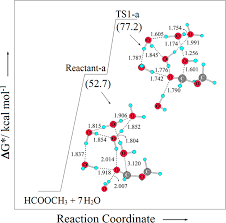
 Revisiting the Mechanism of Neutral Hydrolysis of Esters: Water
Revisiting the Mechanism of Neutral Hydrolysis of Esters: Water
3 мая 2013 г. neutral hydrolysis of activated thioesters have also preferred this general base catalysis mechanism in aqueous medium. It is worthwhile to ...
 Carbonion (ElcB)mechanism of ester hydrolysis. I. Hydrolysis of
Carbonion (ElcB)mechanism of ester hydrolysis. I. Hydrolysis of
glass calomel electrode (Radiometer GK 2021C). Materials. Anhydrous potassium carbonate potassium chlo- ride
 General Basic Catalysis of Ester Hydrolysis and Its Relationship to
General Basic Catalysis of Ester Hydrolysis and Its Relationship to
The action of imidazole as a general basic catalyst offers only a partial ex- planation of the mechanism of enzymatic hydrolysis. Introduction. The hydrogen and
 The Reaction Rate of the Alkaline Hydrolysis of Ethyl Acetate
The Reaction Rate of the Alkaline Hydrolysis of Ethyl Acetate
base and ester draw closer to each other. Previous works on this kinetics This mechanism of the basic hydrolysis of esters was proposed by Day and Ingold.
 General base catalysis of ester hydrolysis
General base catalysis of ester hydrolysis
2 1990 669-673. 0002-7863/93/1515-6045$04.00/0 mechanism of catalysis of the hydrolysis of aliphatic esters has.
 Studies on the BAL2 mechanism for ester hydrolysis
Studies on the BAL2 mechanism for ester hydrolysis
71 1841 (1993). The preparation and alkaline hydrolysis of "0-methyl 2
 Organic Chemistry Fifth Edition
Organic Chemistry Fifth Edition
Acid-Catalyzed Hydrolysis of Esters - Mechanism. Page 24. First stage Mechanism of Ester Hydrolysis in Base. Page 52. First stage: formation of tetrahedral ...
 Steric Effects in the Hydrolysis of N-Acylimidazoles and Esters of p
Steric Effects in the Hydrolysis of N-Acylimidazoles and Esters of p
classical general base mechanisms. Nucleophilic catal- ysis of ester to general base catalysis. To assess the generality of these effects a study of steric ...
 The Mechanism of Hydrolysis of Imidate Salts. The Importance of
The Mechanism of Hydrolysis of Imidate Salts. The Importance of
L'hydrolyse des sels imidates anti conduit toujours aux produits ester amine quelque soit le p H du milieu rkactionnel. En milieu acide ou legerement basique
 Carbonion (ElcB)mechanism of ester hydrolysis. I. Hydrolysis of
Carbonion (ElcB)mechanism of ester hydrolysis. I. Hydrolysis of
mechanism is that for normal alkaline hydrolysis of esters in eq 2a it is preequilibrium formation of a car- banion with subsequent elimination of R'O
 General Basic Catalysis of Ester Hydrolysis and Its Relationship to
General Basic Catalysis of Ester Hydrolysis and Its Relationship to
The action of imidazole as a general basic catalyst offers only a partial ex- planation of the mechanism of enzymatic hydrolysis. Introduction. The hydrogen and
 General base catalysis of ester hydrolysis
General base catalysis of ester hydrolysis
Both nucleophilic and general base mechanisms of catalysis by acetate anions are observed for the hydrolysis of substituted phenyl formates with leaving
 MECHANISM AND KINETICS OF CARBOXYLIC ESTER
MECHANISM AND KINETICS OF CARBOXYLIC ESTER
ESTERIFICATION. BY J. N. E. DAY AND C. K. INGOLD. Received 4th September 1941. Arrangement. I. Multiplicity of Mechanism. 2. Bimolecular Basic Hydrolysis
 21.7 HYDROLYSIS OF CARBOXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVES
21.7 HYDROLYSIS OF CARBOXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVES
term saponification can be used to refer to the hydrolysis in base of any carboxylic acid derivative. The mechanism of ester saponification involves the
 HYDROLYSIS 2016.pdf
HYDROLYSIS 2016.pdf
carbon centre such as with carboxylic acid derivatives including esters
 Carbonion (ElcB)mechanism of ester hydrolysis. I. Hydrolysis of
Carbonion (ElcB)mechanism of ester hydrolysis. I. Hydrolysis of
modes of HO~ attack on malonate esters are conceivable a priori (1 and 2a and 2b). In eq 1 the mechanism is that for normal alkaline hydrolysis of.
 A Facile Base-catalyzed Ester Hydrolysis Involving Alkyl-Oxygen
A Facile Base-catalyzed Ester Hydrolysis Involving Alkyl-Oxygen
(4) base catalysis. Reaction 1 is of course the ordinary mechanism by which most esters undergo base-catalyzed hydrolysis.4 Anchimeric catalysis (2)has been.
 The mechanism of hydrolysis of a cobalt(III)-bound phosphate ester
The mechanism of hydrolysis of a cobalt(III)-bound phosphate ester
and mechanism of base hydrolysis of a well-defined and robust pentaamminecobalt(III) complex of p-nitrophenylphosphate(1.
 Solvent Effects and Ester Interchange in Basic Hydrolysis of Esters
Solvent Effects and Ester Interchange in Basic Hydrolysis of Esters
The saponification of ethyl acetate and methyl acetate has been measured at 30° in dioxane-water mixtures containing additional solvents found earlier to
 Lecture 6: Hydrolysis Reactions of Esters and Amides - Objectives
Lecture 6: Hydrolysis Reactions of Esters and Amides - Objectives
draw the mechanism of ester hydrolysis under acidic and basic reaction conditions;. • account for the irreversibility of the hydrolysis reaction under basic