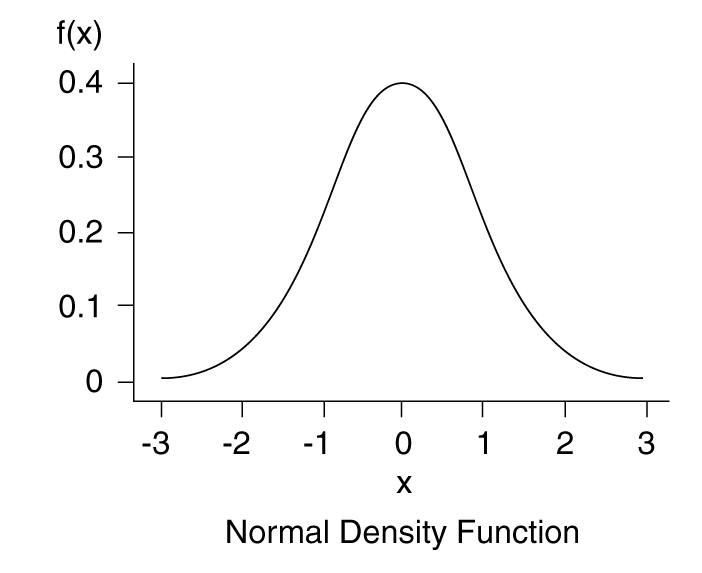
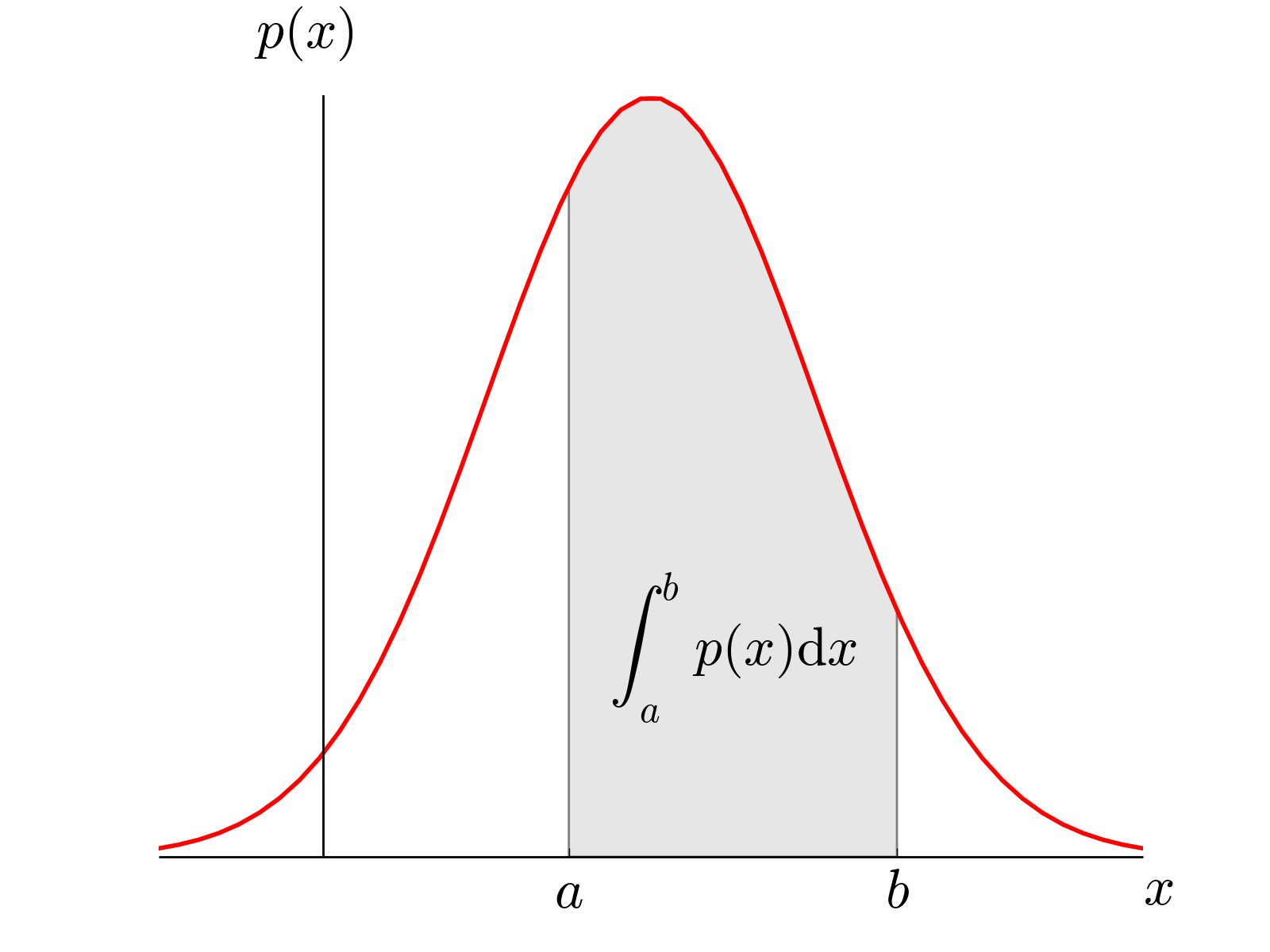
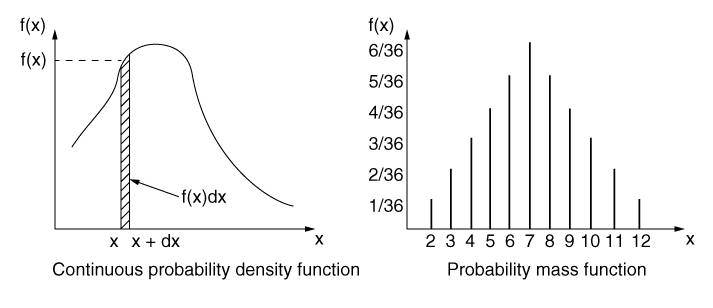
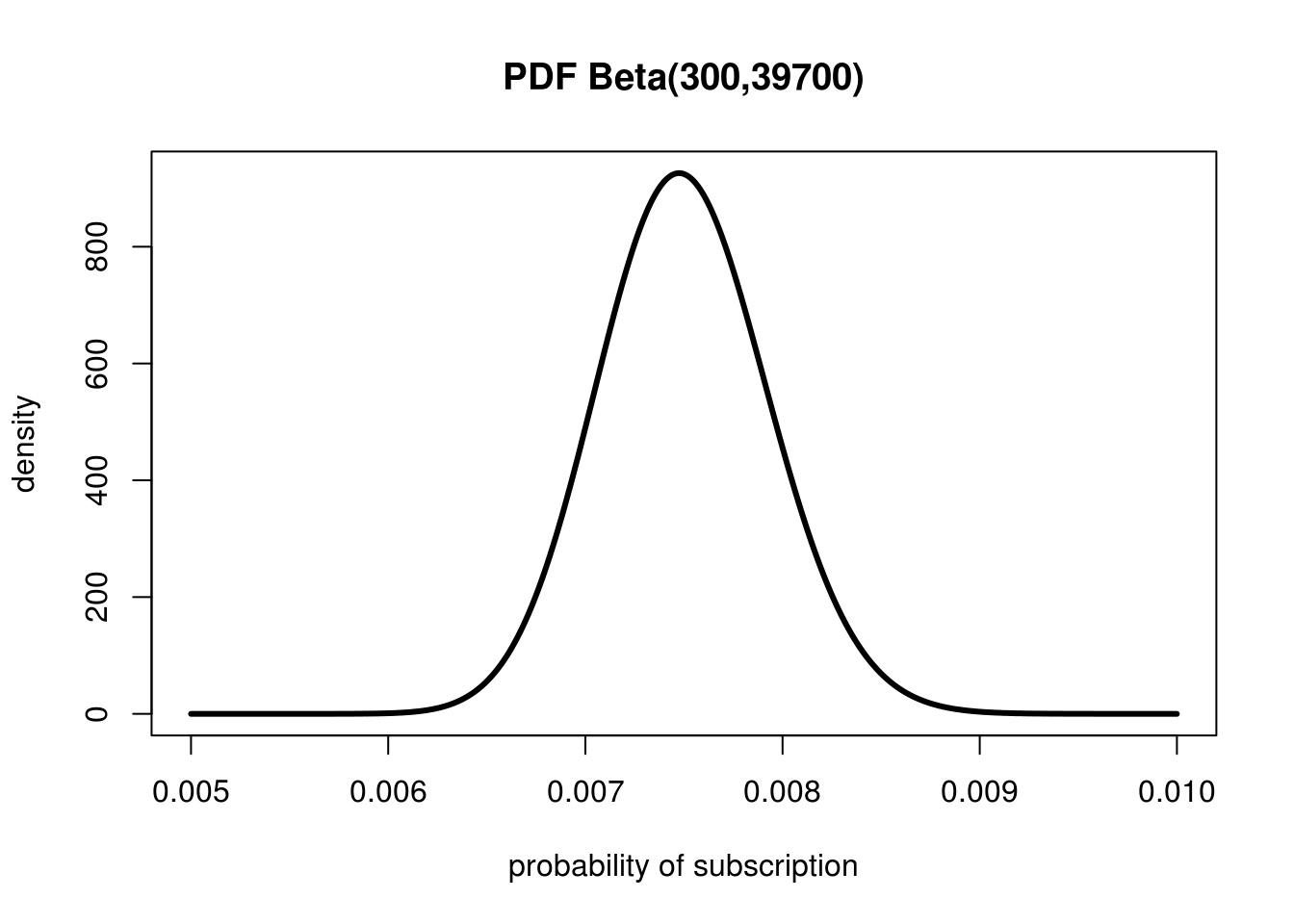
probability ppt
|
PPT ON PROBABILITY THEORY &STOCHASTIC PROCESS
prior probabilities because they are determined prior to the decision about taking the preparatory course. • The conditional probability P(A |
|
Chapter 5 - Elementary probability
9 avr. 2019 Probability theory is the foundation upon which the logic of inference is built. It helps us to cope up with uncertainty. In general ... |
|
4. Basic probability theory
Lect04.ppt Probability of event A is denoted by P(A) P(A) ? [0 |
|
PROBABILITY.ppt [Read-Only]
Find the probability of drawing a full house. (three of one rank and two of another rank) in receiving 5 cards from a deck of. 52 cards. |
|
Detection of Targets in Noise and Pulse Compression Techniques
MIT Lincoln Laboratory. Radar Course_7.ppt. ODonnell 10-26-01. The Detection Problem. Probability of False. Alarms. Voltage. |
|
On the separability of unitarily invariant random quantum states-the
22 févr. 2018 high probability PPT (i.e. they have a positive semidefinite partial transpose). Aubrun's idea was developed and generalized in many ... |
| Multiphoton and tunneling ionization of atoms in an intense laser field |
|
Présentation PowerPoint
30 sept. 2017 the probability of achieving tumor control and of developing normal tissue complications after radiotherapy as a function of radiation dose. |
|
ECE 313 — Probability with Engineering Applications Fall 2000
ECE 313 — Probability with Engineering Applications. Fall 2000. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. University of Illinois at Urbana- |
|
Lecture Stat 302 Introduction to Probability - Slides 1
Textbook: A first course in probability 8th edition by Sheldon Ross. Website: http://people.cs.ubc.ca/~arnaud/stat302.html. |
|
Lecture Notes 1 Basic Probability - Stanford University
Probability law (measure or function) is an assignment of probabilities to events(subsets of sample space?) such that the following three axioms are satis?ed: P(A) 0 for allA(nonnegativity) P(?) = 1(normalization) IfAandBare disjoint (AB=) then P(A B) = P(A) + P(B)(additivity) More generally3’ |
|
Example 3 - Suppose we throw a die once What is probability
The description of the course is as follows: This course introduces the basic notions of probability theory and de- velops them to the stage where one can begin to use probabilistic ideasinstatisticalinferenceandmodellingandthestudyofstochastic processes Probability axioms Conditional probability and indepen- dence |
|
Crash Course on Basic Statistics - Massachusetts Institute of
variables with probability distributions { Random errors in data have no probability distribution but rather the model param-eters are random with their own distribu-tions { Mathematical routines analyze probability of a model given some data The statisti-cian makes a guess (prior distribution) and then updates that guess with the data |
|
Introduction to probability theory - The University of Sydney
To calculate the probability of an event we simply need to ?nd out the total number of possible outcomes of an experiment and the number of outcomes which correspond to the given event Exercise 1 What are your chances of winning a ra?e in which 325 tickets have been sold if you have one ticket? Exercise 2 |
|
LECTURE NOTES ON PROBABILITY STATISTICS AND LINEAR ALGEBRA
Statistics and probability also play explicit roles in our understanding and modelling of diverse processes in the life sciences These are typically processes where the outcome is in?uenced by many factors each with small effect but |
|
Searches related to probability ppt filetype:pdf
11 7 – Basic Concepts of Probability Objective: TSW calculate the probability of an event Chapter 1 © 2008 Pearson Addison-Wesley All rights reserved 12-1-2 Probability The likelihood of an event occurring In the study of probability any observation or measurement of a random phenomenon is an experiment |
What is probability with example?
- What is probability Example 3 Suppose we throw a die once. What is the probability of getting a number greater than 4 ? Total outcomes that can occur are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 Total number of outcomes = 6 Numbers greater than 4 = 5 & 6 Number of outcomes where number is greater than 4 = 2 Probability of gettin (????)
What are the key points of probability?
- KEY POINT Ratios and probabilities can be written as a percentage or as a decimal fraction of 1. For example, a 3 : 1 ratio can be written as 75% : 25% or 0.75 : 0.25. A 50% probability can be written as 0.5. PEDIGREES 215 The Punnett square produces the same expected ratio in the F2 – 3 with rosettes : 1 smooth. There is an important point here.
How do you calculate probability for multiple events?
- To calculate probability for multiple events you must first calculate the probability of each independent event. Then you multiply the probabilities of each independent event with one another. What is the difference between probability and odds?
What are the axioms of probability?
- Axioms of Probability • Probability law (measure or function) is an assignment of probabilities to events (subsets of sample space ?) such that the following three axioms are satis?ed: 1. P(A) ? 0, for all A(nonnegativity) 2. P(?) = 1 (normalization) 3. If Aand B are disjoint (A?B= ?), then P(A?B) = P(A)+ P(B) (additivity) More generally, 3’.
|
PPT ON PROBABILITY THEORY &STOCHASTIC PROCESS - IARE
prior probabilities because they are determined prior to the decision about taking the preparatory course • The conditional probability P(A B) is called a posterior |
|
4 Basic probability theory
Lect04 ppt S-38 145 Definition: The conditional probability of event A given that event B Furthermore, by the theorem of total probability (slide 7), we get |
|
Lecture Stat 302 Introduction to Probability - Slides 1
Textbook: A first course in probability, 8th edition by Sheldon Ross Website: Probability theory yields mathematical tools to deal with uncertain events |
|
Conditional Probability, Bayes Theorem - MIT OpenCourseWare
'the probability of A given B' P(A ∩ B) P(AB) = , provided P(B)=0 P(B) B A A n B Conditional probability: Abstractly and for coin example January 1, 2017 3 / |
|
Review of Probability
definition will converge to the true probability as n T →∞ The probability that the 1st experiment had outcome A Conditional Probability Independence |
|
Adding and multiplying probabilities
change the probabilities of the outcomes of the other event Page 11 Independent events: example I toss a coin twice ○ First event: the first toss is heads or tails |
|
Probability of Simple Events - artemate
Students will be able to find the probability of a simple event Students will be able to understand the distinction between simple events and compound events |
|
71 Sample space, events, probability
topic of probability which is used in Definition: sum of the probabilities of the simple events Example: Probability of a sum of 7 when two dice are rolled |
|
Chapter 2: Probability Concepts and Applications - UWCENTRE
A probability of 1 means that an event is always expected to occur • The sum of the simple probabilities for all possible outcomes of an activity must equal 1 |