How is a CT scan performed on a dog?
CT scans are non-invasive and are not painful.
The table on which the animal is laying is slowly advanced into the part of the machine that performs the scan (called the gantry).
An x-ray tube rotates 360\xb0 around the patient to record the x-rays from many angles, creating slices..
How is the BVA elbow scored?
The certificate will show a grade for each elbow, the overall grade is determined by the higher grade.
A dog will be given a grade between 0 and 3.
We recommended that breeders only breed from dogs with an overall grade of 0..
Is a CT scan better than an MRI for a dog?
For spinal cord imaging, veterinary CT often requires an iodine-based contrast dye to highlight the spinal cord, which can carry risk and add time to the process.
In summary, veterinary MRI is the best option for soft tissue, muscles, the spinal cord, brain, ears and nose..
What is a FCP elbow?
Fragmented coronoid process (FCP) is the most common form of elbow dysplasia in dogs.
In this disease, a fragment of bone and cartilage of one of the bones of the elbow joint (ulna) becomes detached and breaks off from its usual position..
What is canine elbow?
In dogs, the elbow joint involves three bones: the humerus, ulna and radius.
These bones must all work together perfectly to give your dog pain-free movement in their elbow joint..
What is diagnostic imaging of canine elbow dysplasia?
The most commonly used diagnostic technique is radiography, although computed tomography is sometimes needed.
Developmental orthopedic disease of the elbow is most common in large-breed dogs.
Radiology is usually the first-line diagnostic modality..
What is diagnostic imaging of canine elbow dysplasia?
The most commonly used diagnostic technique is radiography, although computed tomography is sometimes needed.
Developmental orthopedic disease of the elbow is most common in large-breed dogs.
Radiology is usually the first-line diagnostic modality.Aug 11, 2023.
What is dog elbow score?
Each elbow joint x-ray is assessed by BVA/KC scrutineers and the degree of elbow dysplasia present is indicated by a scale of 0 to 3 (0 being the best and 3 being the most severe).
Only the highest grade of the two elbows is taken as the elbow grade for that dog..
Where is the elbow located on a dog?
The elbow is the first joint in the dog's leg located just below the chest on the back of the foreleg.
The long bone that runs down from the elbow of the foreleg is the forearm..
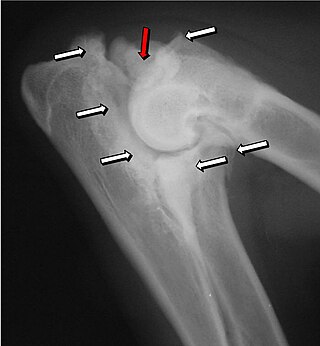
Where is the elbow positioned in xray dogs?
For the orthogonal image, the elbow is imaged in a craniocaudal direction, which reduces magnification and geometric distortion.
The dog or cat is positioned in ventral recumbency, with the affected thoracic limb pulled cranially, placing the elbow in the center of the x-ray cassette/imaging detector..
Why does a dog need a CT scan?
CT examinations are most valuable when looking at bony structures or the lungs.
It can also be used to look at soft tissues such as the abdominal organs.
CT images are sometimes enhanced with the use of intravenous contrast agents..
- For the orthogonal image, the elbow is imaged in a craniocaudal direction, which reduces magnification and geometric distortion.
The dog or cat is positioned in ventral recumbency, with the affected thoracic limb pulled cranially, placing the elbow in the center of the x-ray cassette/imaging detector. - Most dogs are diagnosed with elbow dysplasia by physical examination and by doing a thorough lameness evaluation at 4 to 12 months of age.
In mild cases, however, affected dogs may not show lameness until 7 or 8 years of age, when arthritis kicks in.