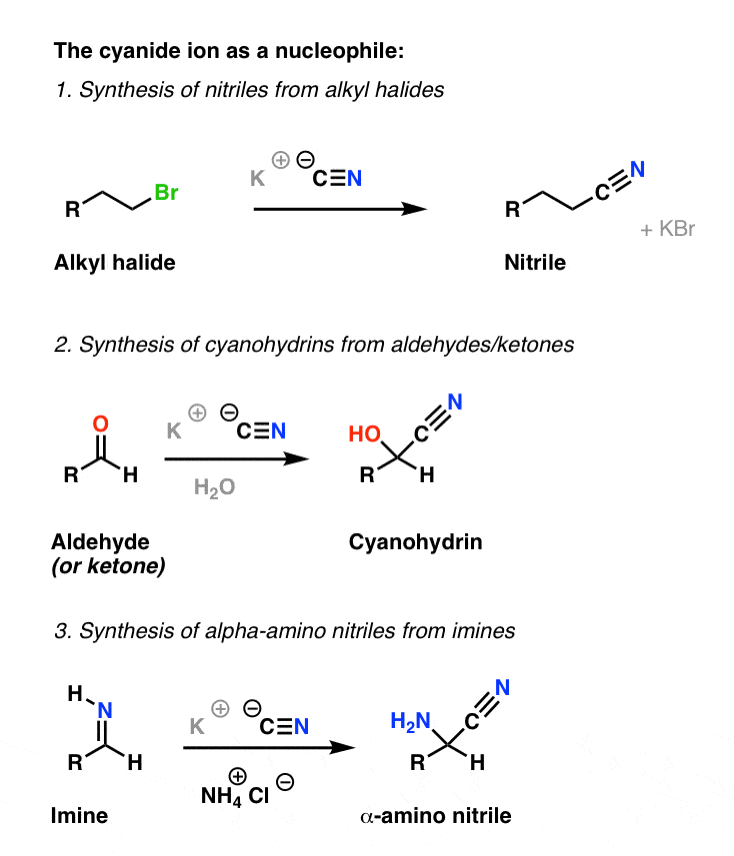
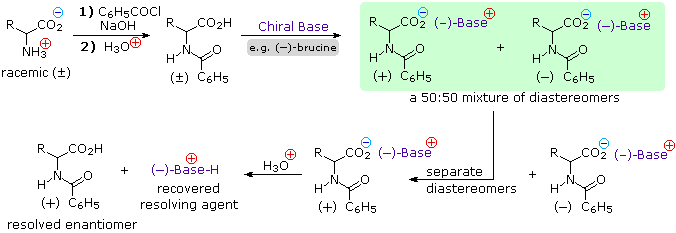
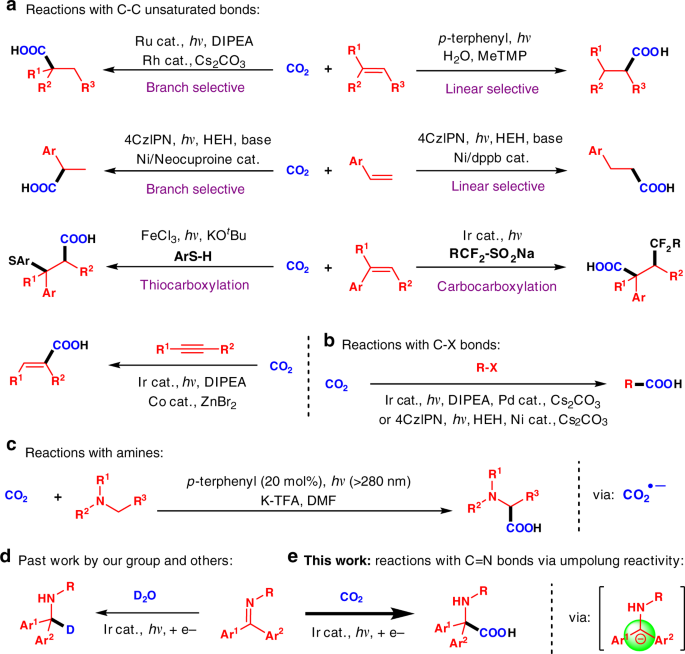
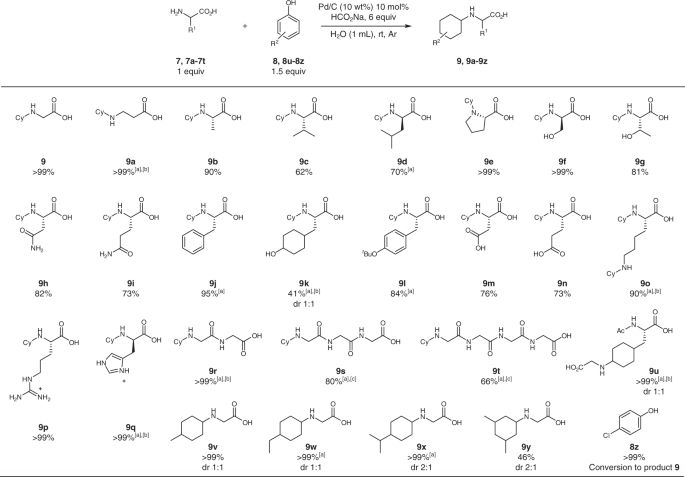
amine and amino acid reaction
What is an amine molecule?
Amines are molecules that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds. The nitrogen atom in an amine has a lone pair of electrons and three bonds to other atoms, either carbon or hydrogen. Various nomenclatures are used to derive names for amines, but all involve the class-identifying suffix –ine as illustrated here for a few simple examples:
How do amino acids react with amines?
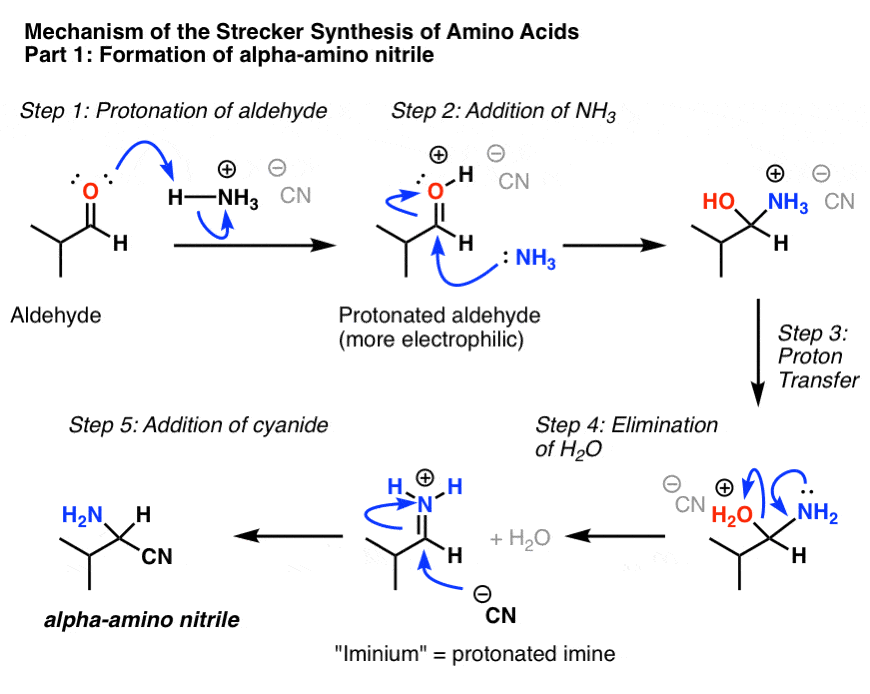
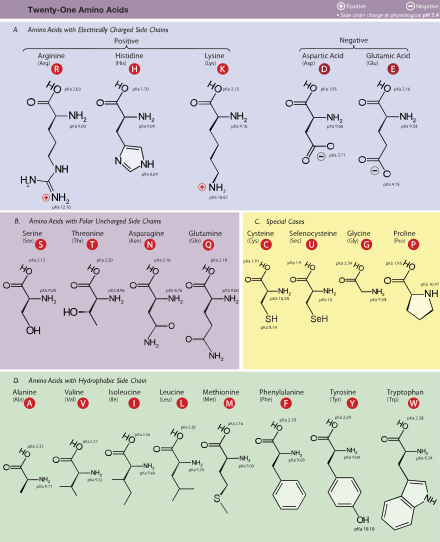
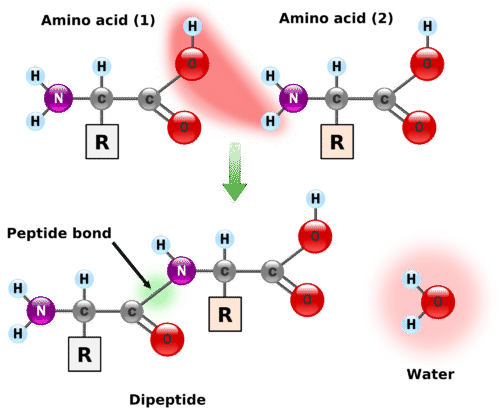
Amino acids undergo reactions characteristic of carboxylic acids and amines. When the carboxyl group of one amino acid molecule reacts with the amino group of the other amino acid molecule, an amide bond is formed, causing the release of a molecule of water (H 2 O).
Overview
Amines characteristically form salts with acids; a hydrogen ion, H+, adds to the nitrogen. With the strong mineral acids (e.g., H2SO4, HNO3, and HCl), the reaction is vigorous. Salt formation is instantly reversed by strong bases such as NaOH. Neutral electrophiles (compounds attracted to regions of negative charge) also react with amines; alkyl halides (R′X) and analogous alkylating agents are important examples of electrophilic reagents. A salt is formed by addition; R3N becomes R3NR′+X−. RNH2+ R′X → RR′N+H2X−→ RNH2RR′NH + RN+H3X− britannica.com
Addition
Amines characteristically form salts with acids; a hydrogen ion, H+, adds to the nitrogen. With the strong mineral acids (e.g., H2SO4, HNO3, and HCl), the reaction is vigorous. Salt formation is instantly reversed by strong bases such as NaOH. Neutral electrophiles (compounds attracted to regions of negative charge) also react with amines; alkyl halides (R′X) and analogous alkylating agents are important examples of electrophilic reagents. A salt is formed by addition; R3N becomes R3NR′+X−. RNH2+ R′X → RR′N+H2X−→ RNH2RR′NH + RN+H3X− britannica.com
Substitution
Acylation is one of the most important reactions of primary and secondary amines; a hydrogen atom is replaced by an acyl group (a group derived from an acid, such as RCOOH or RSO3H, by removal of ―OH, such as RC(=O)―, RS(O)2―, and so on). Reagents may be acid chlorides (RCOC1, RSO2C1), anhydrides ((RCO)2O), or even esters (RCOOR′); the products are amides of the corresponding acids. Britannica Quiz Facts You Should Know: The Periodic Table Quiz The reaction with phosgene, COC12 (the acid chloride of carbonic acid, H2CO3), has major industrial importance. It can result in simple acylation to form ureas (amides of carbonic acid), RNHCONHR, but it is usually carried out under conditions that favour the conversion of primary amines to isocyanates: RNH2+ COCl2→ RN=C=O + 2HCl). Isocyanates are themselves acylating agents, of a type that also includes isothiocyanates (RN=C=S), ketenes (R2C=C=O), and carbon dioxide (O=C=O). They react more or less readily with primary and most secondary amines to form, respectively, ureas, thioureas (RNHCSNHR), amides, and salts of carbamic acid (RNHCO2−RNH3+). Reaction with nitrous acid (HNO2), which functions as an acylating agent that is a source of the nitrosyl group (―NO), converts aliphatic primary amines to nitrogen and mixtures of alkenes and alcohols corresponding to the alkyl group in a complex process. R2CH―CR2―NH2+ HNO2→ R2CH―CR2NHNO → britannica.com
Oxidation
Amines can burn in air, producing water, carbon dioxide, and either nitrogen or its oxides. Milder oxidation, using reagents such as NaOCl, can remove four hydrogen atoms from primary amines of the type RCH2NH2 to form nitriles (R―C≡N), and oxidation with reagents such as MnO2 can remove two hydrogen atoms from secondary amines (R2CH―NHR′) to form imines (R2C=NR′). Tertiary amines can be oxidized to enamines (R2C=CHNR2) by a variety of reagents. R2CH―CH2NR′2 + Hg(OAc)2 → R2C=CH―NR′2 britannica.com
Elimination
The principal reaction of quaternary ammonium compounds is the Hofmann degradation, which takes place when the hydroxides are strongly heated, generating a tertiary amine; the least-substituted alkyl group is lost as an alkene. britannica.com
Uses of amines
Examples of direct uses of amines and their salts are as corrosion inhibitors in boilers and in lubricating oils (morpholine), as antioxidants for rubber and roofing asphalt (diarylamines), as stabilizers for cellulose nitrate explosives (diphenylamine), as protectants against damage from gamma radiation (diarylamines), as developers in photography (aromatic diamines), as flotation agents in mining, as anticling and waterproofing agents for textiles, as fabric softeners, in paper coating, and for solubilizing herbicides. Some polyfunctional amines are valuable pharmaceuticals, such as ephedrine and epinephrine (adrenaline), and anesthetics, such as novocaine. Many important products require amines as part of their syntheses. Methylamine is utilized in the production of the analgesic meperidine (trade name Demerol) and the photographic developer Metol (trademark), and dimethylamine is used in the synthesis of the antihistamine diphenhydramine (trade name Benadryl), the solvent dimethylformamide (DMF), and the rocket propellant 1,1-dimethylhydrazine. The synthesis of the insect repellent N,N-diethyl-m-toluamide (DEET) incorporates diethylamine while that of the synthetic fibre Kevlar requires aromatic amines. Polyurethanes are formed from methylenedianiline via its diisocyanate. Other products utilizing amines in their synthesis include spandex, caffeine, explosives (e.g., 2,3,4,6-tetranitro-N-methylaniline [TNA] and 2,4,6-N-tetranitroaniline [Tetryl]), pesticides, fungicides, herbicides, azo dyes, and some triphenylmethane dyes. britannica.com

Amine Synthesis Reactions

Amine Synthesis Reactions Organic Chemistry

Introduction to Amino Acids
|
Chapter 6 Amines and Amides
Learn the major chemical reactions of amines and amides and learn how to predict with —NH2 as the amino substituent. ... the amino acid arginine; also. |
|
Reactions of Amines
Amines are completely converted to ammonium salts by acids. • Ammonium salts are completely -The major natural amino acids all have "S" configuration. |
|
Selection of Amine Amino Acids Salt Systems for CO2 Capture
Among these is gas absorption with chemical reaction using aqueous amines one of the most frequently used methods. Aqueous amino acids could be an |
|
The Reaction of Amines with Amino Acid N-Carboxy Anhydrides
The reaction of amines with X-carboxyanhydridcs of -amino acids proceeds to yield either a ureido acid (attack at the. 2-carbonyl of the oxazolidinedionc |
|
Temperature Dependent Enthalpy of CO2 Absorption for Amines
The thermodynamics of carbamate formation from the reaction of amines or amino acids with CO2 in post combustion CO2 capture processes is studied in this |
|
CARBONYL-AMINE REACTIONS IN PROTEIN CHEMISTRY
I1 . The Chemistry of Carbonyl Groups of Amino Groups. and of the Carbonyl-. I11 . Reaction of Carbonyl Compounds with Amino Acids and Proteins . . |
|
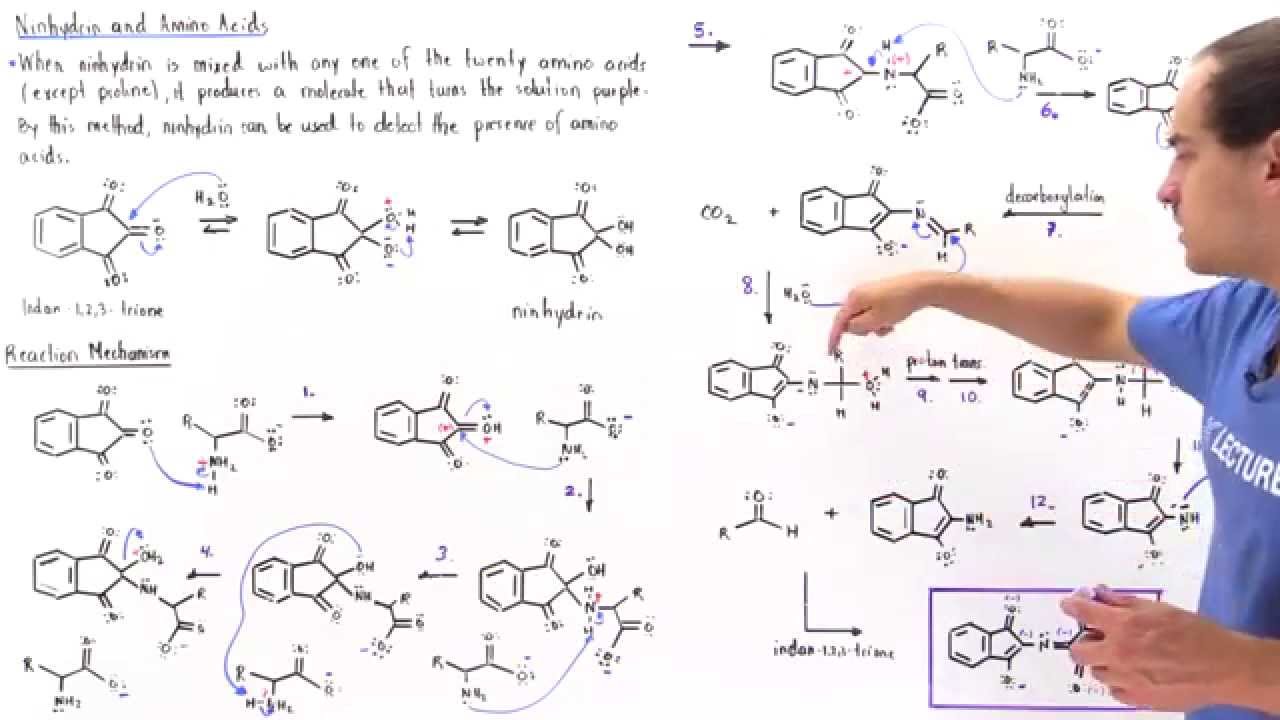
Mechanism of the ninhydrin reaction
a Schiffs base with the amino acid (I) The ketimine formed. (reaction a) undergoes decarboxylation yielding the aldehyde and an intermediate amine |
|
The Reaction of Aminonitriles with Aminothiols: A Way to Thiol
19 Oct 2018 In ribosomes peptide bonds are formed by the reaction of the amine group of an amino acid with an ester function. |
|
THE NINHYDRIN REACTION WITH AMINES AND AMIDES
ined and discussed the interaction of amino-acids and ammonium salts with triketohydrindene hydrate (ninhydrin). They showed that the ninhydrin reaction |
|
Novel Enzymatic Method for Imine Synthesis via the Oxidation of
4 May 2022 of Primary Amines Using D-Amino Acid Oxidase from ... synthesis of PPEA and the reaction mechanism were investigated using the pkDAO variant ... |
|
Reaction of amines and amino acids with aqueous and nonaqueous
Under anhydrous conditions, ninhydrin in glacial acetic acid reacts with a number of amino acids, as well as amines and imino acids, to produce discernible colors Hence, the reagent cannot be considered specific for imino acids under such circumstances |
|
CARBONYL-AMINE REACTIONS IN PROTEIN - ScienceDirect
Reaction of Carbonyl Compounds with Amino Acids and Proteins 156 carbonyl-amine reaction in protein chemistry, however, has been recognized only |
|
N-Silylation of amines and amino acid esters under neutral - CORE
BSA, is useful for the conversion of amines or amino acid esters to the corresponding silyl derivatives, reactions including racemization in peptide synthesis 9 |