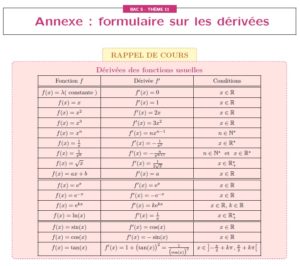
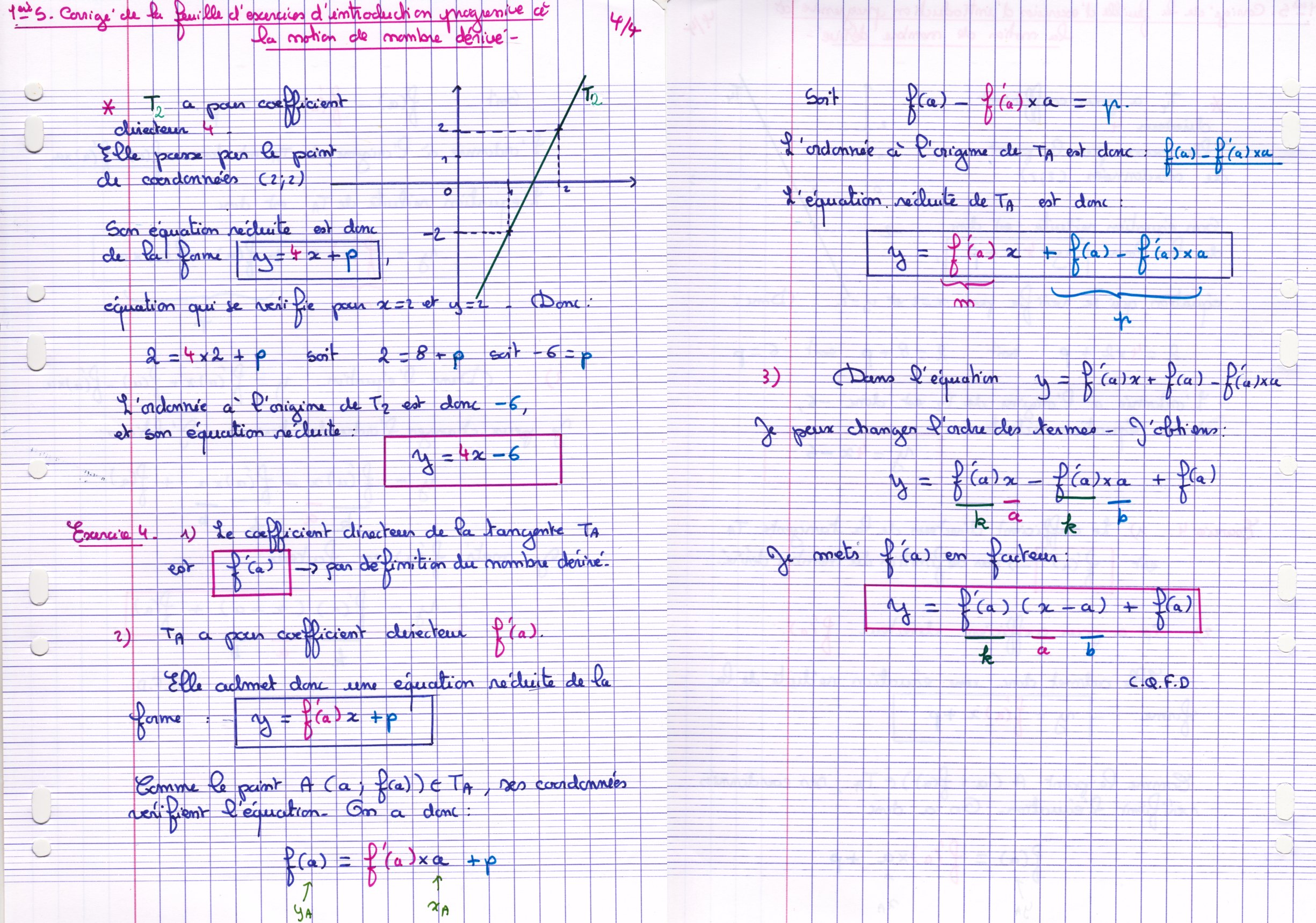
coefficient 1ere s si
|
The international system of units (SI)
velocity is the meter per second (m/s or m • s-1) and that for angular velocity is the radian per second (rad/s or rad • s-1) Some derived SI units have special names and symbols Almost all physical measurements of science industry and trade can be expressed in terms of these units or other combinations For convenience however other |
|
Guide for the Use of the International System of Units (SI)
Essential data express or interpret quantitative results All such data shall be given in acceptable units In those cases where — the sole use of acceptable units would compromise good communication or — units other than acceptable units have been specified as a contractual requirement values of quantities shall be given in acceptable units fo |
|
Tables of SI Units and Prefixes
Table III a SI Units prefixes Table III b Binary prefixes for Bytes Table IV Accepted non-SI units Table V Accepted non-SI units with experimental values Table VI Units deprecated by the SI Spelling differences References and Links Table I Basic Units defined by Conférence Générale des Poids et Mesures (CGPM) in the latest SI-brochure |
|
APPENDIX 11 PHYSICAL QUANTITIES AND THEIR SI UNITS
electric Ωresistance R ohm kg m2/C2 s emf ξ volt V kg m2/C s2 energy E joule J kg m2/s2 force F newton N kg m/s2 frequency f hertz Hz s-1 heat Q joule J kg m2/s2 illumination E lux (lumen per square meter) lx cd/m2 inductance L henry H kg m2/C2 magnetic flux φ weber Wb kg m2/C s potential difference V volt V kg m2/C s2 |
What is the coefficient of the term C D E?
In the term c d e , the factors are c , d , and e . A coefficient is a number multiplied by a variable. In the term 14 c , the coefficient is 14 . In the term g , the coefficient is 1 . [Wait, why?] Want to learn more about terms, factors, and coefficients? Check out this video. What is the coefficient of the term 7 y in the expression 9 + 7 y ?
What are the SI units used for?
The SI units preferred for use are the units (together with their multiples and submultiples). The SI is constructed from seven base units, which are adequate to describe most of the measurements used in science, industry and commerce. Table 1. The SI Base Units.
What is the difference between a factor and a coefficient?
A factor is one part of a product. In the term 8 x , the factors are 8 and x . In the term c d e , the factors are c , d , and e . A coefficient is a number multiplied by a variable. In the term 14 c , the coefficient is 14 . In the term g , the coefficient is 1 . [Wait, why?] Want to learn more about terms, factors, and coefficients?
What is a coherent SI unit?
The coherent SI unit for such a quantity is the ratio of two identical SI units and may be expressed by the number 1. However, the number 1 generally does not appear in the expression for the value of a quantity of dimension one. For example, the value of the refractive index of a given medium is expressed as n = 1.51 × 1 = 1.51.
2.1 Essential data
Essential data express or interpret quantitative results. All such data shall be given in acceptable units. In those cases where — the sole use of acceptable units would compromise good communication, or — units other than acceptable units have been specified as a contractual requirement, values of quantities shall be given in acceptable units fo
2.1.1 Tables and graphs
In tables, values of quantities expressed in acceptable units and the corresponding values expressed in other units may be shown in parallel columns, with the acceptable-unit column preceding the other-unit column. In graphs, axes labeled in other units shall be given secondary status. This may preferably be done by placing scale marks on and label
3.2 Fundamental Constants Data Center
Questions concerning the more fundamental aspects of the SI and subtle aspects of proper SI usage may be directed to: physics.nist.gov
SI base unit Base quantity
length mass time electric current thermodynamic temperature amount of substance luminous intensity physics.nist.gov
SI coherent derived unit Derived quantity
area volume speed, velocity acceleration wavenumber density, mass density specific volume current density magnetic field strength luminance amount-of-substance concentration amount concentration , concentration physics.nist.gov
Name
square meter cubic meter meter per second meter per second squared reciprocal meter kilogram per cubic meter cubic meter per kilogram ampere per square meter ampere per meter candela per square meter mole per cubic meter physics.nist.gov
Symbol
dynamic viscosity moment of force surface tension angular velocity angular acceleration heat flux density, irradiance heat capacity, entropy specific heat capacity, specific entropy specific energy thermal conductivity energy density electric field strength electric charge density surface charge density electric flux density, electric displ
5 Units Outside the SI
Units that are outside the SI, that is, non-SI units, may be divided into three categories: — those units that are accepted for use with the SI by the CIPM and hence this Guide; — those units that are not accepted for use with the SI by the CIPM, but are temporarily accepted for use with the SI by this Guide; and — those units that are not accept
5.1 Units accepted for use with the SI
The following four sections discuss in detail the units this Guide accepts for use with the SI. physics.nist.gov
5.1.4 Natural and atomic units
In some cases, particularly in basic science, the values of quantities are expressed in terms of fundamental constants of nature. The two most important of these unit systems are the natural unit (n.u.) system used in high energy or particle physics, and the atomic unit (a.u.) system used in atomic physics and quantum chemistry. The use of these un
Kind of quantity
speed action mass electric charge length energy time physics.nist.gov
5.3 Units not accepted for use with the SI
The following two sections briefly discuss units not accepted for use with the SI. physics.nist.gov
5.3.1 CGS units
Table 10 gives examples of centimeter-gram-second (CGS) units having special names. These units are not accepted for use with the SI by this Guide. Further, no other units of the various CGS systems of units, which includes the CGS Electrostatic (ESU), CGS Electromagnetic (EMU), and CGS Gaussian systems, are accepted for use with the SI by this Gui
6.1 Rules and style conventions for unit symbols
The following eight sections give rules and style conventions related to the symbols for units. physics.nist.gov
6.1.2 Capitalization
Unit symbols are printed in lower-case letters except that: the symbol or the first letter of the symbol is an upper-case letter when the name of the unit is derived from the name of a person; and the recommended symbol for the liter in the United States is L. (See Table 6, footnote (b).) Examples: m (meter) Pa (pascal) s (second) lm (lumen)
6.2 Rules and style conventions for SI prefixes
The following eight sections give rules and style conventions related to the SI prefixes. physics.nist.gov
6.2.1 Typeface and spacing
Prefix names and symbols are printed in roman (upright) type regardless of the type used in the surrounding text, and are attached to unit symbols without a space between the prefix name or symbol and the unit name or symbol. This last rule also applies to prefixes attached to unit names. Examples: mL (milliliter) pm (picometer) GΩ (gigaohm) THz
6.2.2 Capitalization
The prefix symbols Y (yotta), Z (zetta), E (exa), P (peta), T (tera), G (giga), and M (mega) are printed in upper-case letters while all other prefix symbols are printed in lower-case letters (see Table 5). Prefix names are normally printed in lowercase letters. physics.nist.gov
6.2.4 Unacceptability of compound prefixes
Compound prefix names or symbols, that is, prefix names or symbols formed by the juxtaposition of two or more prefix names or symbols, are not permitted. Example: nm (nanometer) but not: mμm (millimicrometer) physics.nist.gov
7.12 Proper names of quotient quantities
Derived quantities formed from other quantities by division are written using the words “divided by” or per rather than the words “per unit” in order to avoid the appearance of associating a particular unit with the derived quantity. Example: pressure is force divided by area or pressure is force per area but not: pressure is force per unit area physics.nist.gov
7.13 Distinction between an object and its attribute
To avoid confusion, when discussing quantities or reporting their values, one should distinguish between a phenomenon, body, or substance, and an attribute ascribed to it. For example, one should recognize the difference between a body and its mass, a surface and its area, a capacitor and its capacitance, and a coil and its inductance. This means t
7.14 Dimension of a quantity
Any SI derived quantity Q can be expressed in terms of the SI base quantities length (l ) , mass (m), time (t), electric current (l ) , thermodynamic temperature (T ) , amount of substance (n), and luminous intensity (Iv) by an equation of the form K physics.nist.gov
|
RÉSOLUTION DE SYSTÈMES À DEUX INCONNUES
Notez que la méthode de comparaison pourrait s'avérer difficile à utiliser si aucune des variables n'est facilement isolable en raison de leurs coefficients |
|
Cours 12 : Corrélation et régression
Test sur le coefficient de corrélation de Pearson. Pouvoir tester si une corrélation est significativement différente de. |
|
2.4.3 Le coefficient de corrélation multiple (ou coefficient de
où nfix indique le nombre de variables fixées s'il s'agit d'une corrélation partielle (=0 si c'est une corrélation simple). Remarque: Ce test est plus général |
|
PHY-144 : Introduction à la physique du génie Chapitre 8: Cinétique
Si on ne veut pas s'embarrasser continuellement de la valeur absolue |
|
Validation et compensation : comment ça marche ?
2323.pdf |
|
Systèmes linéaires1
Un tableau de coefficient est dit échelonné réduit s'il est échelonné si les pivots sont tous égaux à 1 |
|
PHQ114: Mecanique I
May 30 2018 si l'objet possède une symétrie de rotation autour de l'axe de la vitesse et le facteur 6?R est alors remplacé par le coefficient approprié. |
|
LES DROITES ET LES PENTES
Si la droite passe par les points et |
|
Baccalauréats STI2D et SSI : un objectif commun pour des profils d
Thèmes liés à l'enseignement technologique au développement durable. Aspect plus mathématique des phénomènes étudiés. Programme de 1ère : L'habitat. Les |
|
EQUATIONS DE DROITES SYSTEMES DEQUATIONS
Deux droites seront parallèles si elles ont le même coefficient directeur. Il n'y a pas de solution au système donc S = . c) Si ( D) et ( D') sont ... |
|
TABLEAU DES COEFFICIENTS 2016-2017 - Albert de Mun
Terminale sont ceux du baccalauréat 2nde ° CLASSES 6° 5° 4° 3° TRIMESTRE 1°L 1°ES |
|
Classe de seconde et cycle termial
, Théâtre) 3 h 00 2 (la 1ère option ou 1 seule option) 3 si LCA) 1 l' option suivante 6 / 16 Enseignements obligatoires Horaires Coefficients Bac Épreuves 1ère Terminale |
|
Le tableau davancement en Première S - Aix - Marseille
6 1 Équation de réaction Ajustement des coefficients stœchiométriques La description de l'état initial est complète si on précise : étudiées en Terminale S |
|
Presentation des filieres aux secondes
reuves de Français dans les trois filières Coefficients : L ES S Ecrit 3 Oral 2 2 Pour une orientation vers la 1ère L : une spécialité à Si la première épreuve concerne le latin |
|
LES DISCIPLINES DU POLE SCIENTIFIQUE : - Lycée Gambetta
2nde 1h30+1h30 L 1h30 ES 1h30 S 1h00+ 2h00 S 3h00+2h00 + Spé SPC Coefficient 6 Coefficient 8 si cette discipline est choisie comme enseignement de spécialité |
|
EPS, AS, Option sport, Enseignement, exploration, complément
choix fait Nbr Heures : 5h/S Sports : Escalade et plongée sous marine Noté : OUI Coefficient : 2 1ere Obligatoire : OUI OUI si choix fait Nbr Heures : 4h/S Sport : Escalade, |

![PDF] Examen bureautique informatique PDF pour réviser ensemble PDF] Examen bureautique informatique PDF pour réviser ensemble](https://www.lhotellerie-restauration.fr/blogs-des-experts/gestion/Media/Carte-Petit.jpg)