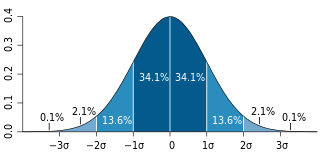
Different measures of spread
A standard deviation (or σ) is a measure of how dispersed the data is in relation to the mean.
Low, or small, standard deviation indicates data are clustered tightly around the mean, and high, or large, standard deviation indicates data are more spread out..
Different measures of spread
The standard deviation is used in conjunction with the mean to summarise continuous data, not categorical data.
In addition, the standard deviation, like the mean, is normally only appropriate when the continuous data is not significantly skewed or has outliers..
How do I calculate standard deviation?
Step 1: Find the mean.
Step 2: For each data point, find the square of its distance to the mean.
Step 3: Sum the values from Step 2.
Step 4: Divide by the number of data points..
How do you analyze standard deviation?
Smaller values indicate that the data points cluster closer to the mean—the values in the dataset are relatively consistent.
Conversely, higher values signify that the values spread out further from the mean.
Data values become more dissimilar, and extreme values become more likely..
How do you calculate standard deviation in biostatistics?
σ = √∑dx2/N when deviations are taken from actual mean. σ = √∑fdx2/N – (∑fdx2/N)2 when deviations are taken from an assumed mean.
In continuous series, calculations can be simplified if we divide the deviations of the midpoints by class Interval..
How do you find standard deviation in biostatistics?
Steps for calculating the standard deviation by hand
1Step 1: Find the mean.
2) Step 2: Find each score's deviation from the mean.
3) Step 3: Square each deviation from the mean.
4) Step 4: Find the sum of squares.
5) Step 5: Find the variance.
6) Step 6: Find the square root of the variance..Measures of variability and correlation
Standard deviation is important because it helps in understanding the measurements when the data is distributed.
The more the data is distributed, the greater will be the standard deviation of that data..
Measures of variability and correlation
Standard deviation measures how far apart numbers are in a data set.
Variance, on the other hand, gives an actual value to how much the numbers in a data set vary from the mean.
Standard deviation is the square root of the variance and is expressed in the same units as the data set..
Measures of variability and correlation
The standard deviation is a measure of spread or variability in descriptive statistics.
It is used for calculating the variance or spread by which individual data points differ from the mean..
What does the standard deviation tell you?
The standard deviation is the average amount of variability in your dataset.
It tells you, on average, how far each value lies from the mean.
A high standard deviation means that values are generally far from the mean, while a low standard deviation indicates that values are clustered close to the mean.Sep 17, 2020.
What is SD in statistical analysis?
Standard deviation is a statistic that measures the dispersion of a dataset relative to its mean and is calculated as the square root of the variance.
The standard deviation is calculated as the square root of variance by determining each data point's deviation relative to the mean..
What is standard deviation in biostatistics?
A standard deviation (or σ) is a measure of how dispersed the data is in relation to the mean.
Low, or small, standard deviation indicates data are clustered tightly around the mean, and high, or large, standard deviation indicates data are more spread out..
What is standard deviation in statics?
The standard deviation is a summary measure of the differences of each observation from the mean.
If the differences themselves were added up, the positive would exactly balance the negative and so their sum would be zero.
Consequently the squares of the differences are added..
What is the purpose of standard deviation?
What Does Standard Deviation Tell You? Standard deviation describes how dispersed a set of data is.
It compares each data point to the mean of all data points, and standard deviation returns a calculated value that describes whether the data points are in close proximity or whether they are spread out..
Where is the standard deviation located?
What Is Standard Deviation? Standard deviation is a statistic that measures the dispersion of a dataset relative to its mean and is calculated as the square root of the variance.
The standard deviation is calculated as the square root of variance by determining each data point's deviation relative to the mean..
Why is standard deviation important in biostatistics?
Standard deviation is important because it helps in understanding the measurements when the data is distributed.
The more the data is distributed, the greater will be the standard deviation of that data..
Why is standard deviation the most important?
Why is the Standard Deviation Important? Understanding the standard deviation is crucial.
While the mean identifies a central value in the distribution, it does not indicate how far the data points fall from the center.
Higher SD values signify that more data points are further away from the mean..