kidney failure due to primary hyperparathyroidism
Is renal calcium excretion a symptom of primary hyperparathyroidism?
Primary hyperparathyroidism: Renal calcium excretion in patients with and without renal stone disease before and after parathyroidectomy. World J Surg. 2002;26:532–5. [ PubMed] [ Google Scholar] 14.
What is primary hyperparathyroidism?
“Primary” means this disorder begins in the parathyroid glands, rather than resulting from another health problem such as kidney failure. In primary hyperparathyroidism, one or more of the parathyroid glands is overactive. As a result, the gland makes too much parathyroid hormone (PTH).
What is renal hyperparathyroidism (rhpt)?
E-mail: ude.sivadcu@bpmacjm. Renal hyperparathyroidism (rHPT) is a common complication of chronic kidney disease characterized by elevated parathyroid hormone levels secondary to derangements in the homeostasis of calcium, phosphate, and vitamin D. Patients with rHPT experience increased rates of cardiovascular problems and bone disease.
What are the complications of hyperparathyroidism?
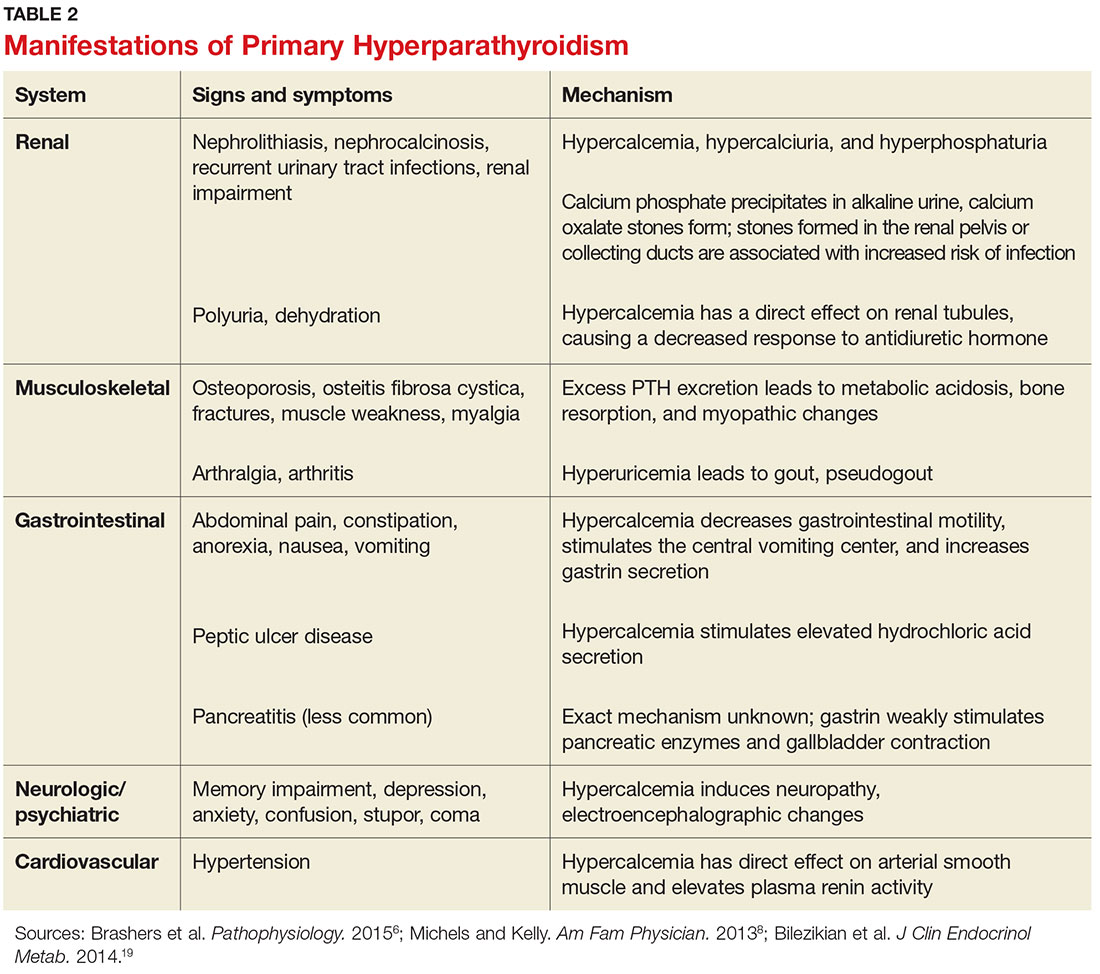
Complications of hyperparathyroidism are mainly related to the long-term effect of too little calcium in your bones and too much calcium in your bloodstream. Common complications include: Osteoporosis. The loss of calcium from bones often results in weak, brittle bones that break easily (osteoporosis). Kidney stones.
What Is Primary Hyperparathyroidism?
Primary hyperparathyroidism is a disorder of the parathyroid glands, four pea-sized glands located on or near the thyroid gland in the neck. “Primary” means this disorder begins in the parathyroid glands, rather than resulting from another health problem such as kidney failure. In primary hyperparathyroidism, one or more of the parathyroid glands i
What Do The Parathyroid Glands do?
The parathyroid glands’ only purpose is to make PTH, which helps maintain the right balance of calcium in your body. PTH raises blood calcium levels by 1. causing bone, where most of your body’s calcium is stored, to release calcium into the blood 2. helping your intestines absorb calcium from food 3. helping your kidneyshold on to calcium and retu
How Common Is Primary Hyperparathyroidism?
In the United States, about 100,000 people develop primary hyperparathyroidism each year.1Primary hyperparathyroidism is one of the most common hormonal disorders. niddk.nih.gov
Who Is More Likely to Develop Primary Hyperparathyroidism?
Primary hyperparathyroidism most often affects people between age 50 and 60. Women are affected 3 to 4 times more often than men.1 The disorder was more common in African Americans, followed by Caucasians, in one large study performed in North America.1 niddk.nih.gov
What Are The Complications of Primary Hyperparathyroidism?
Primary hyperparathyroidism most often affects the bones and kidneys, although it also may play a part in other health problems. niddk.nih.gov
What Are The Symptoms of Primary Hyperparathyroidism?
Most people with primary hyperparathyroidism have no symptoms. When symptoms appear, they’re often mild and similar to those of many other disorders. Symptoms include 1. muscle weakness 2. fatigue 3. depression NIH external link 4. aches and pains in bones and joints View full-sized imageSymptoms of primary hyperparathyroidism People with more seve
What Causes Primary Hyperparathyroidism?
In about 8 out of 10 people with primary hyperparathyroidism, a benign, or noncancerous, tumor called an adenoma has formed in one of the parathyroid glands.2 The tumor causes the gland to become overactive. In most other cases, extra PTH comes from two or more adenomas or from hyperplasia, a condition in which all four parathyroid glands are enlar
How Do Doctors Diagnose Primary Hyperparathyroidism?
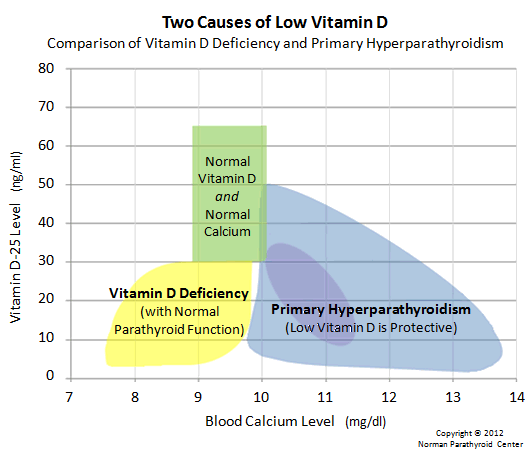
Doctors diagnose primary hyperparathyroidism when a blood test shows high blood calcium and PTH levels. Sometimes PTH levels are in the upper portion of the normal range, when they should drop to low-normal or below normal in response to high calcium levels. Other conditions can cause high calcium, but elevated PTH is the only source in primary hyp
How Do Doctors Treat Primary Hyperparathyroidism?
Guidelines help doctors to decide whether or not parathyroid surgery should be recommended. You might be a candidate for surgery if you meet any of these guidelines 1. Blood calcium > 1 mg/dL above normal 2. Bone density by DXA < -2.5 at any site (lumbar spine, hip, or forearm) 3. History of kidney stones or evidence of kidney stones or calcificati
Should I Change My Diet If I Have Primary Hyperparathyroidism?
You don’t need to change your diet or limit the amount of calcium you get from food and beverages. You will need to take a vitamin D supplement if your vitamin D levels are low. Talk with your health care professional about how much vitamin D you should take. If you lose all your healthy parathyroid tissue and develop lasting low-calcium levels, yo
|
Primary hyperparathyroidism and kidney; recent findings
Patients with chronic renal failure may find secondary hyperparathyroidism Development of kidney failure in primary hyperparathyroidism was related to. |
|
Primary hyperparathyroidism and familial hyperparathyroid syndromes
with osteoporosis renal and metabolic disorders. It frequently low serum phosphate due to renal ... because primary hyperparathyroidism often requires. |
|
Does renal function improve after parathyroidectomy in primary
5 avr. 2019 Introduction: Primary hyperparathyroidism (PHPT) is a common endocrine disorder charac- terised by hypercalcaemia and parathormone increase. |
|
Understanding Hyperparathyroidism in Renal Disease
secondary.8 The former is commonly due to an adenoma or hyperplasia of one or more of the four glands. In rare cases primary hyperparathyroidism can be |
|
Predictors of Renal Function in Primary Hyperparathyroidism
14 févr. 2014 Primary hyperparathyroidism (PHPT) characterized by hypercalcemia and elevated PTH |
|
Primary Hyperparathyroidism
Secondary or reactive |
|
Article
11 nov. 2020 Concomitant primary hyperparathyroidism and systemic lupus ... due to secondary or tertiary hyperparathyroidism due to chronic renal failure. |
|
Basic and clinical aspects of parathyroid hyperplasia in chronic
Secondary hyperparathyroidism is one of the most popular and important abnormalities of mineral metabolism in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD).1 |
|
Distal renal tubular acidosis in primary hyperparathyroidism
29 janv. 2015 Renal tubular dysfunction due to significant hypercalciuria appears to be one of the proposed mechanisms. This case report will highlight a case ... |
|
Article
11 nov. 2020 Concomitant primary hyperparathyroidism and systemic lupus ... due to secondary or tertiary hyperparathyroidism due to chronic renal failure. |









![PDF] Primary hyperparathyroidism and familial hyperparathyroid PDF] Primary hyperparathyroidism and familial hyperparathyroid](https://i1.rgstatic.net/publication/51484460_Primary_Hyperparathyroidism_An_Overview/links/55d8992308ae9d65948f928c/largepreview.png)




![Full text] Management and outcomes of hyperparathyroidism: a case Full text] Management and outcomes of hyperparathyroidism: a case](https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/multimedia/S2173574311000797:gr1.jpeg?xkr\u003due/ImdikoIMrsJoerZ+w9184xd8ym1IgxXJ6I4p31f1upH6Ra9/FExf9t4wRA9EIUj/ul6vGgHA8hYkucearNuu1f9o4SaxZv4gRGhqcFHbFHaLd99Ho4RC5EhQ9FzAp9b8fedOlYzpWTzWXFXH5txKHhHRBi0y2VZ/ZoTa/UzxFbYz2Wb7x33S3xINUb/I8JojAM/IbdGtvHi5Bg4wCt8X9zO4N5vr2Gp2WzCRCf+O0TsYmAY2MLqFm45X7HIeRLCZpL9exGLpP7S1dFBeKYZts0oj9Y9J1b0/kwFoY0L4\u003d)