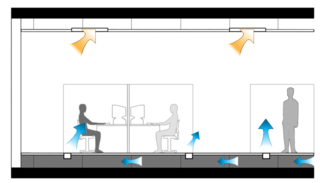
How do you bring air into a building?
Bring more clean outdoor air into spaces by opening windows and doors and using exhaust fans.
Even small openings can help.
Air cleaners (also known as air purifiers) filter air with high-efficiency filters that remove germs from the air..
How does air get into buildings?
Air comes into buildings and leaves by three different ways: Doors and windows, whenever they are opened.
Joints, cracks and openings where parts of the building connect, including floors and walls and around windows and pipes.
Spot ventilation, including fans that pull air from the bathroom..
How does fresh air get into a house?
How Fresh Air Comes into Your Home.
Air comes into buildings and leaves by three different ways: Doors and windows, whenever they are opened.
Joints, cracks and openings where parts of the building connect, including floors and walls and around windows and pipes..
Makeup air unit
Supply ventilation systems use a fan to pressurize your home, forcing outside air into the building while air leaks out of the building through holes in the shell, bath, and range fan ducts, and intentional vents (if any exist)..
What are the reasons for ventilation in a building?
The general purpose of ventilation in buildings is to provide healthy air for breathing by both diluting the pollutants originating in the building and removing the pollutants from it (Etheridge & Sandberg, 1996; Awbi, 2003)..
What is building HVAC?
HVAC stands for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning.
It refers to the systems that regulate and move heated and cooled air throughout residential and commercial buildings, from homes to offices to indoor stadiums..
What is HVAC in building?
HVAC stands for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning.
It refers to the systems that regulate and move heated and cooled air throughout residential and commercial buildings, from homes to offices to indoor stadiums..
What is the difference between fresh air and supply air?
Fresh Air: Air coming directly from outside and is not conditioned.
Supply Air: Air that has been fully conditioned (cooling or heating)..
What is the process of ventilation in a building?
The process of ventilation in buildings represents the exchange of inner, polluted air with the ambient, fresh air.
The air-conditioning and ventilation devices, installed in the engine room of the building, make sure such an exchange is possible.
Channels or ducted units distribute the air to individual rooms..
What is the supply air area?
Supply air refers to the conditioned air that is distributed throughout the living spaces of a building by the furnace system.
This air is heated or cooled by the furnace unit and then delivered through supply ducts to each room or area..
What is the supply of air?
The supply air is the outside air that the HVAC system's air handling unit (AHU) brings in and filters.
The AHU then conditions the air and sends it to the area in need of cooling or heating through your ductwork and supply vents.Mar 25, 2019.
Why do we need air supply?
Air indoors can build up high levels of moisture, odors, gases, dust, and other air pollutants.
To keep the air safe indoors, fresh outdoor air is needed to dilute these indoor pollutants.
To provide good air quality, enough air needs to be brought in and circulated so that it reaches all areas of the home..
Why don t we always supply 100% fresh air into our buildings?
You might then be wondering why we don't rely on 100% fresh air in all buildings.
And the reason is that it is incredibly expensive to do so.
When you take in fresh air from outside, it needs to be conditioned before it can be distributed.
And that takes energy..
- Air Supply Unit (ASU) is equipment used to circulate, supply or replace air from spray paint booth.
Air Supply Unit is commonly known as Air Replacement Plant (ARP), Air Handling Unit (AHU), and Air Makeup Unit (AMU) etc. - For continuous indoor air quality ventilation, a heat or energy recovery ventilator (HRV or ERV) should provide 0.35 air changes per hour.
This calculation must consider the complete occupied volume of the house.
This rate can be more easily calculated by allowing 5 CFM per 100 square feet of floor area. - The main purposes of a Heating, Ventilation and Air-Conditioning (HVAC) system are to help maintain good indoor air quality (IAQ) through adequate ventilation with filtration and provide thermal comfort.
HVAC systems are among the largest energy consumers in schools.