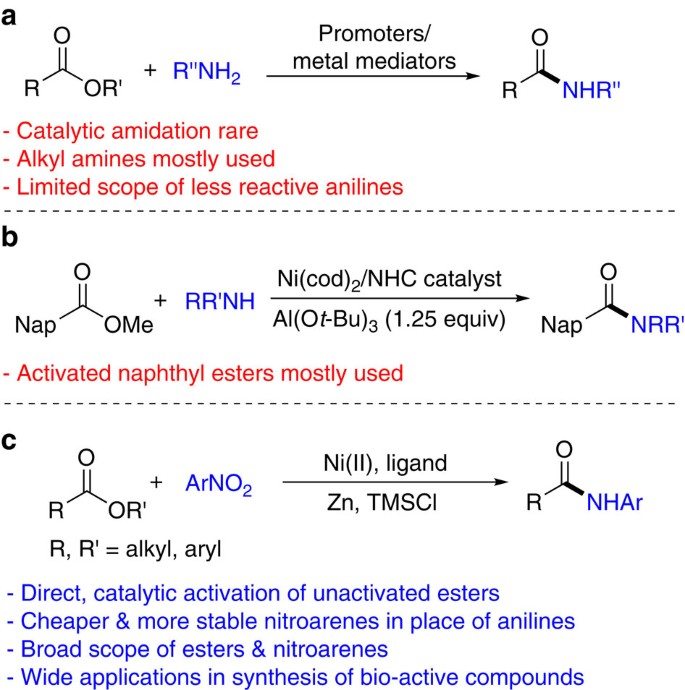
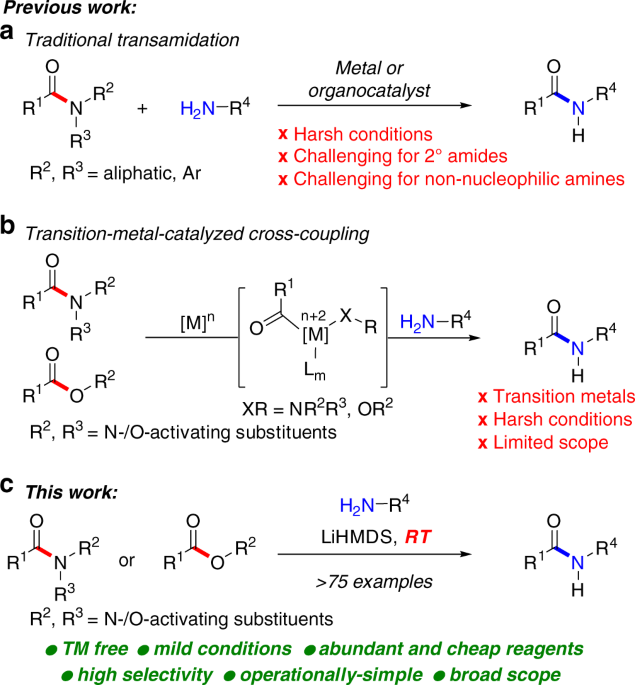
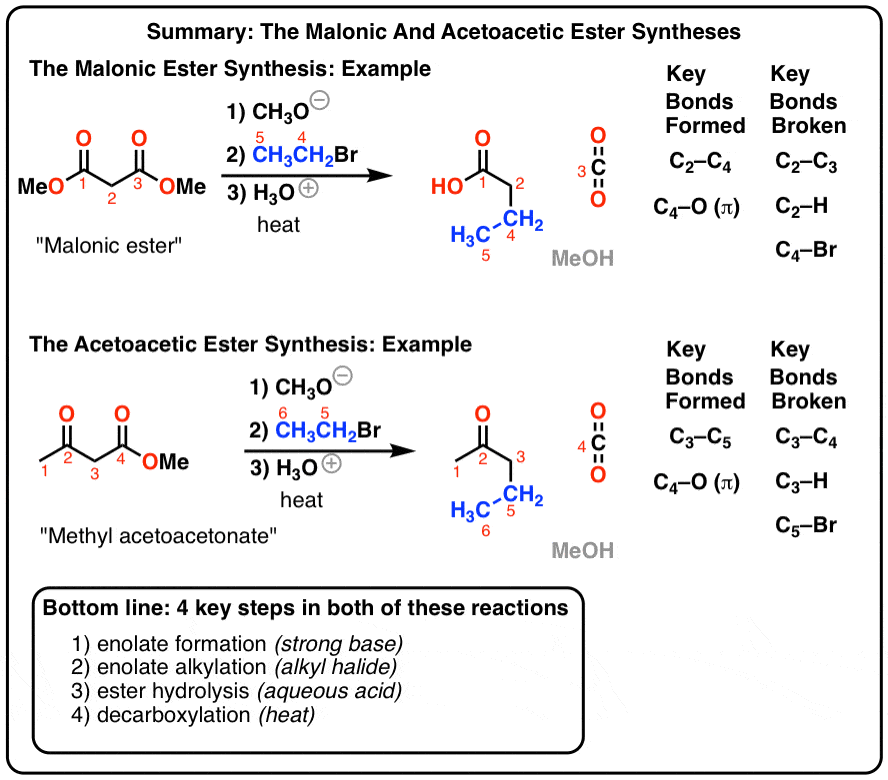
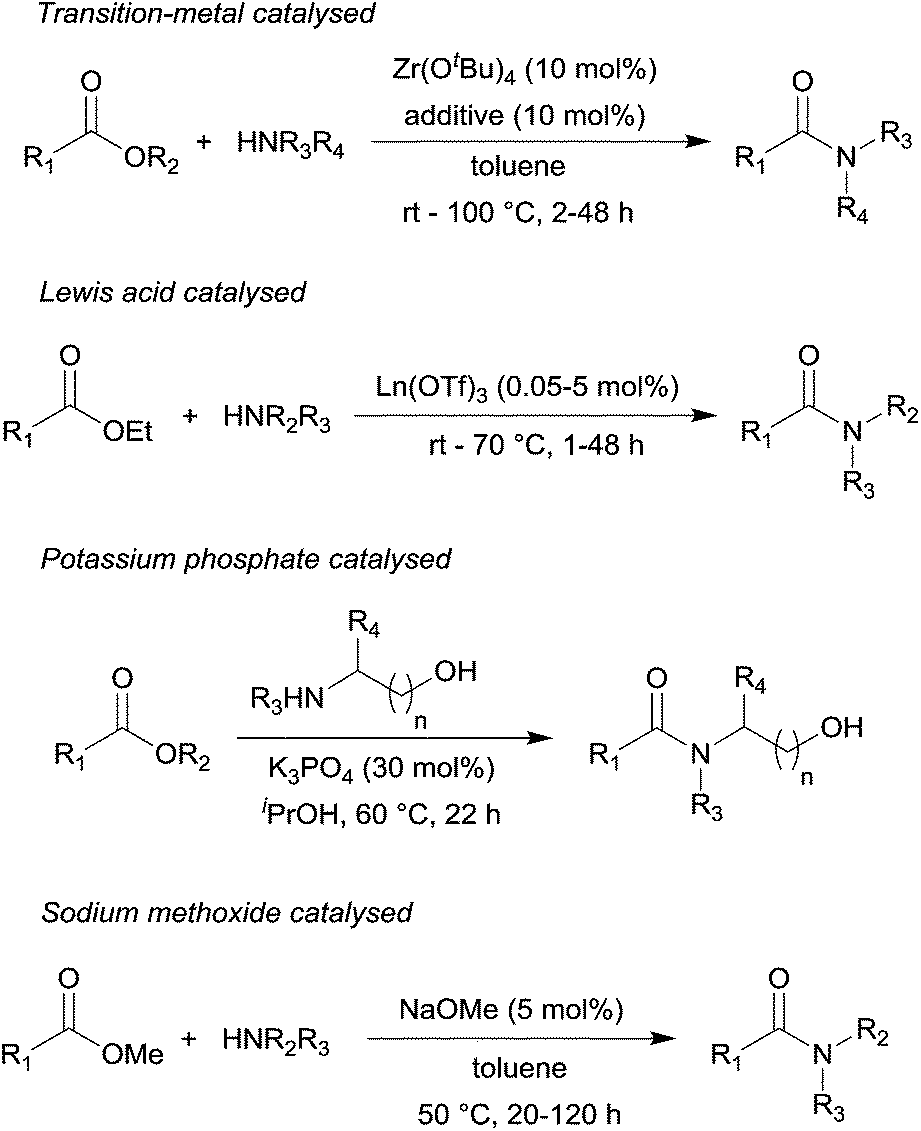
amide ester
What are amines and amides?
“Amides” are what we call an amine that has a single attached carbonyl group. The amide functional group is to amines as esters are to alcohols. Confusingly, the word “amide” is also used to refer to the conjugate base of amines, such as sodium amide ( NaNH 2) and lithium di-isopropyl amide ( LDA ).
What is amide functional group?
The amide functional group is to amines as esters are to alcohols. Confusingly, the word “amide” is also used to refer to the conjugate base of amines, such as sodium amide ( NaNH 2) and lithium di-isopropyl amide ( LDA ). The latter are sometimes differentiated by referring to them as “amide bases”.
How do you convert esters to amides?
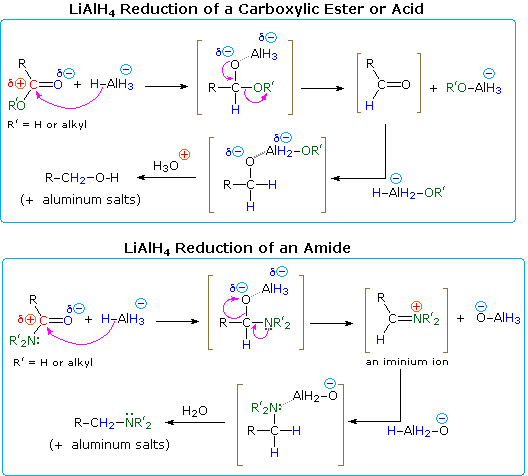
It is possible to convert esters to amides through direct reaction with ammonia or amines. However, these reactions are not commonly used because the formation of an amide using an acid chloride is a much simpler reaction. Esters can undergo hydride reduction with LiAlH 4 to form two alcohols.
Which reaction is not commonly used in the formation of an amide?
However, these reactions are not commonly used because the formation of an amide using an acid chloride is a much simpler reaction. Esters can undergo hydride reduction with LiAlH 4 to form two alcohols. The alcohol derived from the acyl group of the ester will be 1 o and is typically considered the main product of the reaction.
Amides vs Amines: Less Basic, More Acidic
Attaching a carbonyl group to an amine has two drastic effects on the properties of the nitrogen. 1. First, amide nitrogens are considerablyless basic than amine nitrogens. That’s mainly the result of the delocalization of the nitrogen lone pair into the pi bond of the carbonyl.In fact, the most basic position of an amide is not the nitrogen but th
Synthesis of Amides, Part 2: Partial Hydrolysis of Nitriles
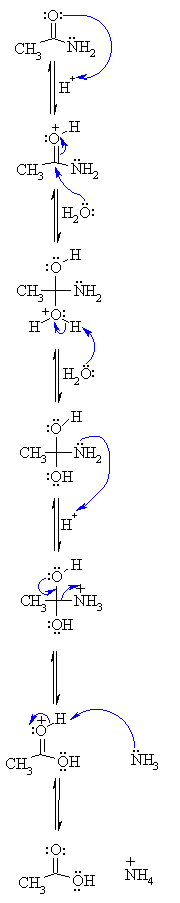
One way to think of nitriles is that they are masked carboxylic acids. If treated with aqueous acid and a lot of heat – sledgehammer conditions – they can be hydrolyzed to carboxylic acids. One of the intermediates in this process is a primary amide. So if we use a slightly kinder, gentler sledgehammer technique, sometimes it’s possible to salvage
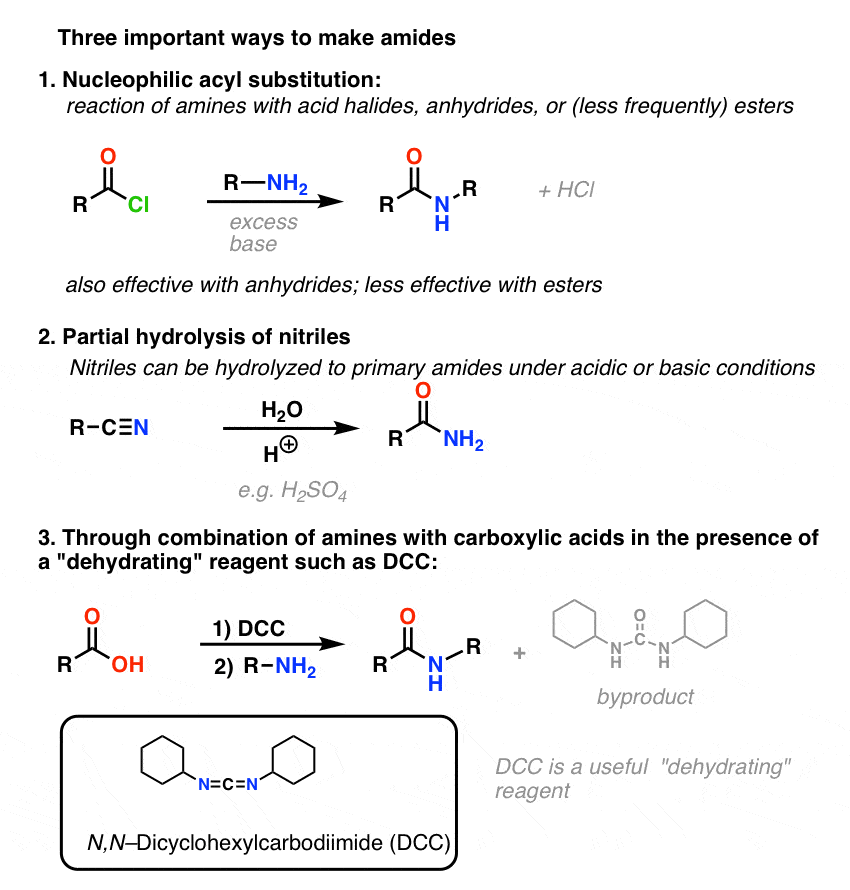
Synthesis of Amides, Part 3: Use of A Dehydrating Reagent
The synthesis of penicillin V in 1957 by John Sheehan’s group at MIT stands as one of the heroic achievements of postwar-era organic chemistry. The key problem was construction of a cyclic amide (the β-lactam ring) which is extremely unstable under acidic conditions. This was of no small importance, as the β-lactam is also key to penicillin’s mecha
Summary: Three Effective Methods For The Synthesis of Amides
Let’s end by summarizing these three important (but by no means exhaustive) ways to make amides: This concludes our post on the main points of amide nomenclature, properties, and synthesis. For a bonus method of amide synthesis, read on. masterorganicchemistry.com
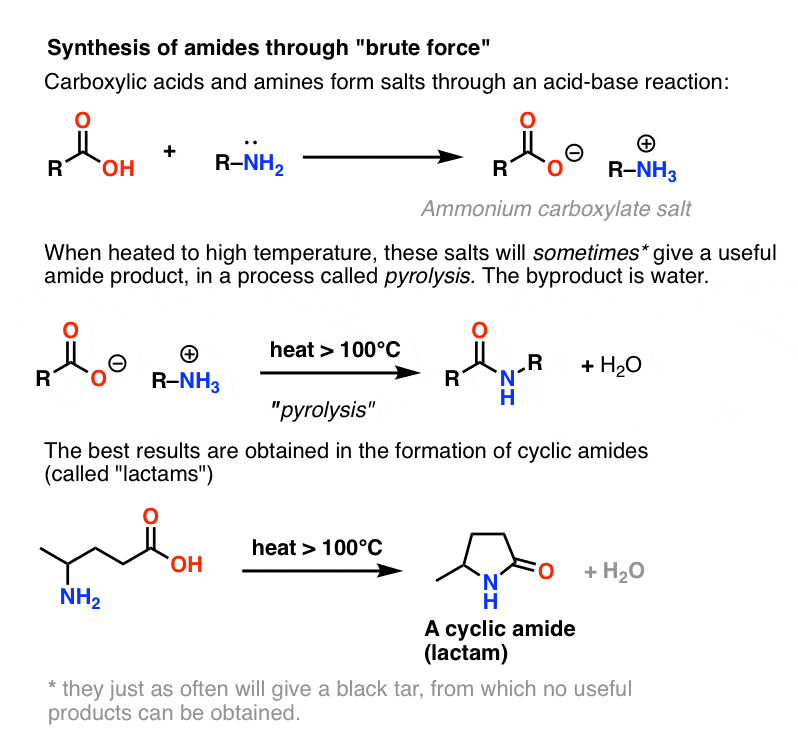
Let Us Briefly Consider A Fourth, Less Important Method: Brute Force
Since it’s usually covered in the textbooks, let’s conclude by considering a fourth possibility – the simplest one imaginable. What if we take a carboxylic acid and combine it with an amine, hoping that an amide will form. What happens? Amines are bases, and carboxylic acids are, well, acids. Add the two together and you get an innocuous salt. Some
Notes
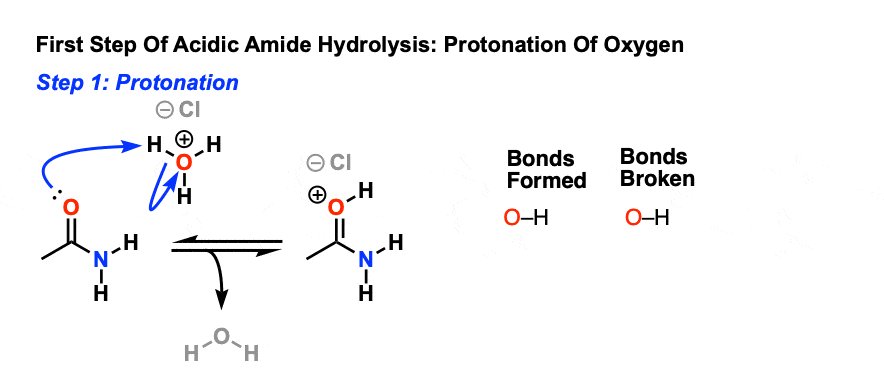
[related articles] A fun, related article: Amides: Humble But Useful(from Chemical & Engineering News). Note 1. There’s also an inductive effect, whereby the electronegative oxygen (electronegativity of 3.44) tugs on the electrons of the attached carbon, which in turn tugs on the electrons of the nitrogen. Note 2. A very common way of carrying out
References and Further Reading
Nitrile hydrolysis: 1. PHENYLACETAMIDE Wilhelm Wenner Org Synth. 1952, 32, 92 DOI: 10.15227/orgsyn.032.0092 The conditions used here for hydration of the nitrile to the amide are rather gentle – this uses a temperature of 40 °C for approximately 1 hr. 2. Halide-directed nitrile hydrolysis James M. Photis Tetrahedron Lett. 1980, 21 (37), 3539-3540 D

Ester vs Amide Local Anesthetics How they differ?

Amides anhydrides esters and acyl chlorides Organic chemistry Khan Academy

Nomenclature and properties of amides Organic chemistry Khan Academy
|
Synthesis and characterization of poly(ester amide amide)s of
7 janv. 2021 Abstract: In this work a series of aliphatic biodegradable poly(ester amide amide) polymers was synthesized by melt. |
|
Is it ester or amide?
True allergic reactions to local anesthetics are rare and usually involve an ester agent. Allergic reactions are seldom caused by amide anesthetic agents. An |
|
Degradable Poly(ester amide)s for Biomedical Applications
27 déc. 2010 These polymers have ester and amide groups on their chemical structure which are of a degradable character and provide good thermal and ... |
|
BIODEGRADABLE POLY (ESTER AMIDE) S: SYNTHESIS AND
dispositions between their amide and ester groups. Synthesis strategies (e.g. ring opening polymerization and polycondensation) will be discussed as well as |
|
Amide-to-Ester Substitution as a Strategy for Optimizing PROTAC
9 déc. 2021 Using model compounds bearing either amides or esters |
|
The Properties of Poly(ester amide)s Based on Dimethyl 25
5 juin 2022 mechanical properties of two series of poly(ester amide)s were analyzed. The increase in the number of methylene groups in the polymer ... |
|
COMPARISON OF THE VASOACTIVITY OF AMIDE AND ESTER
ester-linked local anaesthetics procaine and amethocaine |
|
Amide-to-ester substitution as a strategy for optimizing PROTAC
Using a library of model compounds bearing either amides or esters at various linker-warhead junctions |
|
Sequence-defined oligo/poly(ester-amide-ester)s via an orthogonal
30 sept. 2019 Furthermore two strategies were examined to obtain sequence-defined periodic poly(ester-amide-ester)s through the polycondensation of different ... |
|
Pharmacologie des anesthésiques locaux
4 févr. 2016 (un ester ou un amide);. – Une amine tertiaire. Page 14. Structure chimique. Dépolarisation cellulaire ... |
|
ESTERS V AMIDES AND THE INFLUENCE OF pKa - Oxford
an amide or an ester bond, and side chains may be added to any part of the molecule The differences in drug profile which these variations in molecular |
|
28 CLASSIFICATION OF LOCAL ANESTHETICS ESTERS AMIDES
ESTERS AMIDES Benzocaine Chloroprocaine* Cocaine Proparacaine Tetracaine* are no longer any injectable ester-type local anesthetic products |
|
12 Synthèse des esters et des amides - Chimie PCSI
Comment synthétiser, avec un bon rendement, un ester ou un amide à partir d'un acide carboxylique ? Equation de l'estérification de Fischer : Page 2 -2- Expl : |
|
Autres méthodes de synthèse dun ester (suite) R C OCH3 O R C
2 4 Synthèse des esters 2 5 Synthèse des amides 2 6 Réduction des acides carboxyliques et dérivés 2 5 Synthèse des amides ☞ R C NRR' O amide R |
|
COMMUNICATION Catalytic Ester and Amide to Amine
esters and amides into the corresponding amines and represents a rearrangements; b) Classical amide bond formations via ester amine coupling; c) Direct |