How close are we to a galactic year?
The galactic year, also known as a cosmic year, is the duration of time required for the Sun to orbit once around the center of the Milky Way Galaxy.
One galactic year is approximately 230 million Earth years..
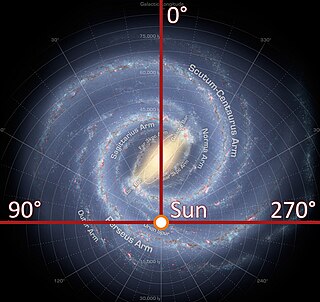
How far are we from Galactic Center?
Our solar system is located about 27,000 light-years from the galactic center within one of the disk's four spiral arms.
One light-year is the distance light travels in a year: about 6 trillion miles (10 trillion kilometers)..
How long does it take to complete a galactic year?
The galactic year, also known as a cosmic year, is the duration of time required for the Sun to orbit once around the center of the Milky Way Galaxy.
One galactic year is approximately 230 million Earth years..
How long is a galactic age?
The galactic year, also known as a cosmic year, is the duration of time required for the Sun to orbit once around the center of the Milky Way Galaxy.
One galactic year is approximately 230 million Earth years..
How long is a galactic orbit?
Even at such a mind-boggling speed, it takes the sun somewhere between 225 million and 250 million years to make a full orbit around the center of the galaxy..
How long is a galactic turn?
Each complete rotation is known as one galactic year or cosmic year.
But most of humanity won't be able to celebrate the Sun's rotation – at least not in our lifetimes because it takes anywhere from 220 to 250 million years for the sun to complete one galactic rotation..
How many galaxies are found till now?
It is estimated that there are between 200 billion (2\xd71011) to 2 trillion galaxies in the observable universe.
Most galaxies are 1,000 to 100,000 parsecs in diameter (approximately 3,000 to 300,000 light years) and are separated by distances on the order of millions of parsecs (or megaparsecs)..
How old is Sun Galactic?
The age of the Sun, according to the Stanford Solar Centre's page How old is the Sun? is approximately 4.57 billion years.
This would put the sun at approximately 20.5 galactic years old..
How old is the universe in galactic years?
Orbiting the Galaxy
It takes our Sun approximately 225 million years to make the trip around our Galaxy.
This is sometimes called our “galactic year”.
Since the Sun and the Earth first formed, about 20 galactic years have passed; we have been around the Galaxy 20 times..
What do galactic astronomers study?
Cosmologists and extragalactic/galactic, planetary, and stellar astronomers study the creation, evolution, and possible futures of the universe and its galaxies, stars, planets, and solar systems..
What does a galactic astronomer do?
Cosmologists and extragalactic/galactic, planetary, and stellar astronomers study the creation, evolution, and possible futures of the universe and its galaxies, stars, planets, and solar systems..
What is galactic Astrophysics?
Galactic astronomy is the study of the Milky Way galaxy and all its contents.
This is in contrast to extragalactic astronomy, which is the study of everything outside our galaxy, including all other galaxies..
What is galactic in science?
Galaxies are vast cosmic islands of stars, gas, dust, and dark matter held together by gravity.
Hubble's keen eye has revealed intricate details of the shapes, structures, and histories of galaxies — whether alone, as part of small groups, or within immense clusters..
Why is it called galactic?
It's galactic" The word, along with galaxy, comes from the Greek phrase galaxias kyklos, "milky circle.".
- definition and length
A cosmic year is the time (about 225 million years) needed for the solar system to revolve once around the centre of the Milky Way Galaxy. - It's galactic" The word, along with galaxy, comes from the Greek phrase galaxias kyklos, "milky circle."
- There are many galaxies, but only one Milky Way galaxy.
It is our galaxy, the galaxy in which our solar is part.
Many other galaxies have been discovered, of various types and sizes, using telescopes on Earth and from orbit, but all unimaginably large and distant.