covid 19 mutated into 30 strains
Viruses constantly change through mutation and sometimes these mutations result in a new variant of the virus.
Some changes and mutations allow the virus to spread more easily or make it resistant to treatments or vaccines.
As the virus spreads, it may change and become harder to stop.
How does COVID create new variants?
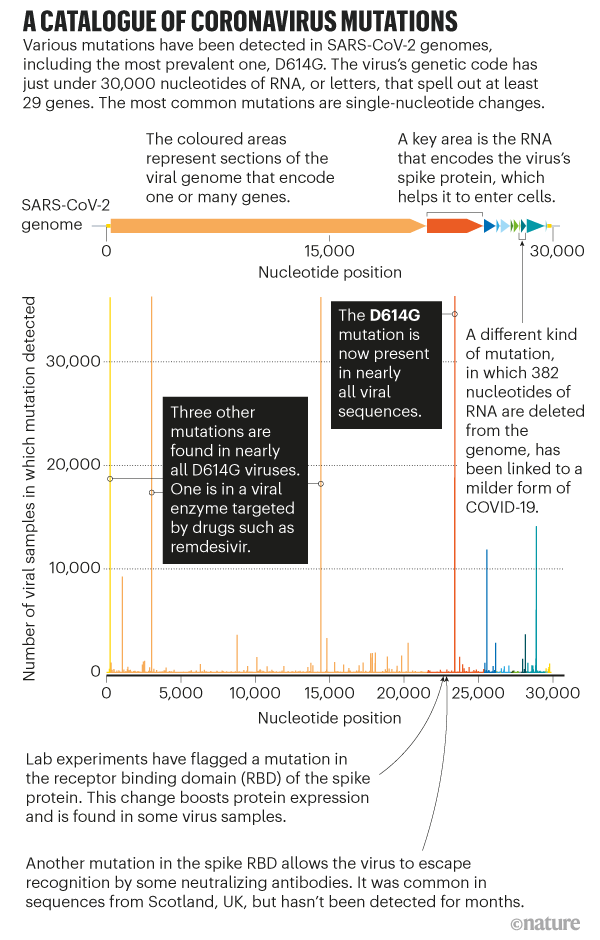
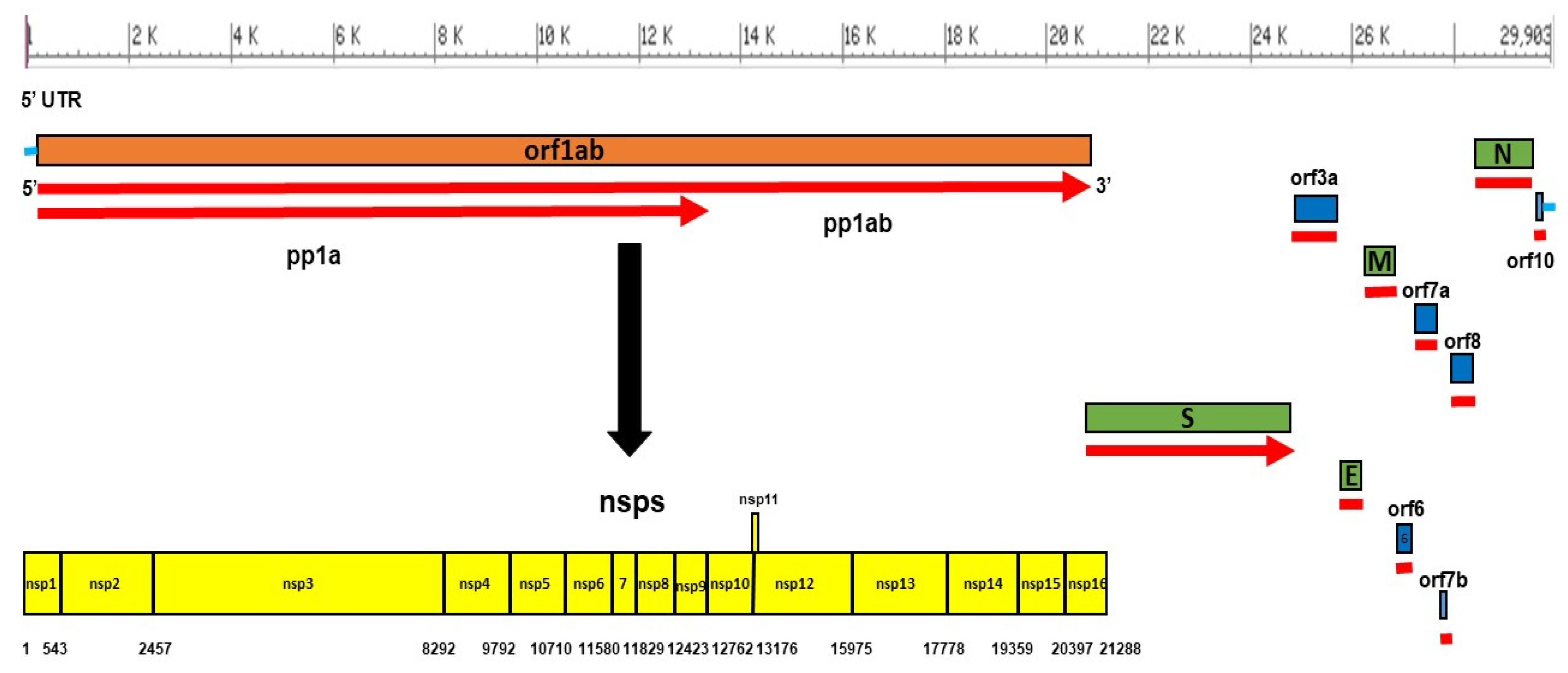
Coronaviruses like SARS-CoV-2—the virus responsible for COVID-19—use RNA to store their genetic information, and copying RNA is more prone to mistakes than copying DNA.
Researchers have shown that when a coronavirus replicates, around 3 percent of its copies contain a new random error, also known as a mutation.
What were the COVID mutations?
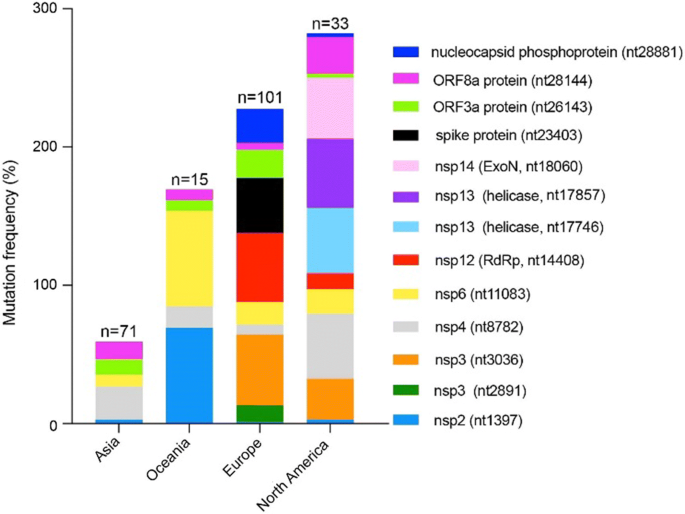
From the genetic sequencing of many virus samples from infected individuals discovered that Gamma variant has accumulated over 22 mutations with about 12 mutations on spike protein.
RBD mutations include: L18F, N501Y, E484K and K 417T.
NTD mutations are also discovered in gamma variant.
What's the new strain of Covid called?
Most recently a strain called JN.1 moved swiftly to become the most widely circulating variant in the United States, accounting for an estimated 83% to 88% of all circulating variants toward the end of January.
|
Genome-wide analysis of SARS-CoV-2 virus strains circulating
RNA virus is responsible for the present devastating COVID?19 pandemic. significant mutation at position 378 was not found in other virus strains ... |
|
Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee June
28 juin 2022 SARS-CoV-2 strain composition of COVID-19 vaccines ... the Omicron S protein has more than 30 mutations 15 of which are in the spike. |
|
Virus strain from a mild COVID-19 patient in Hangzhou represents a
8 juin 2020 For mechanisms exploration we isolated one strain of SARS-CoV-2 (ZJ01) from a mild COVID-19 patient. Thirty-five specific gene mutations were ... |
|
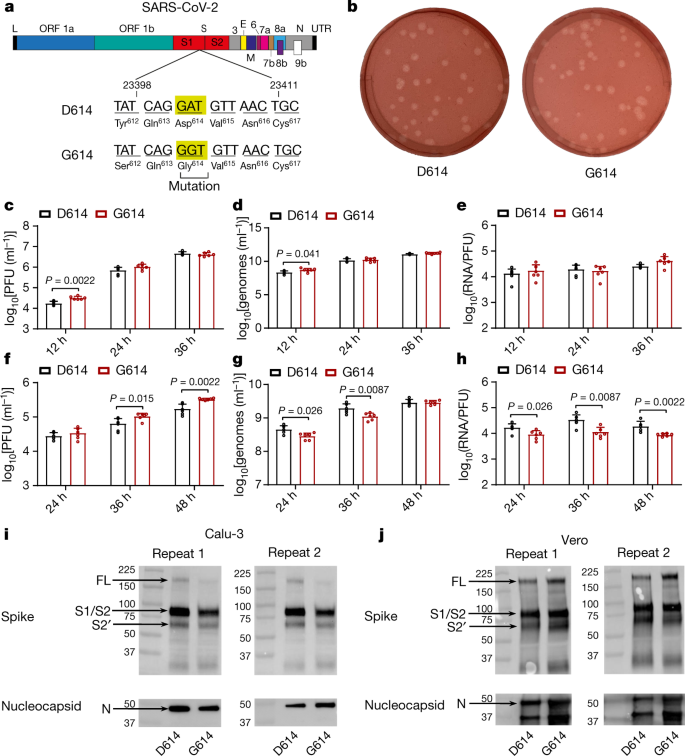
On the Modeling of COVID-19 Transmission Dynamics with Two
21 juin 2022 Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious illness caused by ... The D614G strains is an amino acid mutation in position 614 that ... |
|
On the Modeling of COVID-19 Transmission Dynamics with Two
21 juin 2022 Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious illness caused by ... The D614G strains is an amino acid mutation in position 614 that ... |
|
Arrival and Dissemination of Omicron Lineage SARS-CoV-2 in St
20 août 2022 All COVID-19 positive samples from arrivals at Pulkovo Airport with ... In addition to 30 known S gene SNPs [25] solitary mutations were ... |
|
Variant Analysis and Strategic Clustering to Sub-Lineage of Double
20 avr. 2022 In January 2021 the re-occurrence of COVID-19 infection was at its ... studies reported that two major mutations observed in this strain ... |
|
Mutations and Evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein
19 mars 2022 the viral infection that leads to various levels of COVID-19 severities. ... mutations on the spike protein that occur within these strains ... |
|
COVID-19 Situation Thailand
23 févr. 2022 The Omicron VoC that is now the dominant strain both in Thailand as well as globally currently has several mutations of public health ... |
|
Quantum Deep Learning for Mutant COVID-19 Strain Prediction
4 mars 2022 COVID-19 epidemic strains like Delta and Omicron in order to take action ... from May 30 to June 29 in 2021 to derive 734 mutated SARS-CoV-2 ... |
|
Genome-wide analysis of SARS-CoV-2 virus strains - Nature
RNA virus, is responsible for the present devastating COVID‑19 pandemic SARS‑CoV‑2 strains reported from across the globe to the GISAID database up to 30 March significant mutation at position 378 was not found in other virus strains |
|
Spike mutation pipeline reveals the emergence of a more - bioRxiv
#Members of Sheffield COVID-19 Genomics Group: Adrienne Angyal, Rebecca L Brown, Laura Carrilero, Luke R Green, locally circulating strains, indicative of multiple strain infections this version posted April 30, 2020 binding and entry into host cells and is a major target of neutralizing antibodies (Chen et al , |
|
Risk related to spread of new SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern in
29 déc 2020 · or combinations of mutations may provide the virus with a selective advantage, such as increased The United Kingdom (UK) has faced a rapid increase in COVID-19 The probability of increased circulation of any SARS-CoV-2 strains detected in Finland in a returning traveller from South Africa [30] |
|
Rapid increase of a SARS-CoV-2 variant with multiple spike protein
19 déc 2020 · The reported COVID-19 cases related to the VUI 202012/01 variant are original Wuhan strain, which is higher than current molecular clock infection can lead to accumulation of immune escape mutations at an elevated rate severity was detected in Singapore in the spring and then disappeared [30] |
|
Tracking Changes in SARS-CoV-2 Spike: Evidence that - Cell Press
sion, SARS-CoV-2 could also acquire mutations with fitness ad- vantages and COVID-19 disease at the Sheffield Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust |
|
The Impact of Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Spike on Viral Infectivity
Finally, we determined the sensitivity of the strains with amino acid changes to ten COVID-19 convalescent sera (see STAR Methods) None of the variants and |
|
Virus strain of a mild COVID-19 patient in Hangzhou - medRxiv
13 mar 2020 · The subtypes of COVID-19 were categorized into mild, reproduced in less than 30 bootstrap replicates were collapsed The mutations of ZJ01 when comparing with other strains of SARS- CoV-2 by sequence alignment |
|
Genome-wide variations of SARS-CoV-2 infer evolution - medRxiv
3 mai 2020 · in group B, of which 30 strains were from European and American mutated at the end of January, 10 strains were mutated in February, and the 145 Since the outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan in December 2019, it has |