 Acylium Ion Formation in the Reactions of Carboxylic Acid
Acylium Ion Formation in the Reactions of Carboxylic Acid
tions of benzoic acid and mesitoic acid derivatives indicates that hindered benzoic acid derivatives may react 2.—log k/kts for the rates of hydrolysis of ...
 Solvent Isotope Effects in Catalyzed Hydrolysis of Carboxylic Acid
Solvent Isotope Effects in Catalyzed Hydrolysis of Carboxylic Acid
The latter mechanism is discarded for carboxylic acid derivatives with good leaving groups. (phenyl esters and anhydrides). Solvent isotopeeffects obtained from
 Chapter 21 The Chemistry of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
Chapter 21 The Chemistry of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
21.11 (a). The hydrolysis products consist of the conjugate base of the carboxylic acid and an amine: rates of acid-catalyzed ester and amide hydrolyses is ...
 Acylium Ion Formation in the Reactions of Carboxylic Acid
Acylium Ion Formation in the Reactions of Carboxylic Acid
tions of benzoic acid and mesitoic acid derivatives indicates that hindered benzoic acid derivatives may react 2.—log k/kts for the rates of hydrolysis of ...
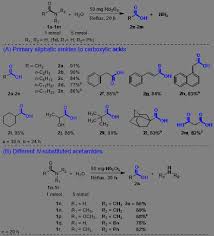 Hydrolysis of Amides to Carboxylic Acids Catalyzed by Nb2O5
Hydrolysis of Amides to Carboxylic Acids Catalyzed by Nb2O5
25 дек. 2020 г. carboxylic acid derivatives while ... 2 (A) Correlation between initial reaction rates of carboxylic acid formation from hydrolysis of.
 IV.* Rate Constants for the Hydrolysis of Some Cyclic Anhydrides
IV.* Rate Constants for the Hydrolysis of Some Cyclic Anhydrides
trans-conformation 38 analogous to the conformational situation in carboxylic esters and other carboxylic acid derivatives.21 Succinic anhydride must neces-.
 HYDROLYSIS 2016.pdf
HYDROLYSIS 2016.pdf
carbon centre such as with carboxylic acid derivatives including esters
 Secondary Deuterium Isotope Effects in the Reactions of Carboxylic
Secondary Deuterium Isotope Effects in the Reactions of Carboxylic
on the rates of hydrolysis of these carboxylic acid derivatives has been determined. In the basic hydrolysis of ethyl acetate in aqueous solution at 25.0
 Intermediates in the Reactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives. IV
Intermediates in the Reactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives. IV
indicated that amide hydrolysis is in general similar to ester hydrolysis. The rate of basic hydrolysis is proportional to the concentrations of amide and
 estimation of hydrolysis rate constants of carboxylic acid ester and
estimation of hydrolysis rate constants of carboxylic acid ester and
Carboxylic Acid Esters. Ester functions are among the most common acid derivatives present in natural as well as man-made chemicals (e.g. lipids
 21.7 HYDROLYSIS OF CARBOXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVES
21.7 HYDROLYSIS OF CARBOXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVES
All carboxylic acid derivatives have in common the fact that they undergo hydrolysis (a cleav- age reaction with water) to yield carboxylic acids. A. Hydrolysis
 HYDROLYSIS 2016.pdf
HYDROLYSIS 2016.pdf
carbon centre such as with carboxylic acid derivatives including esters
 Acylium Ion Formation in the Reactions of Carboxylic Acid
Acylium Ion Formation in the Reactions of Carboxylic Acid
acid derivatives. The applicability of this mechanistic criterion is tested here by investigatingthe effect of substituents on the rates of hydrolysis of
 Solvent Isotope Effects in Catalyzed Hydrolysis of Carboxylic Acid
Solvent Isotope Effects in Catalyzed Hydrolysis of Carboxylic Acid
The latter mechanism is discarded for carboxylic acid derivatives with good leaving groups Solvent isotopeeffects obtained from rate of.
 Acylium Ion Formation in the Reactions of Carboxylic Acid
Acylium Ion Formation in the Reactions of Carboxylic Acid
Acylium Ion Formation in theReactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives. III. The Hydrolysis dioxane a powerful acceleration of the rate of hydrolysis.
 Carboxylic acid participation in amide hydrolysis. External general
Carboxylic acid participation in amide hydrolysis. External general
carboxylic acid promoted amide hydrolysis is presented which involves intermediates of rate constant on the basicity of the aniline derivative. From the.
 The Effect of Charge-Transfer Complexation on the Hydrolysis of
The Effect of Charge-Transfer Complexation on the Hydrolysis of
in the bimolecular rate constants for the reaction be- the hydrolysis of a carboxylic acid derivative by proper complex formation between a donor ...
 Intermediates in the Reactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives. IV
Intermediates in the Reactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives. IV
Intermediates in theReactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives. IV. boxylic acid derivatives has led to the investiga- ... The rate of basic hydrolysis is.
 Chapter 21 The Chemistry of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
Chapter 21 The Chemistry of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
1014 and the discussion on text pp. 1012–1014.) Leaving-group basicities: In the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of an ester
 Hydrolysis of Amides to Carboxylic Acids Catalyzed by Nb2O5
Hydrolysis of Amides to Carboxylic Acids Catalyzed by Nb2O5
25 ????. 2020 ?. KEYWORDS: Nb2O5 Catalyst Amide hydrolysis
 Loudon Chapter 21 Review: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
Loudon Chapter 21 Review: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
Nov 3 2021 · Hydrolysis of derivatives Any of the derivatives of carboxylic acids can be converted back into the acid by using water If it’s a more stable derivative you also need either acid or base as a catalyst
 Solved: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Undergo Hydrolysis To
Solved: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Undergo Hydrolysis To
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Acid Halide Anhydride Ester Amide Acyl Transfer Reactions Background a Transformation b Relative Reactivity c Mechanism Acid Chlorides/Anhydrides Esters a Hydrolysis 5 Amides i Acid catalyzed ii Base promoted b Transesterification Acid hydrolysis Base hydrolysis i Acid catalyzed ii Base catalyzed 6
 171 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives: Properties and Names
171 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives: Properties and Names
Acid catalyzedester hydrolysis is simply the reverse of esterification reaction In this reaction an ester is treated with water in the presence of a strong acid catalyst such as sulfuric acid Base catalyzedester hydrolysis with a base such as NaOH or KOH is known as saponofication The product of saponification
 CARBOXY - authorslibrarycaltechedu
CARBOXY - authorslibrarycaltechedu
18 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives and phenylmethanol (CHCHOH) The chemical shift of the carboxylic acid proton is here about 9 ppm toward lower magnetic fields than that of the hydroxyl proton of the alcohol This behavior parallels that of the en01 hydrogens of 13-dicarbonyl compounds and is similarly related to hydrogen-
 Notes - 19 Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives - CIE Chemistry A
Notes - 19 Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives - CIE Chemistry A
Hydrolysis of acyl chlorides Hydrolysis occurs when an acyl chloride reacts with water The products of hydrolysis are hydrochloric acid and a carboxylic acid The reaction between ethanoyl chloride and water is shown below: CH 3 COCl + H 2 O ? CH 3 COOH + HCl Reactions of acyl chlorides www pmt education
 Searches related to rates of hydrolysis of carboxylic acid derivatives filetype:pdf
Searches related to rates of hydrolysis of carboxylic acid derivatives filetype:pdf
Hydrolysis of an esters is aqueous base is called saponification Each mol of ester hydrolyzed requires 1 mol of base; for this reason ester hydrolysis in aqueous base is said to be “base-promoted” (not catalyzed) Hydrolysis of an ester in aqueous base involves Nucleophilic acyl substitution
What determines the rate of hydrolysis of carboxylic acid derivatives?
- The rate of hydrolysis depends on the leaving group, L. Rank the carboxylic acid derivatives according to their reactivity, from the most reactive to the least reactive. Question: Carboxylic acid derivatives undergo hydrolysis to make carboxylic acids.
What are the derivatives of carboxylic acid?
- Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution 20.1: Nomenclature of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives (please read) O C ROH O C ROR' carboxylic acid -oic acid ester -oate O C RO R' lactone cyclic ester O C RCl acid chloride -oyl chloride O C RO O C R acid anhydride -oic anhydride O C RN R' R'' amide -amide O C RN R'
How are nitriles hydrolyzed into carboxylic acids?
- Nitriles are hydrolyzed in either aqueous acid or aqueous base to give carboxylic acids. The corresponding primary amide is an intermediate in the reaction. Base-promoted mechanism (Fig. 20.8, p. 865) Acid-promoted hydrolysis: 184 20.17: Addition of Grignard Reagents to Nitriles.
How do carboxylic acid derivatives decrease electrophilicity?
- In carboxylic acid derivatives, the partial positive charge on the carbonyl carbon is stabilized by electron donation from nonbonding electrons on the adjacent heteroatom, which has the effect of decreasing electrophilicity.