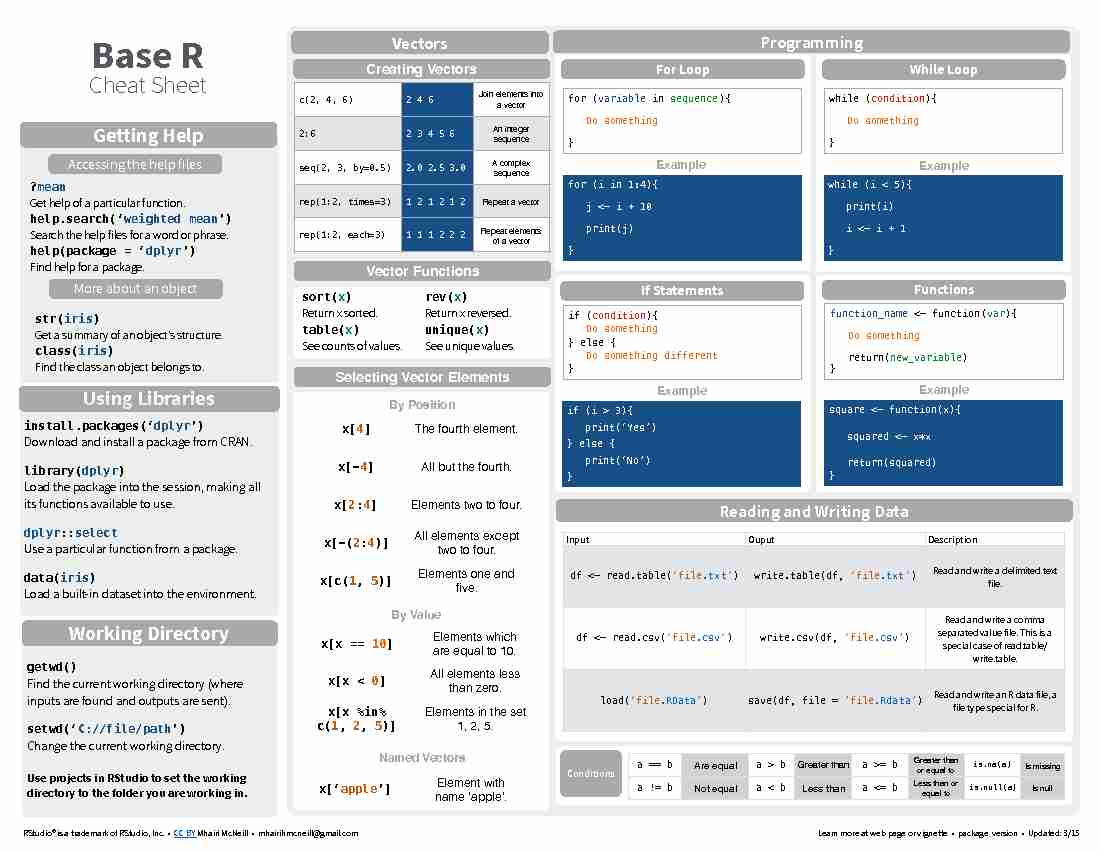
Base R Cheat Sheet RStudio® is a trademark of RStudio, Inc. • CC BY Mhairi McNeill • mhairihmcneill@gmail.com Learn more at web page or vignette • package version • Updated: 3/15InputOuputDescription df <- read.table('file.txt')write.table(df, 'file.txt')Read and write a delimited text file.df <- read.csv('file.csv')write.csv(df, 'file.csv')Read and write a comma separated value file. This is a special case of read.table/write.table. load('file.RData')save(df, file = 'file.Rdata')Read and write an R data file, a file type special for R. ?mean Get help of a particular function. help.search('weighted mean') Search the help files for a word or phrase. help(package = 'dplyr') Find help for a package. Getting HelpAccessing the help filesMore about an objectstr(iris) Get a summary of an object's structure. class(iris) Find the class an object belongs to.ProgrammingFor Loopfor (variable in sequence){ Do something }Examplefor (i in 1:4){ j <- i + 10 print(j) }While Loopwhile (condition){ Do something }Examplewhile (i < 5){ print(i) i <- i + 1 }If Statementsif (condition){ Do something } else { Do something different }Exampleif (i > 3){ print('Yes') } else { print('No') }Functionsfunction_name <- function(var){ Do something return(new_variable) }Examplesquare <- function(x){ squared <- x*x return(squared) }a == bAre equala > bGreater thana >= bGreater than or equal tois.na(a)Is missinga != bNot equala < bLess thana <= bLess than or equal tois.null(a)Is null ConditionsCreating Vectorsc(2, 4, 6)2 4 6Join elements into a vector 2:62 3 4 5 6An integer sequenceseq(2, 3, by=0.5)2.0 2.5 3.0A complex sequencerep(1:2, times=3)1 2 1 2 1 2Repeat a vectorrep(1:2, each=3)1 1 1 2 2 2Repeat elements of a vector Using Librariesinstall.packages('dplyr') Download and install a package from CRAN. library(dplyr) Load the package into the session, making all its functions available to use. dplyr::select Use a particular function from a package. data(iris) Load a built-in dataset into the environment. VectorsSelecting Vector Elements x[4]The fourth element.x[-4]All but the fourth.x[2:4]Elements two to four.x[-(2:4)]All elements except two to four.x[c(1, 5)]Elements one and five.x[x == 10]Elements which are equal to 10.x[x < 0]All elements less than zero.x[x %in% c(1, 2, 5)]Elements in the set 1, 2, 5.By PositionBy ValueNamed Vectors x['apple']Element with name 'apple'.Reading and Writing DataWorking Directorygetwd() Find the current working directory (where inputs are found and outputs are sent). setwd('C://file/path') Change the current working directory. Use projects in RStudio to set the working directory to the folder you are working in. Vector Functionssort(x) Return x sorted.rev(x) Return x reversed.table(x) See counts of values.unique(x) See unique values.
RStudio® is a trademark of RStudio, Inc. • CC BY Mhairi McNeill • mhairihmcneill@gmail.com • 844-448-1212 • rstudio.com Learn more at web page or vignette • package version • Updated: 3/15ListsMatrixesData FramesMaths Functions Types Strings Factors Statistics Distributions as.logicalTRUE, FALSE, TRUEBoolean values (TRUE or FALSE).as.numeric1, 0, 1Integers or floating point numbers.as.character'1', '0', '1'Character strings. Generally preferred to factors.as.factor'1', '0', '1', levels: '1', '0'Character strings with preset levels. Needed for some statistical models. Converting between common data types in R. Can always go from a higher value in the table to a lower value. > a <- 'apple' > a [1] 'apple'The EnvironmentVariable Assignmentls()List all variables in the environment.rm(x)Remove x from the environment.rm(list = ls())Remove all variables from the environment.You can use the environment panel in RStudio to browse variables in your environment. factor(x) Turn a vector into a factor. Can set the levels of the factor and the order.m <- matrix(x, nrow = 3, ncol = 3) Create a matrix from x.wwwwwwm[2, ] - Select a rowm[ , 1] - Select a columnm[2, 3] - Select an elementwwwwwwwwwwwwt(m) Transpose m %*% n Matrix Multiplication solve(m, n) Find x in: m * x = nl <- list(x = 1:5, y = c('a', 'b')) A list is collection of elements which can be of different types. l[[2]]l[1]l$xl['y']Second element of l.New list with only the first element.Element named x.New list with only element named y.df <- data.frame(x = 1:3, y = c('a', 'b', 'c')) A special case of a list where all elements are the same length.t.test(x, y) Preform a t-test for difference between means. pairwise.t.test Preform a t-test for paired data.log(x)Natural log.sum(x)Sum.exp(x)Exponential.mean(x)Mean.max(x)Largest element.median(x)Median. min(x)Smallest element.quantile(x)Percentage quantiles.round(x, n)Round to n decimal places.rank(x)Rank of elements.signif(x, n)Round to n significant figures.var(x)The variance.cor(x, y)Correlation.sd(x)The standard deviation.xy1a2b3cMatrix subsettingdf[2, ]df[ , 2]df[2, 2]List subsettingdf$xdf[[2]]cbind - Bind columns.rbind - Bind rows.View(df)See the full data frame.head(df)See the first 6 rows.Understanding a data framenrow(df) Number of rows. ncol(df) Number of columns. dim(df) Number of columns and rows.Plotting Dates See the lubridate library.Also see the ggplot2 library.Also see the stringr library.Also see the dplyr library.plot(x) Values of x in order.plot(x, y) Values of x against y.hist(x) Histogram of x.Random Variates Density FunctionCumulative DistributionQuantileNormalrnormdnormpnormqnormPoisonrpoisdpoisppoisqpoisBinomialrbinomdbinompbinomqbinomUniformrunifdunifpunifquniflm(x ~ y, data=df) Linear model. glm(x ~ y, data=df) Generalised linear model. summary Get more detailed information out a model.prop.test Test for a difference between proportions. aov Analysis of variance. paste(x, y, sep = ' ') Join multiple vectors together.paste(x, collapse = ' ') Join elements of a vector together.grep(pattern, x)Find regular expression matches in x. gsub(pattern, replace, x)Replace matches in x with a string.toupper(x)Convert to uppercase.tolower(x)Convert to lowercase.nchar(x)Number of characters in a string. cut(x, breaks = 4) Turn a numeric vector into a factor but 'cutting' into sections.
quotesdbs_dbs31.pdfusesText_37[PDF] Cours 4 data frames
[PDF] Package 'wikipediatrend' - CRANR-projectorg
[PDF] Data Mart Consolidation - IBM Redbooks
[PDF] Data mining 1 Exploration Statistique - Institut de Recherche
[PDF] Cours de Data Mining
[PDF] Qu'est-ce que le text and data mining - OpenEdition Books
[PDF] Data Mining & Statistique
[PDF] Cours IFT6266, Exemple d'application: Data-Mining
[PDF] Introduction au Data Mining - Cedric/CNAM
[PDF] Defining a Data Model - CA Support
[PDF] Learning Data Modelling by Example - Database Answers
[PDF] Nouveaux prix à partir du 1er août 2017 Mobilus Mobilus - Proximus
[PDF] règlement général de la consultation - Inventons la Métropole du
[PDF] Data science : fondamentaux et études de cas
