Does bioinformatics include proteomics?
Bioinformatics also includes proteomics, which tries to understand the organizational principles within nucleic acid and protein sequences.
Image and signal processing allow extraction of useful results from large amounts of raw data..
Does proteomics come under bioinformatics?
In order to efficiently and rapidly analyze research data, the field of bioinformatics emerged, revolving around proteomics inquiries.
Bioinformatics, an emerging interdisciplinary field, evolved alongside the Human Genome Project..
How are genomics proteomics and bioinformatics related to each other?
Genomics and proteomics and bioinformatics are multidisciplinary sciences that use different tools and software that help to predict gene expression.
In different genomics methods such as microarrays, SAGE (Serial analysis of gene expression), and CRISPR are used to analyze the gene expression..
How is bioinformatics used in proteomics?
Bioinformatics employs computational techniques and big data analysis to identify, predict, and interpret protein PTMs.
For instance, predictive algorithms can anticipate potential modification sites, guiding experimental design..
Is proteomics part of bioinformatics?
Proteomics methods are essential for studying protein expression, activity, regulation and modifications.
Bioinformatics is an integral part of proteomics research..
Proteomics analysis tools
Proteomics Origins
The first protein studies that can be called proteomics began in 1975 with the introduction of the two-dimensional gel by O'Farrell (119), Klose (87), and Scheele (140), who began mapping proteins from Escherichia coli, mouse, and guinea pig, respectively..
Proteomics analysis tools
The word proteome use in proteomics is a portmanteau of protein and genome.
Bioinformatics is an interdisciplinary field that takes insights from a range of subjects (statistics, biology, mathematics, computer science, chemistry, etc.) to create tools and approaches to understand biological data..
Proteomics book
Proteomics is practically intricate because it includes the analysis and categorization of overall protein signatures of a genome.
Mass spectrometry with LC-MS-MS and MALDI-TOF/TOF being widely used equipment is the central among current proteomics..
Proteomics book
STRING is a proteomic database focusing on the networks and interactions of proteins in a wide array of species.
STRING allows for the searching of one or multiple proteins at a time with the ability to additionally limit the search to the desired species..
Proteomics book
The word proteome use in proteomics is a portmanteau of protein and genome.
Bioinformatics is an interdisciplinary field that takes insights from a range of subjects (statistics, biology, mathematics, computer science, chemistry, etc.) to create tools and approaches to understand biological data..
What are the different types of proteomics in bioinformatics?
Proteomics has three main types: expression proteomics, functional proteomics, and structural proteomics[27].
Expression proteomics.
Expression proteomics is a novel approach that studies the quantitative and qualitative expression of proteins. Structural proteomics. Functional proteomics..What is proteome in bioinformatics?
A proteome is a set of proteins produced in an organism, system, or biological context.
We may refer to, for instance, the proteome of a species (for example, Homo sapiens) or an organ (for example, the liver).
The proteome is not constant; it differs from cell to cell and changes over time..
What is proteomics bioinformatics?
Proteome bioinformatics refers to the study and application of informatics in the field of proteomics.
This chapter provides an overview of computational strategies, methods, and techniques reported in this book for bioinformatics analysis of protein data..
What is the database for proteome analysis?
The Proteome Analysis database provides information on domain structure and function, gene duplication and protein families in different genomes.
A variety of ways to query and compare the data, depending on the objectives of the analysis, is offered..
What is the database used in proteomics?
STRING is a proteomic database focusing on the networks and interactions of proteins in a wide array of species.
STRING allows for the searching of one or multiple proteins at a time with the ability to additionally limit the search to the desired species..
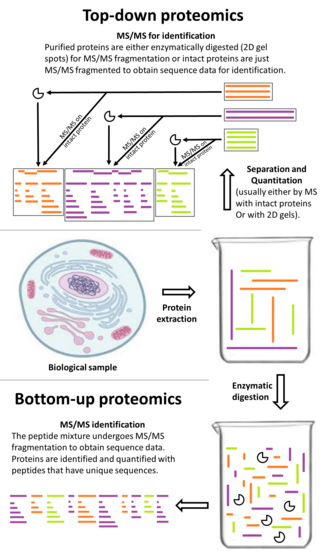
What is the proteomics workflow in bioinformatics?
Integrated Proteomic Workflow: Samples of interest are subjected to protein extraction and digestion.
The resulting peptides are separated by C18 chromatography and directly electrosprayed into the mass spectrometer, where their mass-to-charge ratio and fragmentation spectra is recorded.Mar 13, 2014.
When did proteomics start?
Proteomics Origins
The first protein studies that can be called proteomics began in 1975 with the introduction of the two-dimensional gel by O'Farrell (119), Klose (87), and Scheele (140), who began mapping proteins from Escherichia coli, mouse, and guinea pig, respectively..
Why bioinformatics is essential for protein science and protein engineering?
In structure analysis, many available databases and bioinformatics techniques can help to find the factors governing the folding and stability of proteins and to predict the secondary structures from amino acid sequence..
- A proteome is a set of proteins produced in an organism, system, or biological context.
We may refer to, for instance, the proteome of a species (for example, Homo sapiens) or an organ (for example, the liver).
The proteome is not constant; it differs from cell to cell and changes over time. - Integrated Proteomic Workflow: Samples of interest are subjected to protein extraction and digestion.
The resulting peptides are separated by C18 chromatography and directly electrosprayed into the mass spectrometer, where their mass-to-charge ratio and fragmentation spectra is recorded.Mar 13, 2014 - The word proteome use in proteomics is a portmanteau of protein and genome.
Bioinformatics is an interdisciplinary field that takes insights from a range of subjects (statistics, biology, mathematics, computer science, chemistry, etc.) to create tools and approaches to understand biological data.