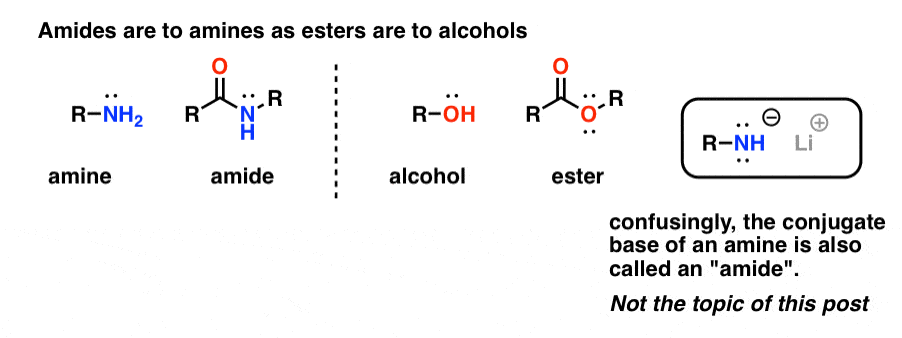
amide conh
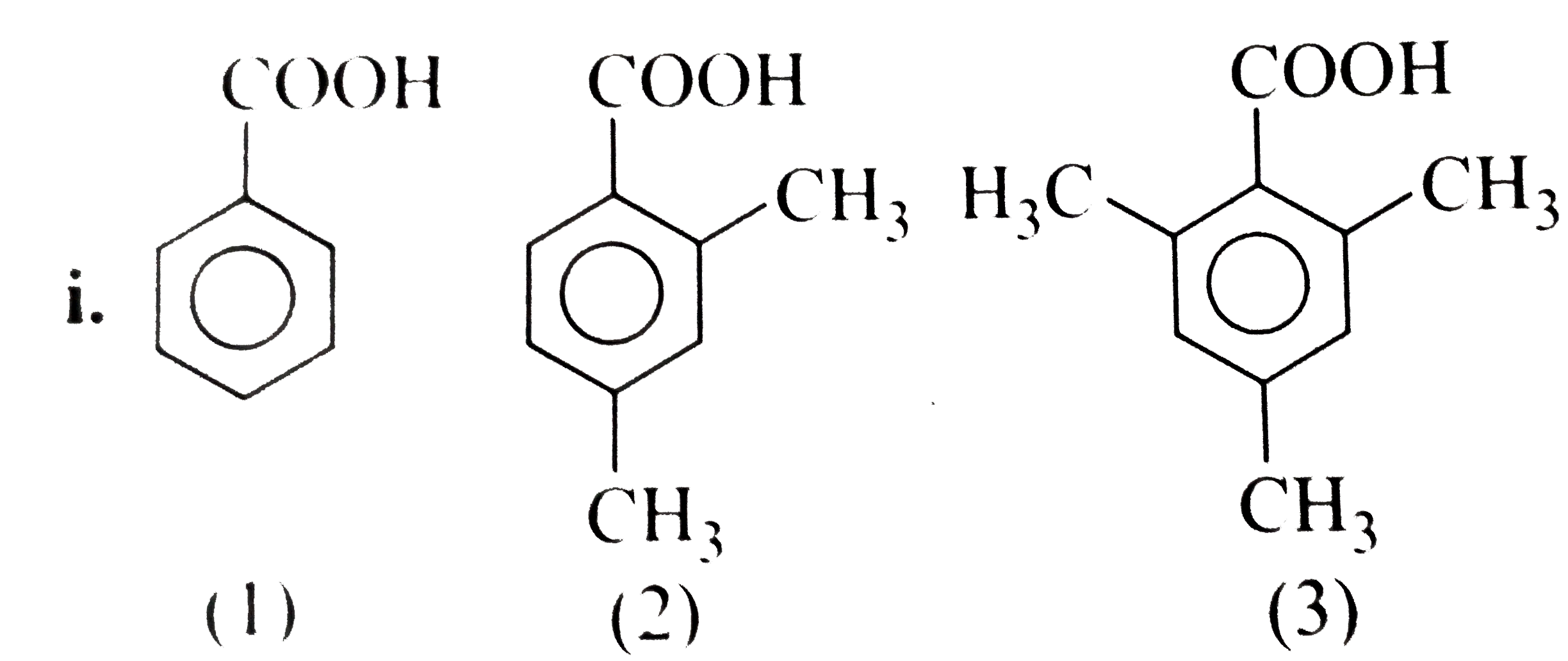
Which amide is a branched oic acid?
The most commonly discussed amide is ethanamide, CH 3 CONH 2 (old name: acetamide). Notice that in each case, the name is derived from the acid by replacing the "oic acid" ending by "amide". If the chain were branched, the carbon in the -CONH 2 group counts as the number 1 carbon atom. For example:
What is the bond structure of CONH2?
CONH2 is 1° amide, in the image it is 2° amide. If you take out that one hydrogen too you will get a 3° amide Amides are derivative of carboxylic acids. It consists of 2 parts, and the bond between carbonyl carbon and nitrogen of ammonia is called is amide bond. The bond structure of 1° amides is as shown in the figure.
What is the amide group derived from acetic acid called?
The core −C (=O)− (N) of amides is called the amide group (specifically, carboxamide group ). In the usual nomenclature, one adds the term "amide" to the stem of the parent acid's name. For instance, the amide derived from acetic acid is named acetamide (CH 3 CONH 2 ).
What is amide linkage -CONH 2?
This substitution results in the formation of the amide linkage, represented as -CONH 2. The fundamental structure of an amide consists of a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to a nitrogen atom (N) with a single bond, and the nitrogen atom is also bonded to two additional substituents, typically hydrogen atoms (H).

Nomenclature and properties of amides Organic chemistry Khan Academy

Properties of Amides

How to Make Amides: Mechanism
|
Identification of the Amide II Band in the cis-Amide 1-Methyluracil in
The bands associated with vibrations of the secondary amide. CONH group (designated in order of decreasing frequency amide. |
|
N&iR
of electrostatic attraction and favourable amide CONH and phenolic ROH hydrogen-bonding interactions. Stability constant determinations from NMR titration |
|
Design Synthesis and mode of action of some benzothiazole
26 mar 2014 In this study ten benzothiazole derivatives bearing amide moiety were ... of hydrogen bonding domain e.g. amide (–CONH–) seems to be. |
|
Nanoporous amide networks based on tetraphenyladamantane for
19 abr 2016 The CO2 capture ability of organic amide polymers has rarely ... Interestingly the polar –CONH– amide functionality is the key. |
|
N&iR
of electrostatic attraction and favourable amide CONH and phenolic ROH hydrogen-bonding interactions. Stability constant determinations from NMR titration |
|
Human monocyte/macrophage adhesion and cytokine production
or aminoethyl amide [CONH(CH2CH2NH)CH |
|
Untitled
and IR spectra indicate deprotonation of the secondary amide. Anion coordination The coordination of amides to metal is ... amide group (-CONH-). |
|
Amide Functionalized Microporous Organic Polymer (Am-MOP) for
18 mar 2014 a new microporous organic polymer with amide (>CONH) functional groups (Am-MOP) on the pore surface and envisage that these amide groups ... |
|
AMIDES
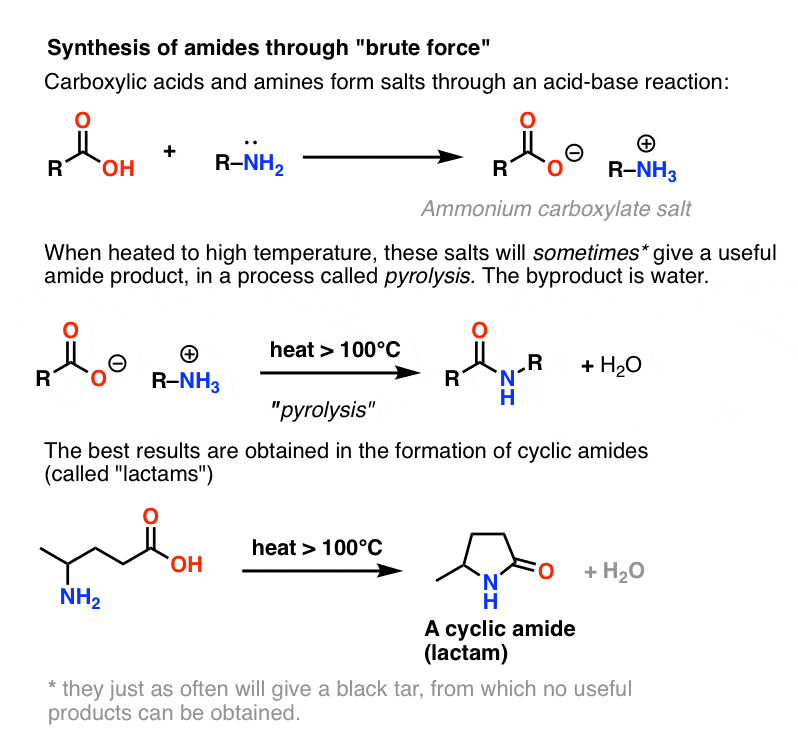
Amides are amine derivatives of carboxylic acids. • Compounds with functional group RCONH dehydrates producing amide CH. 3. COONH. 4 heat CH. 3. CONH. |
|
Intrinsically negative photosensitive polyimides with en- hanced
7 sept 2022 In the 1H-NMR spectra for both of the compounds |
|
The interactions and structure of the -CONH- group in amides and
and phenol molecules involves the amide C=O bond whose frequency The CONH group absorption bands in the solid nylon film are as follows : Main N--It |
|
Quelques exercices sur les amides - TuniSchool
Amide non substitué Eau Carboxylate d ammonium O - → + • Hydrolyse d'un amide ❖ En milieu basique : ➢ Amide non substitué : ( ) 2 R CONH Na OH |
|
Chimie organique générale
Fonction amide: -Dérivé d'amine: R-CONH2 -Amide monosubstitué: R-CONH-R -Amide disubstitué: R-CON −R −R' Rq: Dans les cycles, la fonction amide |
|
Polypeptides et protéines - La physique-chimie et le cinéma
La structure primaire ne tient pas compte de la configuration spatiale de la protéine La liaison peptidique est une fonction amide (–CONH–) qui lie de chaque côté |
|
CONH - ScienceDirectcom
frequencies, the '(amide” frequencies, are not observed in the spectra of amides having a cis -CO?;H- configuration The geometrical structure of the cis cm- |
|
AMIDES
Amides are amine derivatives of carboxylic acids • Compounds with functional dehydrates producing amide CH 3 COONH 4 heat CH 3 CONH 2 + H 2 O |
|
Nomenclature des composés organiques - Serveur UNT-ORI
Un groupement acétyle = CH3CO-, abréviation Ac, par exemple AcOH = acide acétique CH3COOH 9 3 Amides Un amide est caractérisé par l'enchaînement : |






![Full text] A novel hydrolysis-resistant lipophilic folate Full text] A novel hydrolysis-resistant lipophilic folate](https://www.mdpi.com/molecules/molecules-23-02615/article_deploy/html/images/molecules-23-02615-g036-550.jpg)


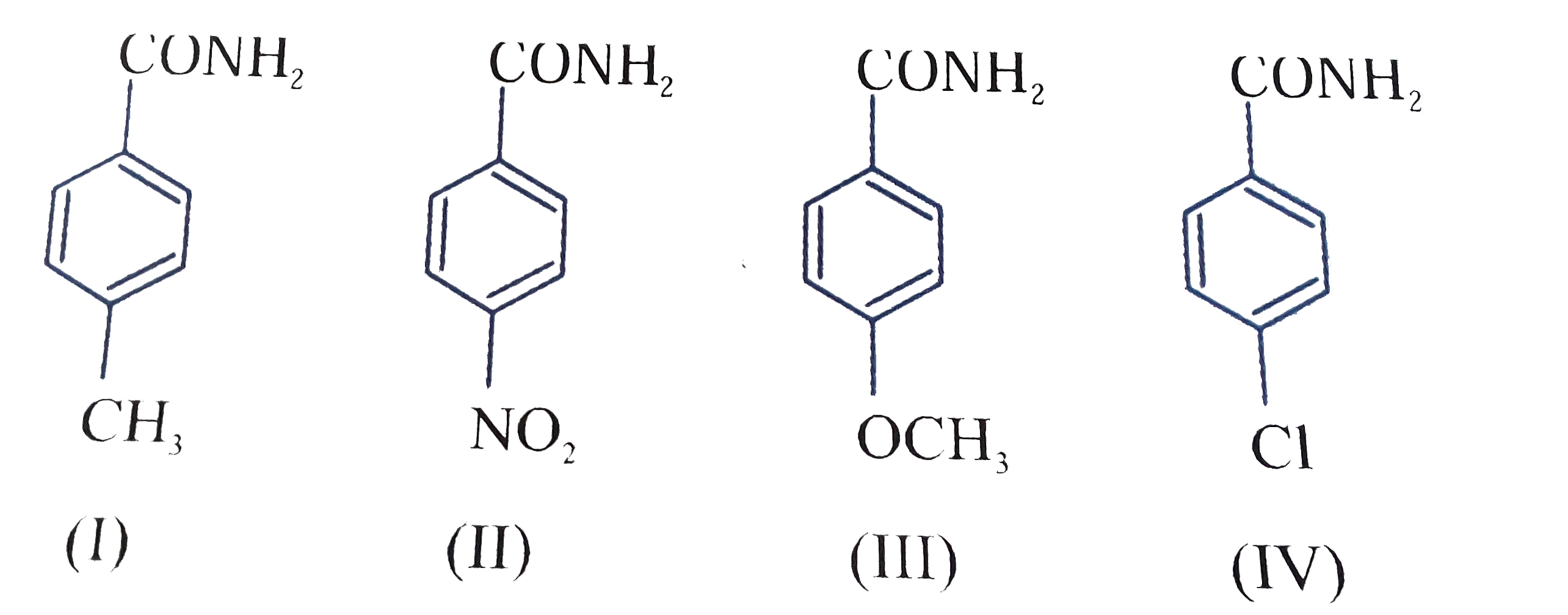






![PDF] Ceric Ammonium Nitrate (CAN) Promoted Efficient Solid Phase PDF] Ceric Ammonium Nitrate (CAN) Promoted Efficient Solid Phase](https://www.vedantu.com/question-sets/f23ee0e4-4b81-4b9e-94a0-20bd5dc9eb791670140931082097681.png)