enzyme exemple
|
Enzymes: principles and biotechnological applications
enzyme that is commonly encountered in first-year laboratory sessions on enzyme kinetics) can remove a phosphate group from a variety of substrates Other enzymes demonstrate much higher specificity which is described as absolute speci-ficity For example glucose oxidase shows almost total specificity for its substrate β-D-glucose |
|
Six Major Classes of Enzymes and Examples of Their Subclasses
Shared properties with chemical catalysts Enzymes are neither consumed nor produced during the course of a reaction Enzymes do not cause reactions to take place but they greatly enhance the rate of reactions that would proceed much slower in their absence They alter the rate but not the equilibrium constants of reactions that they catalyze Diff |
What are the basic functions of enzymes?
Enzymes usually function within a moderate pH and temperature range. Enzymes execute of two basic functions in biological object. They are catalytic and regulation. Most enzyme-catalyzed reactions are highly efficient, proceeding from 103 to 108 times faster than uncatalyzed reactions.
What is the simplest model to represent how an enzyme works?
This is the simplest model to represent how an enzyme works. The substrate simply fits into the active site to form a reaction intermediate. In this model the enzyme molecule changes shape as the substrate molecules gets close. The change in shape is 'induced' by the approaching substrate molecule.
What is enzyme specificity?
Enzyme specificity is the absolute specificity of protein catalysts to identify and bind to only one or a few molecules. In this process the enzyme carries a defined arrangement of atoms in their active site to bind with the substrate. This active site on the enzyme should have a shape that accurately matches the substrates.
What is an example of an enzyme name?
Most commonly used enzyme names have the suffix "-ase" attached to the substrate of the reaction, for example, glucosidase, urease, sucrase; or to a description of the action performed, for example, lactate dehydrogenase and adenylate cyclase.
Biologic catalysts
Shared properties with chemical catalysts Enzymes are neither consumed nor produced during the course of a reaction. Enzymes do not cause reactions to take place, but they greatly enhance the rate of reactions that would proceed much slower in their absence. They alter the rate but not the equilibrium constants of reactions that they catalyze. Diff
Regulation
Enzyme activity can be regulated — that is, enzymes can be activated or inhibited so that the rate of product formation responds to the needs of the cell. attic.volgmed.ru
Enzyme classification
Enzymes are divided into six major classes with several subclasses. Oxidoreductases are involved in oxidation and reduction. Transferases transfer functional groups (e.g., amino or phosphate groups). Hydrolases transfer water; that is, they catalyze the hydrolysis of a substrate. Lyases add (or remove) the elements of water, ammonia, or car
NOMENCLATURE_OF ENZYMES
Each enzyme is assigned two names. The first is its short, recommended name, convenient for everyday use. The second is the more complete systematic name, which is used when the enzyme must be identified without ambiguity. attic.volgmed.ru
A. Recommended name
Most commonly used enzyme names have the suffix "-ase" attached to the substrate of the reaction, for example, glucosidase, urease, sucrase; or to a description of the action performed, for example, lactate dehydrogenase and adenylate cyclase. [Note: Some enzymes retain their original trivial names, which give no hint of the associated enzymic reac
Enzyme structure
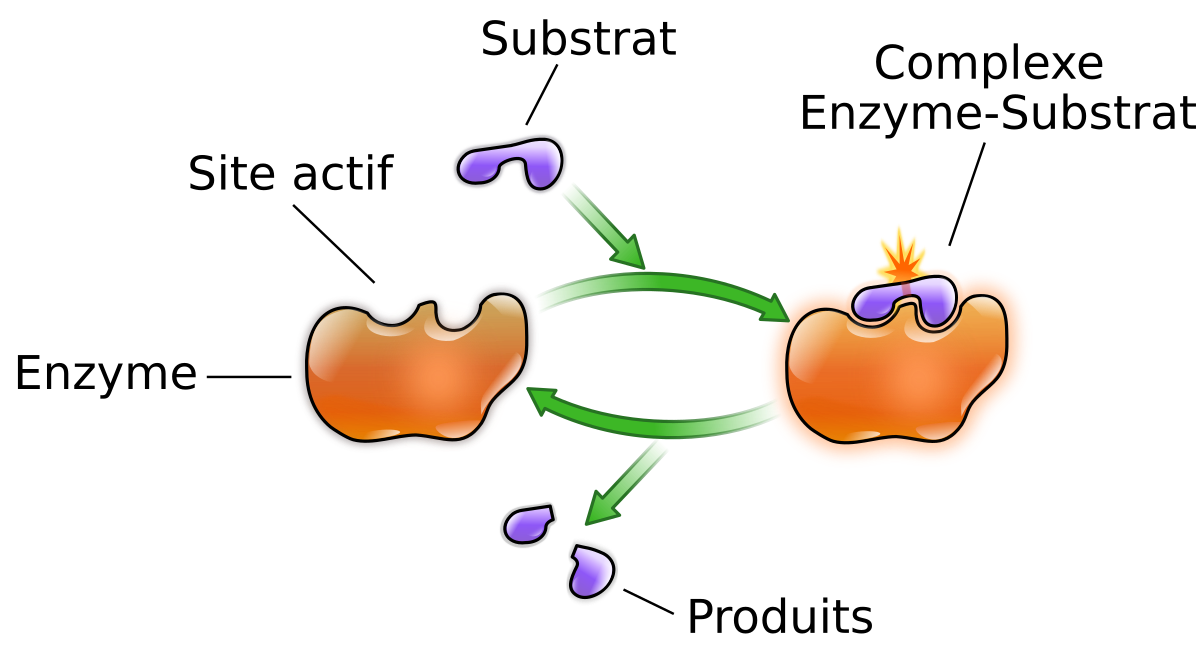
Active sites Enzyme molecules contain a special pocket or cleft called the active site. The active site contains amino acid side chains that create a three-dimensional surface complementary to the substrate. The active site binds the substrate, forming an enzyme-substrate (ES) complex. ES is converted to enzyme-product (EP), which subsequently di
Specificity
The specificity of an enzyme is determined by the functional groups of the substrate, the functional groups of the enzyme, and the physical proximity of these functional groups. Two theories have been proposed to explain the specificity of enzyme action. Lock and key theory. The enzyme active site is complementary in conformation to the substrate
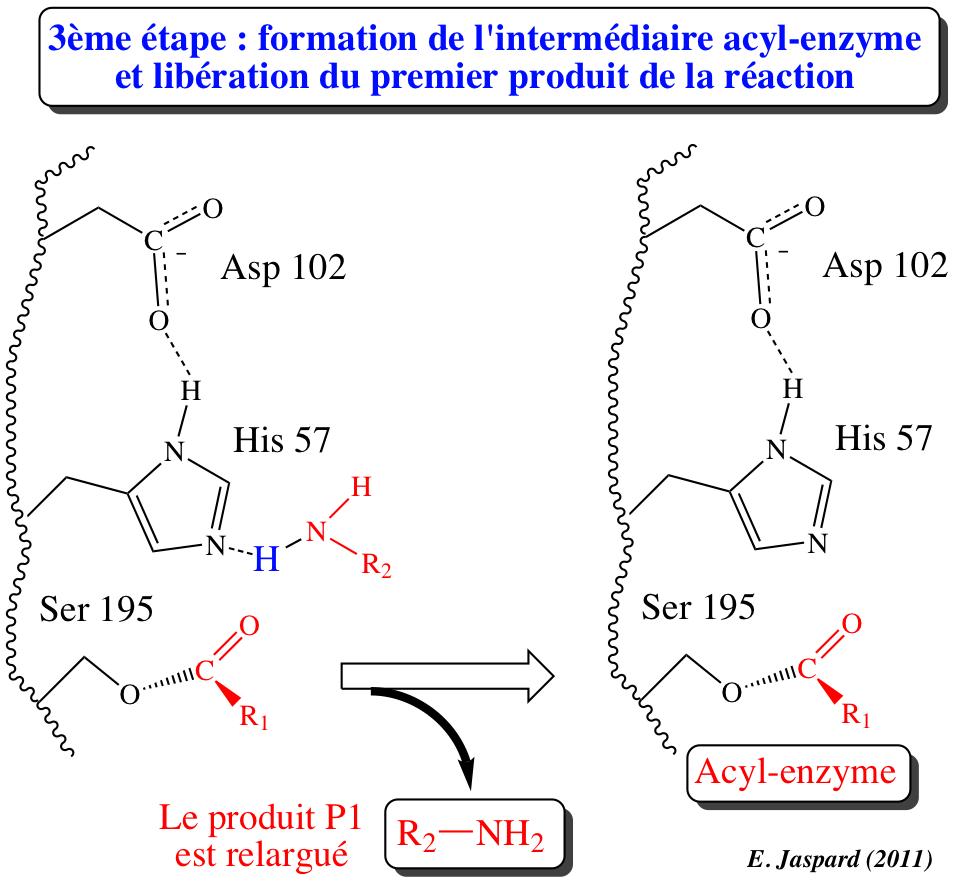
CATALYTIC MECHANISM OF CHYMOTRYPSIN
Chymotrypsin hydrolyzes specific peptide bonds of denatured proteins. Proteolysis in the absence of chymotrypsin. The scissile bond is shown in blue. The carbonyl carbon, which carries a partial positive charge, is attacked by a hydroxyl group from water. An unstable tetrahedral oxyanion intermediate is formed, which is the transition state c
Some General Strategies of Enzymatic Catalysis
Proximity and orientation Transition state stabilization Acid-base catalysis Nucleophilic catalysis Electrophilic catalysis Covalent catalysis attic.volgmed.ru
The functional group of thiamine pyrophosphate
(shown in blue) participates in formation of a covalent intermediate. base on the enzyme (B:) abstracts a proton from thiamine, creating a carbanion (general acid-base catalysis). The carbanion is a strong nucle-ophile, and attacks the positively charged keto group on the substrate. A covalent intermediate is formed, which is stabilized by re

Six types of enzymes Chemical Processes MCAT Khan Academy

Enzymes

Enzymes
|
Les enzymes sont des protéines douées dune activité biologique
Exemple l'hydrolyse du saccharose : Saccharose + H2O – ? fructosidase ? Glucose + fructose. SUBSTRATS. PRODUITS. Sans enzyme |
|
Les enzymes : Applications industrielles et analytiques
Par exemple la figure 1 montre une enzyme |
|
Corrigé
La vitesse initiale d'une réaction enzymatique fournit une mesure de exemple : l'enzyme glucose oxydase et ses substrats : le glucose et le dioxygène. |
|
6-Activité enzymatique (Biochimistes).pdf
la valeur maximale de l'activité de certaines enzymes peut être très loin du pH physiologique. - par exemple la phosphatase alcaline possède une activité |
|
Les enzymes allostériques
— Chaque molécule de substrat qui se lie augmente la probabilité de transition de la forme inactive à la forme active. 2. Modèle séquentiel: Koshland (1966):. |
|
Chapitre 2 : Structure et différentes formes des enzymes Introduction
Exemple: la ?-galactosidase d'E. Coli qui hydrolyse le lactose est une enzyme de diagnostic médicalutilisée dans la détection des bactéries coliformes |
|
La formation du miel un exemple de catalyses enzymatiques
Grâce à l'action de 2 enzymes produites par les cellules de l'abeille l'invertase et la glucose oxydase |
|
Enzymes
Pour comprendre comment les enzymes peuvent être spécifiques nous examinons la et le de la fonction enzymatique. substrat structure de l'enzyme modèle clé- |
|
Le mariage réussi du plastique et des enzymes
par exemple le fameux « 7e continent » de plastique. (Figure 3). L'innovation de Carbios. (Figure 1) est basée sur une technologie enzymatique. |
|
Les enzymes
Les enzymes sont des protéines douées d'une activité biologique Exemple : la dégradation du glucose substrat fondamental des cellules vivantes |
|
Généralités sur les enzymes 1 Les enzymes sont des protéines
Exemples : la trypsine possède une activité protéolytique et une activité estérasique mais ces réactions font appel à un mécanisme identique (hydrolyse d'une |
|
4-Enzymespdf
?Les enzymes sont en général des protéines globulaires ?Le site actif (modèle clé-serrure) est formé d'un site de fixation et d'un site catalytique : |
|
M1 Chimie des biomolécules (2021) Cinétique enzymatique
Les enzymes sont des protéines qui catalysent des réactions chimiques La cinétique enzyma- tique a le même objectif que la cinétique chimique : obtenir des |
|
Cours enzymologiepdf
Ces enzymes qui hydrolysent (par addition d'une molécule d'eau) différentes liaisons chimiques Exemples : les phosphatases les peptidases (ex: |
|
Quelques enzymes végétales à potentiel antimicrobien - Érudit
électrophorétiques de certaines enzymes à potentiel antimicrobien Ces gnons (les Zygomycètes par exemple) cée comme substrat modèle des IS-13- |
|
NOMENCLATURE DES ENZYMES ET TYPES DE REACTIONS
Ø d'abord le nom du substrat Ø puis le type de réaction catalysée Ø on ajoute enfin le suffixe ase Par exemple : - glucose-6-phosphate isomérase - |
|
Chapitre I : Les enzymes ; Notions Générales
Exemple : La phosphoglucomutase est une enzyme de la glycogénogenèse qui catalyse la réaction: glucose-6-phosphate en glucose-1-phosphate comme toutes les |
|
Les enzymes : Applications industrielles et analytiques - Megazyme
Par exemple la figure 1 montre une enzyme la pectinase en tout début de catalyse au moment où le substrat le pectate (en jaune) sLest diffusé dans le |
|
Les enzymes allostériques - Faculté de Médecine dOran
— Chaque molécule de substrat qui se lie augmente la probabilité de transition de la forme inactive à la forme active 2 Modèle séquentiel: Koshland (1966): |
| Enzyme - Magadh University |
| Enzymes and Their Functions - Cornell University |
| Enzymes and Their Functions - Cornell University |
| Enzyme final lab - University of Pennsylvania |
| Enzymes and Their Functions - Cornell University |
| Le |
What is an example of an enzyme?
- Enzymes are generally named after the substrate affected, and their names usually end in - ase.
. For example, enzymes that break down proteins are called proteases.
. While lipases break down lipids, carbohydrases break down carbohydrates.
. The compounds that enzymes act upon are known as substrates.
Are enzymes consumed or produced during the course of a reaction?
- Enzymes are neither consumed nor produced during the course of a reaction. b.
. Enzymes do not cause reactions to take place, but they greatly enhance the rate of reactions that would proceed much slower in their absence.
. They alter the rate but not the equilibrium constants of reactions that they catalyze.
What is a conjugated enzyme called?
- biological active conjugated enzyme (simple enzyme + cofactor) is called a holoenzyme.
. A cofactor can be linked to the protein portion of the enzyme either covalently or non-covalently.
. Some cofactors aresimple metal ionsand othercofactors are complex organic groups, which are also calledcoenzymes.
. Cofactors
How many substrate molecules can an enzyme molecule convert into product?
- Typically, each enzyme molecule is capable of transforming 100 to 1000 substrate molecules into product each second.
. The number of molecules of substrate converted to product per enzyme molecule per second is called the turnover number.
|
Enzymologie élémentaire - CHUPS Jussieu
19 jui 2002 · 1 1 Enzyme 13 1 2 Exemple d'enzyme : l'anhydrase carbonique 15 1 3 Substrat 16 1 4 Produit 17 Chapitre 2 : La réaction enzymatique |
|
Les enzymes des biocatalyseurs - Le site Formation des Maîtres
TP n°1 (suite) Activité d'une enzyme sur différents substrats Exemple 1 On appelle substrat la molécule sur laquelle s'exerce l'action catalytique d'une enzyme |
|
Les enzymes - UNF3S
Un enzyme est une protéine qui agit comme catalyseur biochimique, un L' enzyme accélère la réaction sans modifier l'état Le modèle Michaelis et Menten |
|
Les enzymes
II-Comment expliquer les propriétés catalytiques des enzymes ? Les enzymes interviennent dans la transformation d'un substrat en produit Exemple, l' hydrolyse |
|
Enzymologie
Une enzyme accroit la vitesse d'une réaction chimique, et ne catalyse Ce modèle explique la spécificité de l'enzyme pour son substrat, mais il n'explique |
|
Structure et mécanisme daction des enzymes-BENSAAD
Enzyme : protéine présentant des propriétés de catalyse spécifique d'une réaction chimique Exemple : glucose-6-Phosphate isomérase : D-glucose-6-P |
|
Méthodes de mesure des activités enzymatiques - Remedeorg
L'activité enzymatique se mesure par la vitesse de la réaction de le tampon complexe un cation activateur de l'enzyme ; par exemple, Ca2+ des DNAses ou |