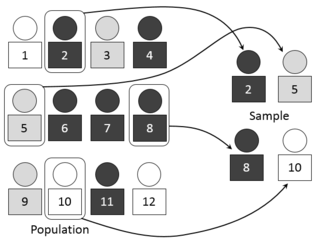
- #1 – Statistical Sampling
Statistical sampling is a method that uses probability theory to select a sample that is representative of the population.
First, the auditor determines the sample size and selects the sample using a random or systematic selection process. How audit sampling is done?
Audit sampling is an investigative tool in which less than 100% of the total items within the population of items are selected to be audited.
It is an auditing technique that provides supporting evidence that allows auditors to issue audit opinions without having to audit every single item and transaction..
How do auditors determine sample size?
It involves examining a small subset of a company's financial records in order to draw conclusions about the entire population.
Audit sampling is used to identify potential discrepancies or errors in a company's financial statements or records that might otherwise go undetected..
How do auditors select samples?
There are two main methods of audit sampling: statistical sampling and non-statistical sampling.
Statistical sampling involves using probability theory to select a sample representative.
Non-statistical sampling, on the other hand, involves using auditor judgment to select a sample representative of the population..
How do I choose an audit sample?
. 38 To determine the number of items to be selected for a particular sample for a test of controls, the auditor should consider the tolerable rate of deviation from the controls being tested, the likely rate of deviations, and the allowable risk of assessing control risk too low..
How do you audit a sample?
There are two main methods of audit sampling: statistical sampling and non-statistical sampling.
Statistical sampling involves using probability theory to select a sample representative.
Non-statistical sampling, on the other hand, involves using auditor judgment to select a sample representative of the population..
How do you calculate audit sample?
Sample size calculations depend on four variables: • Size of population.
Degree of accuracy required.
Degree of confidence required.
How often you expect your audit criteria to be met..
How large should an audit sample be?
For populations between 52 and 250 items, a rule of thumb some auditors follow is to test a sample size of approximately 10 percent of the population, but the size is subject to professional judgment, which would include specific engagement risk assessment considerations..
How many types of audit sampling are there?
There are two main methods of audit sampling: statistical sampling and non-statistical sampling.
Statistical sampling involves using probability theory to select a sample representative.
Non-statistical sampling, on the other hand, involves using auditor judgment to select a sample representative of the population..
In which audit procedure would sampling be appropriate?
Sampling can be used for both tests of controls and direct tests of account balances and assertions. *Audit procedures such as inquiry, observation, and analytical procedures are the primary audit procedures involving audit sampling..
Types of statistical sampling in auditing
Audit sampling is the method used among auditors to form their opinion on the grounds of the evidence gathered.
By using audit sampling method auditors should gather enough competent evidence leading to a reasonable basis for their conclusions.
Audit sampling is used for various tests of controls..
What are the methods of audit sample testing?
Audit sampling is an investigative tool in which less than 100% of the total items within the population of items are selected to be audited.
It is an auditing technique that provides supporting evidence that allows auditors to issue audit opinions without having to audit every single item and transaction..
What are the methods of audit sample testing?
Determining the Sample Size.
To determine attribute testing sample sizes, the auditor needs to determine the value for three inputs: desired confidence level, tolerable exception rate, and expected exception rate.
The compliance table sample size is based on the following expectations..
What are the methods of audit sample testing?
There are two main methods of audit sampling: statistical sampling and non-statistical sampling.
Statistical sampling involves using probability theory to select a sample representative.
Non-statistical sampling, on the other hand, involves using auditor judgment to select a sample representative of the population..
What audit sampling involves?
Audit sampling is the method used among auditors to form their opinion on the grounds of the evidence gathered.
By using audit sampling method auditors should gather enough competent evidence leading to a reasonable basis for their conclusions.
Audit sampling is used for various tests of controls..
What is audit sampling for test of controls?
Audit sampling is the method used among auditors to form their opinion on the grounds of the evidence gathered.
By using audit sampling method auditors should gather enough competent evidence leading to a reasonable basis for their conclusions.
Audit sampling is used for various tests of controls..
What is sample testing in audit?
The definition of audit sampling is: 'The application of audit procedures to less than 100% of items within a population of audit relevance such that all sampling units have a chance of selection in order to provide the auditor with a reasonable basis on which to draw conclusions about the entire population.' ( 1).
What is sampling test in auditing?
Audit sampling is an investigative tool in which less than 100% of the total items within the population of items are selected to be audited.
It is an auditing technique that provides supporting evidence that allows auditors to issue audit opinions without having to audit every single item and transaction..
What is the minimum sample size for audit?
As a general rule, a statistical sample should contain 50 to 100 cases for each sample or sub-group to be analysed..
What is the percentage of audit sampling?
01 Audit sampling is the application of an audit procedure to less than 100 percent of the items within an account balance or class of transactions for the purpose of evaluating some characteristic of the balance or class..
What is the purpose of audit sample?
The objective of audit sampling is to ensure that all items that make up a population stand an equal chance of selection.
This objective cannot be achieved if the auditor deliberately avoids items that are difficult to locate or deliberately avoids certain items..
What is the reason for audit sampling?
Increased efficiency and reduced cost: Audit sampling allows the auditor to test a smaller subset of items from the population, rather than testing every item in the population.
This can increase the efficiency of the audit and reduce the cost, while still providing a high level of assurance on the population..
What is the role of audit testing?
A well designed control only achieves its objective and manages risk if it is being followed.
Audit testing is all about ensuring the actual controls you are relying upon to effectively manage risk are operating properly..
What is the sample size for audit testing?
For populations between 52 and 250 items, a rule of thumb some auditors follow is to test a sample size of approximately 10 percent of the population, but the size is subject to professional judgment, which would include specific engagement risk assessment considerations..
What is the sampling interval in auditing?
First, the auditor would determine a sampling interval based on the total value of the population and the desired sample size.
For example, if the auditor wants a sample size of 100, the sampling interval would be $1,000,000 / 100 = $10,000.
Next, the auditor would select a random start point within the first interval..
What is the significance of audit sampling?
The purpose of audit sampling is to appropriately test the right samples and determine the operating effectiveness of controls in the organization.
But, before proceeding with this technique, the auditor should review and consider the sampling method, sample size, acceptable rate of deviation..
Why do auditors use samples for their testing?
The use of sampling is widely adopted in auditing because it offers the opportunity for the auditor to obtain the minimum amount of audit evidence, which is both sufficient and appropriate, in order to form valid conclusions on the population..
Different Types of Audit Test
1- Audit Substantive tests.2- Risks Assessment tests.3- Tests of Detailed Balances.4- Dual Purpose Tests.5- Analytical procedure tests.- First, the auditor would determine a sampling interval based on the total value of the population and the desired sample size.
For example, if the auditor wants a sample size of 100, the sampling interval would be $1,000,000 / 100 = $10,000.
Next, the auditor would select a random start point within the first interval. - For populations between 52 and 250 items, a rule of thumb some auditors follow is to test a sample size of approximately 10 percent of the population, but the size is subject to professional judgment, which would include specific engagement risk assessment considerations.
- Sampling can be used for both tests of controls and direct tests of account balances and assertions. *Audit procedures such as inquiry, observation, and analytical procedures are the primary audit procedures involving audit sampling.
- The definition of audit sampling is: 'The application of audit procedures to less than 100% of items within a population of audit relevance such that all sampling units have a chance of selection in order to provide the auditor with a reasonable basis on which to draw conclusions about the entire population.' ( 1)
- There are two main methods of audit sampling: statistical sampling and non-statistical sampling.
Statistical sampling involves using probability theory to select a sample representative.
Non-statistical sampling, on the other hand, involves using auditor judgment to select a sample representative of the population.