cp et cv definition
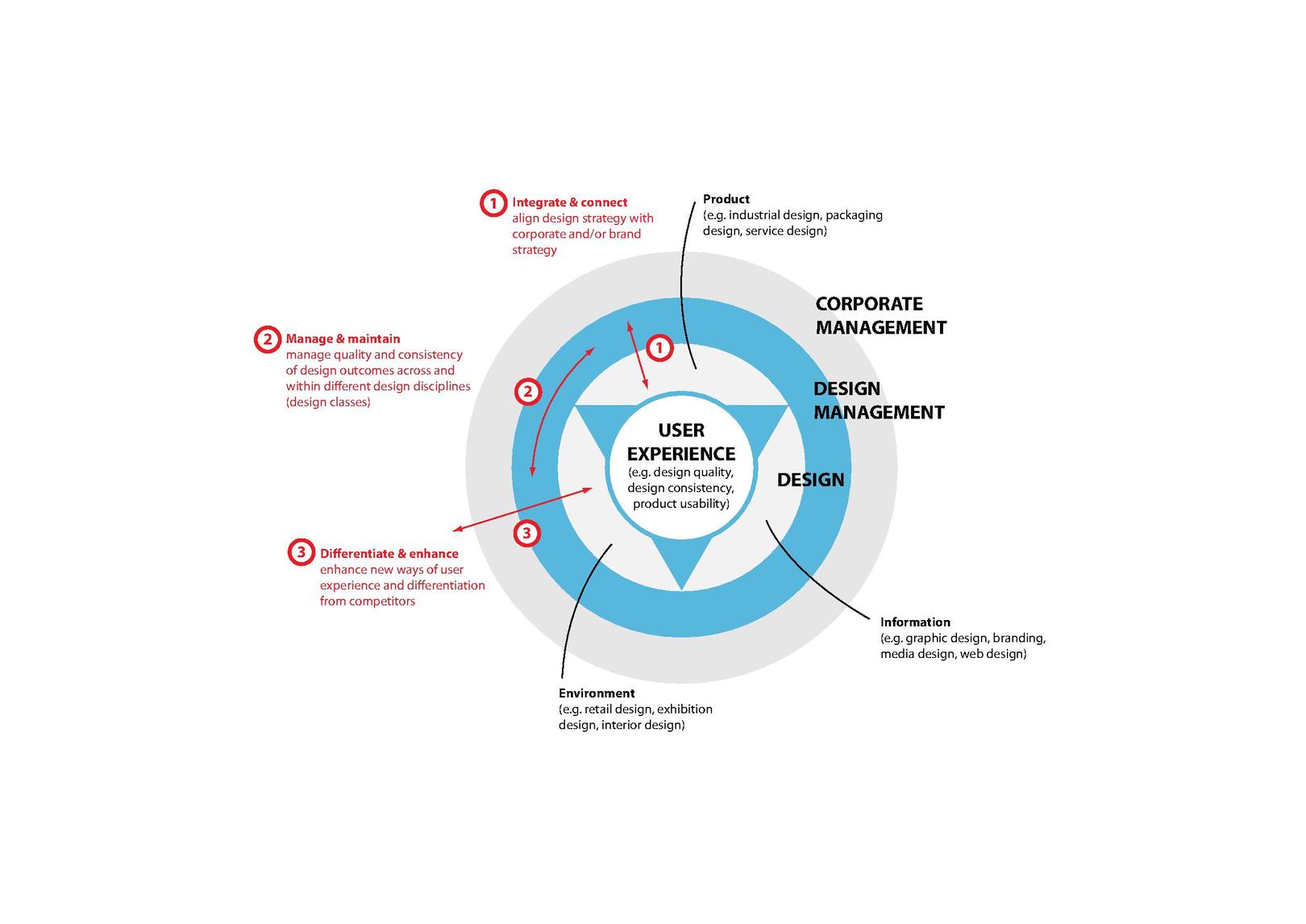
|
A note on the variation of specific heats in ideal gases
A note on the variation of specific heats in ideal gases Most diatomic gases such as nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2) at or near room temperature have specific heats (cv and cp) that are almost constant However as the temperature (T) rises above about 700 K the specific heat begins to rise Because the relation remains valid where R is the |
|
Chemical Thermodynamics Survival Kit
The quantity C Pm is a temperature-dependent quantity for most real (i e nonideal) gases and a number of liquids and solids It is usually expressed in the form C Pm 2 = d + eT + fT (12) where the constants a b and c have been tabulated for most substances |
|
Difference in Cp and Cv
Difference in Cp and Cv From the definitions of Cp and Cv PV dq dq Cp Cv dT dT −=− (1) Substitution of the definition of entropy gives PV SS Cp Cv T TT ⎡⎤∂∂ −=⎢− ⎣⎦∂∂ ⎥ (2) These partials are converted from the total differential obtained from Sf= (TV) VT SS dS dT dV TV ∂∂ =+ ∂∂ which when divided by dT at |
|
Specific heat capacities of gases (Cp & Cv) and
Definition : the specific heat of material is defined as the quantity of heat required to raise temperature of unit mass of the material through 1 degree Unit: In C G S calories per gram per ???? In S I it is Joules per Kg per ???? ????= ????∙θ (or) |
|
Thermodynamics GENERAL
i cp = Cp/m ii cv = Cv/m c The heat capacity of a substance depends on how the substance is heated c At constant volume as heat is acquired heat capacity Cv is i dV = 0 ii dq = du iii cv = dq/dT = du/dT iv dq = cvdT + dw: First Law d At constant pressure as heat is acquired heat capacity Cp is i cp = dq/dT ii dq = cvdT + pdα |
C'est quoi CP et Cv ?
On constate que l'eau a une capacité calorifique qui est le double de celle de la plupart des corps.
Pour les gaz, suivant que l'échauffement est réalisé à pression constante ou à volume constant on parle de Cp ou Cv, il s'agit de la capacité calorifique molaire (l'unité est le J. mol-1.Comment calculer CP et Cv ?
cv = du/dT (J/kg/K) cp = dh/dT (J/kg/K)
C'est quoi le CP de l'eau ?
Capacité calorifique massique :
Toujours à 25°C, pour l'eau liquide, la capacité calorifique massique vaudra 4180 J. kg -1.
K -1 ou 4,18 J.g -1.
K -1.- air : 1,256 kJ m−3 K.
H = E + p * V
where h in the specific enthalpy, p is the pressure, v is the specific volume, and e is the specific internal energy. During a process, the values of these variables will change. Let’s denote the change by the Greek letter delta (which looks like a triangle). So “delta h” means the change of “h” from state 1 to state 2 during a process. Then, for a
Delta H = Delta E + p * Delta V
The enthalpy, internal energy, and volume are all changed, but the pressure remains the same. From our derivation of the enthalpy equation, the change of specific enthalpy is equal to the heat transfer for a constant pressure process: www1.grc.nasa.gov
Delta H = CP * Delta T
where delta T is the change of temperature of the gas during the process, and cis the specific heat capacity. We have added a subscript “p” to the specific heat capacity to remind us that this value only applies to a constant pressure process. The equation of state of a gas relates the temperature, pressure, and volume through a gas constant R . Th
p * Delta V = R * Delta T
Now let us imagine that we have a constant volume processwith our gas that produces exactly the same temperature change as the constant pressure process that we have been discussing. Then the first law thermodynamics tells us: www1.grc.nasa.gov
Delta E = Delta Q – Delta W
where q is the specific heat transfer and wis the work done by the gas. For a constant volume process, the work is equal to zero. And we can express the heat transfer as a constant times the change in temperature. This gives: www1.grc.nasa.gov
Delta E = Cv * Delta T
where delta T is the change of temperature of the gas during the process,and cis the specific heat capacity. We have added a subscript “v” to the specific heat capacity to remind us that this value only applies to a constant volume process. Even though the temperature change is the same for this process and the constant pressure process, the value
CP = Cv + R
The specific heat constants for constant pressure and constant volume processes are related to the gas constant for a given gas. This rather remarkable result has been derived from thermodynamic relations, which are based on observations of physical systems and processes. In the kinetic theory of gases, this result is derived from considerations of
Gamma = CP / Cv
“Gamma” is just a number whose value depends on the state of the gas. For air, gamma = 1.4 for standard day conditions. “Gamma” appears in several equations which relate pressure, temperature, and volume during a simple compression or expansion process. Because the value of “gamma” just depends on the state of the gas, there are tables of these val
H = E + p * V
where h in the specific enthalpy, p is the pressure, v is the specific volume, and e is the specific internal energy. During a process, the values of these variables will change. Let’s denote the change by the Greek letter delta (which looks like a triangle). So “delta h” means the change of “h” from state 1 to state 2 during a process. Then, for a
Delta H = Delta E + p * Delta V
The enthalpy, internal energy, and volume are all changed, but the pressure remains the same. From our derivation of the enthalpy equation, the change of specific enthalpy is equal to the heat transfer for a constant pressure process: www1.grc.nasa.gov
Delta H = CP * Delta T
where delta T is the change of temperature of the gas during the process, and cis the specific heat capacity. We have added a subscript “p” to the specific heat capacity to remind us that this value only applies to a constant pressure process. The equation of state of a gas relates the temperature, pressure, and volume through a gas constant R . Th
p * Delta V = R * Delta T
Now let us imagine that we have a constant volume processwith our gas that produces exactly the same temperature change as the constant pressure process that we have been discussing. Then the first law thermodynamics tells us: www1.grc.nasa.gov
Delta E = Delta Q – Delta W
where q is the specific heat transfer and wis the work done by the gas. For a constant volume process, the work is equal to zero. And we can express the heat transfer as a constant times the change in temperature. This gives: www1.grc.nasa.gov
Delta E = Cv * Delta T
where delta T is the change of temperature of the gas during the process,and cis the specific heat capacity. We have added a subscript “v” to the specific heat capacity to remind us that this value only applies to a constant volume process. Even though the temperature change is the same for this process and the constant pressure process, the value
CP = Cv + R
The specific heat constants for constant pressure and constant volume processes are related to the gas constant for a given gas. This rather remarkable result has been derived from thermodynamic relations, which are based on observations of physical systems and processes. In the kinetic theory of gases, this result is derived from considerations of
Gamma = CP / Cv
“Gamma” is just a number whose value depends on the state of the gas. For air, gamma = 1.4 for standard day conditions. “Gamma” appears in several equations which relate pressure, temperature, and volume during a simple compression or expansion process. Because the value of “gamma” just depends on the state of the gas, there are tables of these val
|
Premier et Second Principes
d'enthalpie dh par unité de masse sont (par définition des capacité calorifiques connues et ta- bulées) : de = cv(T)dT et dh = cp(T)dT. |
|
Reaction chimique - Thermodynamique - Cinétique
standard c'est-à-dire sous 0. P . 2. Exemples. Capacité calorifique molaire standard. - Définition : 0. 0. 0. 0 m m. Cp. nCp et Cv. |
|
Résumé de la thermodynamique
15 févr. 2012 Par la définition de ? et le fait que CP ? CV = nR CV = nR/(? ? 1). La température c 2012 Richard MacKenzie ... |
|
NOTES DE COURS DE THERMODYNAMIQUE Nicolas Pavloff
leur cursus vérifier une formule ou la définition précise d'un concept En définissant ? = CP /CV cela donne (toujours pour un gaz parfait). CV =. |
|
Difference in Cp and Cv
Difference in Cp and Cv. From the definitions of Cp and . Cv. P. V dq dq. Cp Cv. dT. dT. ?. = ?. (1). Substitution of the definition of entropy gives. |
|
Chapitre 3 LES GAZ PARFAITS : EXEMPLES DE CALCULS DE
R est la constante des gaz parfaits Cv et Cp sont les chaleur spécifiques molaires à T |
|
Transformation adiabatique dun gaz parfait
Transformation adiabatique : d´emonstration (suite). Remplac¸ant et simplifiant par R on obtient : CP P dV + CV V dP = 0. Divisons les 2 membres par CV V P |
|
CP ?CV = nR.
It follows that for an isothermal process involving an ideal gas ?U = 0. Another state property of interest to us is the enthalpy of the system |
|
Lecture 9: Relationships between properties
17 oct. 2019 ? is small except for gases so CP ? CV . So for solids and liquids we often (lazily) just give “heat capacity”. Graeme Ackland. Lecture 9 ... |
|
PROBL`EMES DE THERMODYNAMIQUE (L3) et leurs corrigés
1?) Donner les définitions de CvCp |
|
Premier et Second Principes
On écrira que l'énergie interne e et l'enthalpie h par unité de masse sont pour un gaz parfait e = cvT et h = cpT avec cp/cv = ? cp = ?r ? ? 1 cv = r ? ? |
|
LA THERMODYNAMIQUE
il faut avoir recours au concept de la capacit´e calorifique molaire CV CP qui se d´efinit comme la chaleur requise pour ´elever de 1 |
|
Gaz parfaits et idéaux
On appelle gaz parfait un gaz idéal dont les capacités thermiques massiques cp et cv sont constantes Pour un tel gaz l'énergie interne et l'enthalpie sont des |
|
Chapitre 3 LES GAZ PARFAITS : EXEMPLES DE CALCULS DE
On pose la définition de ? ? := Cp Cv Le coefficient ? est une caractéristique du gaz parfait considéré qui dépend de son atomi- |
|
Chapitre III Gaz parfaits
Pour appliquer ces formules à une masse m de gaz parfait il suffi de multiplier Cv Cp r par m et de remplacer v par V le volume effectivement occupé par la |
|
Thermodynamique - mmelzani
Tout comme CV est utile pour calculer U Cp est utile pour calculer H On dispose de deux modèles de la matière pour faire ceci : celui du gaz parfait et celui |
|
D] Premier principe de la thermodynamique
Relation entre Cp et Cv : On pose ? = (Cp / Cv) qui est une constante • Valeurs de Cp et Cv : Définition de la capacité calorifique d'un système : |
|
Chapitre 5:
1 DEFINITIONS Une autre définition plus mathématique de ce principe : « Au cours d'une Cp - n Cv = nR ? pour 1 mole Cp - Cv = R |
|
PREMIER PRINCIPE DE LA THERMODYNAMIQUE ENERGIE
Cp : chaleur massique à pression constante Cv : chaleur massique à volume constant La quantité totale de chaleur Q1 gagnée par S1 au cours de la |
|
SPE MP Lycée DAUDET
1°) Définitions Pour un gaz parfait on a la relation de Mayer: cp†cv=R Cette définition montre comme l'entropie est reliée au «désordre» d'un |
C'est quoi CP et CV ?
Il s`agit de la quantité de chaleur à fournir à un système pour élever sa température de 1°C. On distingue Cp, capacité calorifique à pression constante et Cv, à volume constant.Quand Est-ce que CP CV ?
Cas des gaz
Pour les gaz, suivant que l'échauffement est réalisé à pression constante ou à volume constant on parle de Cp ou Cv, il s'agit de la capacité calorifique molaire (l'unité est le J. mol-1. K-1).Comment calculer CP et CV ?
On a donc :
1cv = du/dT (J/kg/K)2cp = dh/dT (J/kg/K)- Une grande capacité thermique signifie qu'une grande quantité d'énergie peut être stockée, moyennant une augmentation relativement faible de la température. La capacité thermique massique s'exprime en joules par kilogramme kelvin, de symbole J K?1 kg?1.
| Difference in Cp and Cv - showardsdsmtedu |
| Measurement of Cp/Cv for Argon Nitrogen |
| Definition: A curriculum vitae also known as a CV includes |
| Heat Capacities of Gases - Florida State University |
| Cp/Cv ratio expt - Simon Fraser University |
| Cp/Cv - documentsepflch |
|
Définition de lOMS des cas de COVID-19
7 août 2020 · Définition de l'OMS des cas de COVID-19 actualisée dans « La surveillance de la santé publique dans le contexte de la COVID-19 », publié le |
|
Définition de cas – Maladie à coronavirus (COVID-19)
Définition de cas – Maladie à coronavirus (COVID-19) Ces définitions de cas* sont à des fins de surveillance et sont à jour en date du 18 février 2021 Elles ne |
|
COVID-19 - SPLF
13 mar 2020 · Définition de cas d'infection au SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) - Mise à jour le 13/03/ 2020 Les modifications suivantes ont été apportées par rapport |
|
Définition de cas dinfection au SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)_21012021
21 jan 2021 · Toute personne, ayant ou non été en contact à risque(voir définition ci-dessous) avec un cas confirmé dans les 14 jours précédant l'apparition |
|
Proposition De Definition De Nouveaux Termes Pour Le Glossaire
11 juil 2017 · Sigle : (001) terme cité dans la définition d'acronyme mais non défini La définition proposée serait : -'Abréviation composée à partir des lettres |
|
Définition de référence de lOCDE des investissements - OECD
22 mai 2008 · Publié en anglais : OECD Benchmark Definition of Foreign Direct 4e édition de la Définition de référence des investissements directs |
|
Pour une définition du « numérique » - CORE
Pour une définition du « numérique » Marcello Vitali-Rosati On ne peut pas parler d'édition numérique sans appro- fondir le sens du mot « numérique |
|
Definition_de_cas_covid-19_rca_last_version_13_april_2020pdf
13 avr 2020 · DEFINITION DE CAS DE COVID-19 D'APPLICATION EN RCA des besoins de la surveillance épidémiologique les définitions de cas comme |
|
CIVD - SRLF
Question 1 : quelle définition et quelle classification doivent être utilisées en pratique clinique ? La coagulation intravasculaire disséminée (CIVD) est |