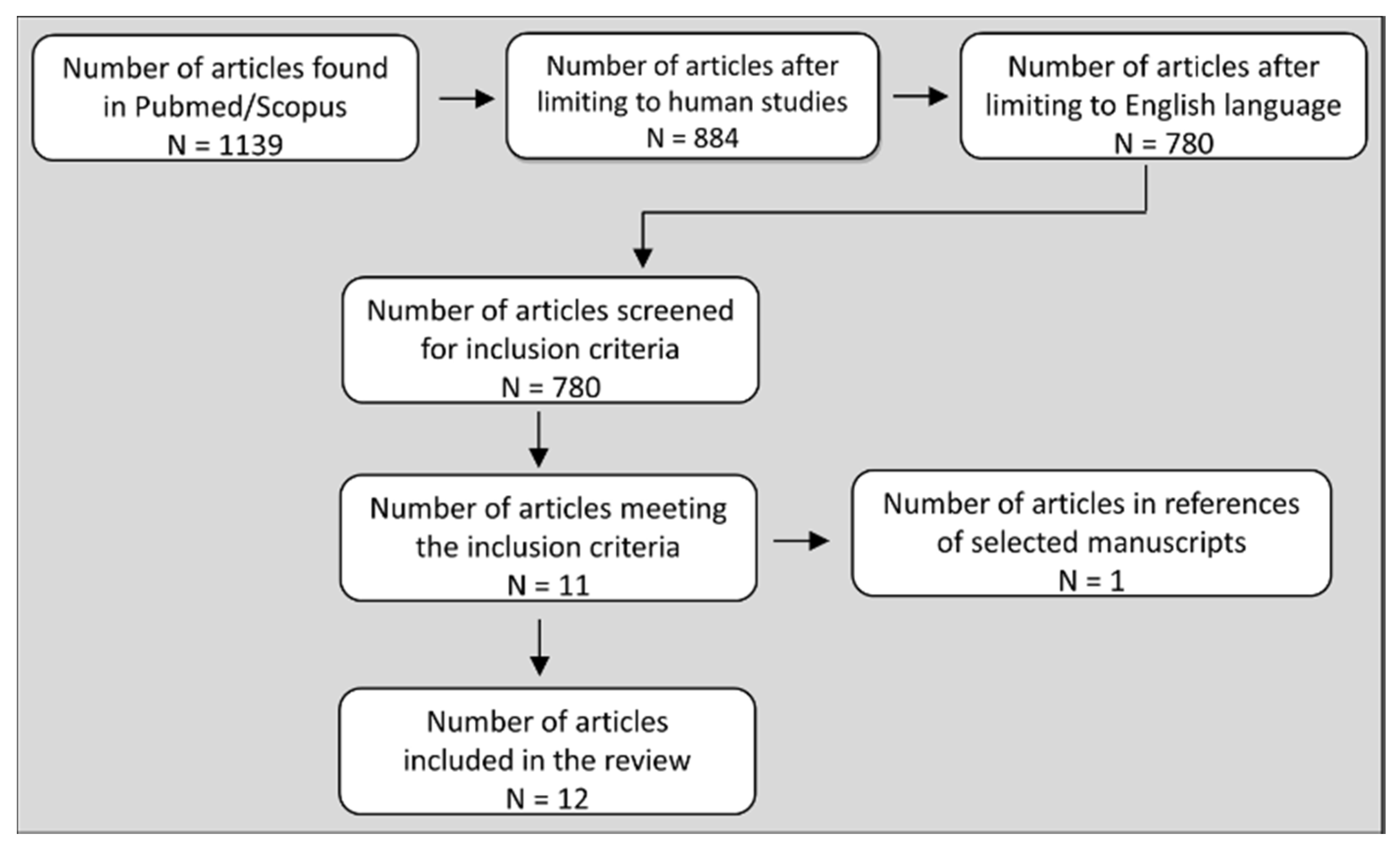
static vs dynamic exercise blood pressure
|
Cardiovascular responses to static exercise
In light static exercise the heart rate and blood pressure increase much more than during dynamic exercise at the same oxygen uptake level. Heavy static |
|
Effect of static and dynamic exercise on heart rate and blood
Effect of static and dynamic exercise on heart rate and blood pressure variabilities. Med. reported between light static versus rhythmic handgrip (11). |
|
Comparison of hemodynamic responses to static and dynamic
of dynamic and static components of the exercise. exercise blood pressure; exercise cardiac output; exercise total peripheral resistance; muscle mass and |
|
Haemodynamic effects of static and dynamic exercise in males with
During dynamic exercise the arterial blood pressure increase per litre increase in cardiac output was significantly less than during static exercise |
|
Responses to Static (Isometric) Exercise
Static exercise involves the contraction of skeletal muscle without a blood pressure cuff will then be used on the exercised arm to demonstrate the ... |
|
Hemodynamic Predictors of Myocardial Oxygen Consumption
dynamic exercise (average heart rate 147 beats/min) and static exercise using 17% MVC of the left hand. Mean myocardial blood flow (MBF) was 181 ml/100 gm |
|
Anxiolytic and Blood Pressure Effects of Acute Static Compared to
Key words: Diastolic dynamic exercise. perceived exertion |
|
Comparison of cardiovascular responses to static-dynamic effort and
STATIC-DYNAMIC VS DYNAMIC EFFORT/DeBusk et al. creased heart rate systolic blood pressure and rate-pressure product at the onset ofischemic ST-segment. |
|
Comparison of cardiovascular responses to static-dynamic effort and
STATIC-DYNAMIC VS DYNAMIC EFFORT/DeBusk et al. creased heart rate systolic blood pressure and rate-pressure product at the onset ofischemic ST-segment. |
|
Heart Rate Variability and Blood Pressure during Dynamic and
13 déc. 2013 Static vs. dynamic contractions of identical small muscles e. g. during submaximal handgrip exercise |
|
Effect of static and dynamic exercise on heart rate and blood
Purpose: This study examines the effect of static and dynamic leg exercises on heart rate variability (HRV) and blood pressure variability (BPV) in humans |
|
Comparison of hemodynamic responses to static and dynamic
of dynamic and static components of the exercise exercise blood pressure; exercise cardiac output; exercise total peripheral resistance; muscle mass and |
|
(PDF) Cardiovascular Response to Exercise: Static v/s Dynamic
18 jui 2020 · Blood pressure and Heart rate was recorded at rest Subject was instructed to sit on cycle ergometer and start doing cycling at the rate |
|
Effect of static and dynamic exercise on heart rate - ResearchGate
This study examines the effect of static and dynamic leg exercises on heart rate variability (HRV) and blood pressure variability (BPV) in humans |
|
Cardiovascular responses to static exercise - JSTOR
Due to the higher increase in blood pressure even light static exercise causes much higher strain on the heart than an equivalent amount of dynamic exercise |
|
Static Effects - UT Southwestern Medical Center
Responses to Static (Isometric) Exercise (or other device) as blood pressure and heart rate are monitored over a period of time A second |
|
Cardiovascular effects of static and dynamic exercise SpringerLink
The cardiovascular response to static exercise has often been quantified on Regression analysis of heart rate (HR) or blood pressure (BP) against the |
|
Cardiovascular responses to static and dynamic contraction during
Abstract Previous studies suggest that the blood pressure response to static contraction is greater than that caused by dynamic exercise In anesthetized cats |
|
Heart Rate Variability and Blood Pressure during Dynamic - NCBI
13 déc 2013 · Static vs dynamic contractions of identical small muscles e g during submaximal handgrip exercise elicited similar HR and BP response [19] |
|
Differential Cardiovascular Responses to Static and Dynamic
23 sept 2022 · Results: Both exercises increased systolic brachial and central blood pressures whereas diastolic pressures was increased only after the hand |
Does static or dynamic exercise increase blood pressure more?
Abstract. In light static exercise the heart rate and blood pressure increase much more than during dynamic exercise at the same oxygen uptake level. Heavy static exercise is characterized by a failure of the local blood flow to adjust to the oxygen demands of the exercising muscles.What is the difference between dynamic and static exercise blood pressure?
In dynamic exercise the systolic but not diastolic pressure rises. In contrast, in static exercise both systolic and diastolic pressures rise, probably as a result of reflexes arising in the muscles and conveyed to cardiovascular centers in the medulla and hypothalamus.What happens to blood pressure in static exercise?
During static exercise in normal subjects, the mean arterial pressure increases as a result of an increase in heart rate and thereby cardiac output with no significant change in stroke volume or systemic vascular resistance.- Blood pressure (BP) response varies depending on the type of exercise. During dynamic exercise, systolic BP increases, but diastolic and mean arterial pressures remain nearly identical, varying within a few mm Hg from their levels at rest.
|
Cardiovascular Response to Exercise: Static v/s Dynamic - AIMDR
Keywords: Blood Pressure (BP); Systolic Blood Pressure (SBP); Diastolic Blood Pressure (DBP); Electrocardiograph (ECG); Isometric Handgrip (IHG); Handgrip |
|
Cardiovascular responses to static exercise - JSTOR
In light static exercise the heart rate and blood pressure increase much more than during dynamic exercise strain on the heart than an equivalent amount of dynamic exercise tilation in static exercise is compared to the respective |
|
Responses to Static (Isometric) Exercise - UT Southwestern
exhibited in dynamic exercise, and any increase in cardiac output is due almost entirely to increases in heart rate In addition, as muscular exertion is relatively |
|
Haemodynamic effects of static and dynamic exercise in males with
during static exercise in every hypertensive man, this did not occur in any of the control subjects During dynamic exercise, the arterial blood pressure increase per litre increase in cardiac output STATIC V S DYNAMIC EXERCISE |
|
Cardiovascular Responses to Exercise
sponses to dynamic aerobic activity, static exercise, and dynamic resistance stroke volume (SV) (Figure 13 1b) and heart rate (HR) Interval Exercise versus |
|
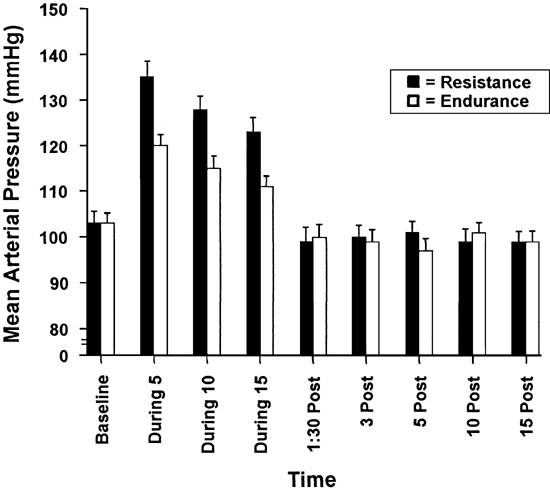
The effects of isometric and dynamic resistance exercise on - Uncg
exercise systolic and/or diastolic blood pressure compared to the control condition The Effects of Dynamic Resistive Exercise Training on Blood Pressure Table 6−Comparison of acute resistive and static exercise studies 60 |