alternating current formula
|
Formulae For ALTERNATING CURENT
I 0 707I 70 7 I 2 = = RMS values are also called apparent or effective values Phase difference Between the EMF (Voltage) and the Current in an AC Circuit |
|
Class 12
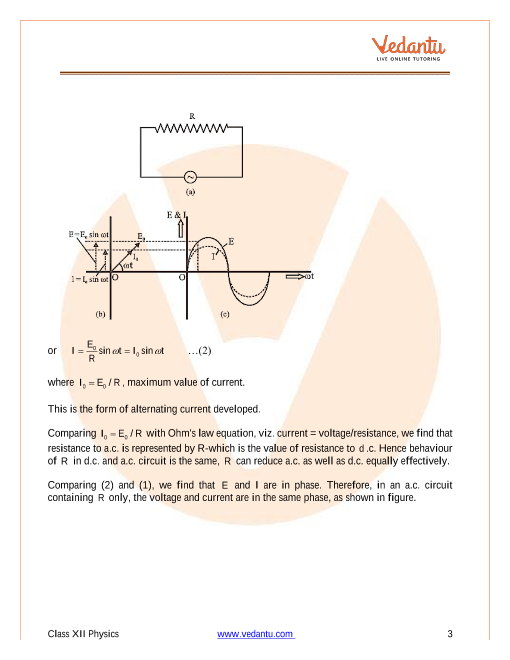
It is current whose magnitude changes with time and direction reverses periodically I=I0sin t where I0 is the peak value of a c and =2п/T is the frequency |
What is the formula for the AC system?
In the case of an alternating current AC, power is calculated by the formula: P=I_{rms}*V_{rms} where both I_{rms} and V_{rms} are the root-mean-square values of current and voltage respectively.
Power is always measured in Watts.What is the formula of AC?
Let's dive into some of the key formulas related to alternating current.
Starting with the basics, the AC voltage can be represented as v = V0sinωt while the AC current is denoted as i = I0sinωt.
Further, Capacitive Reactance is given by V0/I0 = 1/ωC = Xc.31 juil. 2023What is the formula of alternating current phase?
An alternating current is given by the equation, i=3√2sin(100πt+π/4) and an alternating voltage is given by the equation, E=220√2sin(100πt+π/2).
Equation of alternating current is given by I= 10√2sin(100πt+π/6).
The time taken by current to reach the root mean square value from t=0 is t'.
|
Formulae For ALTERNATING CURENT
CHAPTER FORMULAS & NOTES. Page 5. 5. Wattless Current. The component of current differing in phase by π/2 relative to the voltage is called wattles current. |
|
Class 12 - Important Formulas Chapter 7 - Alternating Current
It is current whose magnitude changes with time and direction reverses periodically. I=I0sin t where I0 is the peak value of a.c. and =2п/T is the frequency. |
|
Www.gradeup.co
The following formula gives the alternating current. I = I0 sin ωt. I = I0 sin (2π/T) t where I0 is the peak value of Alternating Current (AC) Angular |
|
AC Voltage and Current: Batteries produce a steady fixed voltage
The power company produces a time-varying voltage AC |
|
Calculation of alternating current losses in stacks and coils made of
(Received 12 August 2013; accepted 9 October 2013; published online 1 November 2013). A homogenization method to model a stack of second generation High |
|
On the Alternating Current Resistance of Solenoidal Coils
Hickman* has proposed a formula for calculating the alternating current resistance of a fairly long solenoid. His formula is as follows. R__ _ UO/J. + G + K |
|
An integration method of deriving the alternating current resistance
2. Derivation of formulas using complex power series. 103. IV. Alternating-current resistance and inductance of a |
|
Alternating current distribution in cylindrical conductors
dielectric. Asymptotic formulas for the alternating current resistance R and inductance L of the line at high frequencies are obtained which |
|
Computational and numerical analysis of AC optimal power flow
AC-OPF is an optimization model that considers the full AC power flow equations. It is the most accurate representation of power flow in a network assuming the |
|
GCE Physics Unit 4 Option A Alternating Currents
From the equation above the maximum emf = ωBAN. This is the peak voltage |
|
Formulae For ALTERNATING CURENT
periodically is called alternating current. Instantaneous value: It is the value of alternating current and voltage ... CHAPTER FORMULAS & NOTES. |
|
Chapter 12 Alternating-Current Circuits
After an initial “transient time” an AC current will flow in the circuit as a The above equation indicates that the maximum value of the current is. |
|
Alternating Current RC Circuits
or interesting circuits operate under alternating current conditions - think computers radios leading to the differential equation dq(t) q(t). |
|
An integration method of deriving the alternating current resistance
Derivation of formulas using complex power series. 103. IV. Alternating-current resistance and inductance of a return circuit. |
|
On the Alternating Current Resistance of Solenoidal Coils
Alternating Current Resistance of Solenoidal Cotils. 699-. Using only the first approximation for finite frequencies the following formula. |
|
Chapter 24: Alternating-Current Circuits
Calculate the resistance from the average power and the rms voltage using equation 21-6. Then from the resistance and rms voltage |
|
Alternating current distribution in cylindrical conductors
dielectric. Asymptotic formulas for the alternating current resistance R and inductance L of the line at high frequencies are obtained which |
|
On the alternating current resistance of solenoidal coils
The following equations which were established in the author's previous paper |
|
On the alternating current resistance of solenoidal coils
The following equations which were established in the author's previous paper |
|
Alternating Current Circuits
707 = 170 Volts. 13.2 Equations for Alternating Current Circuits. The circuit below contains an ac voltage source (like an ac generator or just |
Alternating Current Formulas
Understanding alternating current formulas is essential for analyzing and solving problems related to this type of electrical current. Here's a comprehensive guide to the fundamental formulas of alternating current:
Examples
1. Instantaneous Voltage Formula: V(t) = Vm * sin(ωt + φ)
2. Effective Voltage Formula: Vrms = Vm / √2
3. Instantaneous Current Formula: I(t) = Im * sin(ωt + φ)
4. Instantaneous Power Formula: P(t) = V(t) * I(t)
Exercises
Practice using alternating current formulas to solve circuit and power-related problems with the following exercises:
- Calculate the instantaneous voltage and current at a given time using the relevant formulas.
- Determine the effective voltage and current for a sinusoidal waveform with known peak values.
- Calculate the power dissipated in a resistor or a load connected to an alternating current source.
- Analyze phase relationships between voltage and current in capacitive and inductive circuits.
Solutions:
- Substitute the time value into the instantaneous voltage and current formulas to calculate their values.
- Divide the peak voltage or current by √2 to obtain the effective values.
- Multiply the instantaneous voltage and current at each time instant to calculate the instantaneous power.
- Use phasor diagrams or trigonometric relationships to determine phase differences and power factors.
Case Study
Scenario: A technician needs to analyze the behavior of an alternating current circuit in a residential building.
Use Case: The technician applies alternating current formulas to calculate voltage drops, power consumption, and phase relationships in the circuit.
Subcategories
Key subcategories related to alternating current formulas include:
- Instantaneous Voltage and Current
- Effective Voltage and Current
- Power Calculations
- Phase Relationships
Notes
1. Alternating current is characterized by its variation over time, typically represented by sinusoidal waveforms.
2. Effective voltage and current provide a measure of the equivalent direct current that produces the same power in resistive loads.
3. Phase relationships between voltage and current affect the power factor and efficiency of electrical systems.
4. Alternating current formulas are fundamental for circuit analysis, power distribution, and equipment design in electrical engineering.
Step-by-Step Guide
- Identify the type of alternating current waveform and its parameters, including peak voltage, frequency, and phase angle.
- Apply the relevant formulas to calculate instantaneous and effective values of voltage, current, and power.
- Analyze the behavior of alternating current circuits by considering phase relationships, impedance, and power factor.
- Use simulation software or laboratory experiments to verify theoretical calculations and understand practical implications.
- Optimize circuit designs and power distribution systems based on alternating current formulas to ensure efficiency and reliability.
Cases and Scenarios
1. Case: An electrical engineer designs an alternating current power supply for industrial equipment.
Solution: The engineer calculates the required voltage, current ratings, and power factor correction to meet the equipment's operational requirements.
2. Case: A technician troubleshoots a malfunctioning electrical system in a commercial building.
Solution: The technician uses alternating current formulas to analyze voltage sags, harmonics, and phase imbalances affecting the system's performance.
3. Case: A student studies the behavior of reactive components in alternating current circuits.
Solution: The student performs laboratory experiments to measure phase shifts, reactance, and impedance in capacitive and inductive circuits.
Questions and Answers
- Question: What is the effective voltage of a sinusoidal waveform with a peak voltage of 100V?
- Answer: The effective voltage is approximately 70.7V, calculated as Vrms = Vm / √2.
- Question: How does phase difference affect power distribution in alternating current systems?
- Answer: Phase differences between voltage and current affect the power factor, leading to reactive power components and inefficiencies in power transmission.
- Question: What is the significance of the power factor in alternating current circuits?
- Answer: The power factor represents the ratio of real power to apparent power and indicates the efficiency of power usage in electrical systems.
- Question: How can alternating current formulas be applied in practical engineering applications?
- Answer: Alternating current formulas are used in circuit analysis, equipment design, power system optimization, and troubleshooting electrical faults.
Multiple Choice Questions
- Question: What is the formula for calculating effective voltage?
- Answer A: Vrms = Vm / 2
- Answer B: Vrms = Vm / √2 (Correct)
- Answer C: Vrms = Vm * √2
- Answer D: Vrms = Vm * 2
- Question: What does the power factor represent in alternating current systems?
- Answer A: The ratio of real power to apparent power (Correct)
- Answer B: The total power dissipated in the circuit
- Answer C: The frequency of the alternating current waveform
- Answer D: The voltage drop across the load
- Question: Which component measures the phase difference between voltage and current?
- Answer A: Multimeter
- Answer B: Oscilloscope
- Answer C: Power analyzer (Correct)
- Answer D: Function generator
- Question: What happens when the phase angle between voltage and current is zero?
- Answer A: Maximum power transfer occurs
- Answer B: The power factor is unity (Correct)
- Answer C: The circuit becomes purely resistive
- Answer D: No power is transferred
Key Points to Remember
- Alternating current formulas are essential for analyzing voltage, current, and power in AC circuits.
- Effective voltage and current provide a measure of the equivalent DC values for sinusoidal waveforms.
- Phase relationships and power factor affect the efficiency and performance of electrical systems.
- Practical applications of alternating current formulas include circuit design, power system optimization, and fault diagnosis.
|
Alternating Current - UCF Department of Physics
v, i = instantaneous potential difference / current V, I = maximum potential difference / current → voltage/current amplitude |
|
Alternating Current - WordPresscom
c) In resonance the power factor of the circuit is one CHAPTER FORMULAS NOTES Page 6 6 Half – Power Frequencies |
|
Chapter 24: Alternating-Current Circuits - CSUN
Calculate the resistance from the average power and the rms voltage using equation 21-6 Then, from the resistance and rms voltage, solve for the rms current |
|
ALTERNATING CURRENT - Gneet
The rms value of alternating current is defined as that value of the steady current, which Q) If the voltage in ac circuit is represented by the equation |
|
Alternating Current Physics-03 (Leph_10704) - Central Institute of
Formula ✓ Graph ✓ Phasor • Frequency of ac and what does it depend upon • peak and rms value of alternating current/voltage; Module 5 • AC circuits |
|
Alternating Current Circuits
707 = 170 Volts 13 2 Equations for Alternating Current Circuits The circuit below contains an ac voltage source (like an ac generator, or just |
|
Fundamentals of Alternating Current - School of Electrical
Manipulate the general equation of a sinusoidal signal to determine its amplitude , frequency, phase shift at any time ❑ Compute peak, RMS, and average values |
























![PDF*] Physics chapterwise Notes Study Material formulas Theory PDF*] Physics chapterwise Notes Study Material formulas Theory](https://d2n7zouke881gi.cloudfront.net/physics+Formula+chapter3+Current+Electricity/physics+Formula+chapter3+Current+Electricity-02.jpg)