tp conduction convection terminale s
|
Cours
Terminale S - Spécifique - Page 3/6 Sciences Physiques au Lycée III 1 Modes La convection est un transfert porté par un mouvement de matière Elle ne se |
|
Thermiquepdf
convection forcée : le mouvement du fluide est induit par une cause s-1 d'air à 300°C On dispose pour cela de tubes de diamètre extérieur 50 mm et d |
|
TP quantifier un transfert thermique
conduction convection rayonnement Compétences attendues Associer l'échauffement d'un système à l'énergie reçue stockée sous forme d'énergie interne |
|
Transferts thermiques
Q6 Expérience 3 : Décrire l'expérience réalisée par le professeur avec les clous illustrant les transferts thermiques par conduction dans un métal |
|
Transmission de la chaleur 1
Il existe 3 modes de transferts thermiques : la conduction la convection et le rayonnement Analysons ces modes de transfert de chaleur dans l'habitat : 2 |
|
TS 20 Les transferts thermiques dans un bâtiment
Notions et contenus du programme de Term S Transferts d'énergie entre systèmes macroscopiques : Transferts thermiques : conduction convection rayonnement |
Quel sont les 3 type de chaleur ?
Il existe trois modes de transfert d'énergie thermique : la conduction, la convection et le rayonnement thermique.
La conduction se produit lorsque les flux de chaleur passent d'un corps à un autre, par contact.Comment calculer le flux thermique par conduction ?
II : LA CONDUCTION.
Le flux thermique F qui traverse la surface S est égal à la quantité de chaleur qui la traverse par unité de temps.
Il vaut donc : Q étant la quantité de chaleur qui a traversé S pendant le temps t.
L'unité de F est le J.s-1, c'est-à-dire le watt : on appelle aussi F la puissance thermique.Quels sont les 2 modes de transfert de la chaleur sur Terre ?
Il existe deux modes de transfert d'énergie thermique : la convection et la conduction.
- En convection on caractérise le flux de chaleur Φ qui est extrait par le fluide de température T0 d'une paroi de surface S `a la température TP par : Φ = h S (TP − T0) o`u Φ est en W att, S en m2, T en Kelvin et o`u h désigne le coefficient d'échange entre la paroi et le fluide (en W.m−2.
K−1).
|
Thermique.pdf
La chaleur s'écoule sous l'influence d'un gradient de température des hautes vers Coefficient de transfert de chaleur par convection. (W m-2 °C-1). Tp. |
|
Bilan thermique du corps humain
Puissance conduction |
|
TP Géothermie correction Nous savons que le gradient
Nous émettons 2 hypothèses : la convection la conduction. Nous observons donc un transfert de chaleur avec déplacement de matière : il s'agit d'une. |
|
Transfert thermique isolation v2
Conduction. Au travers du vide. Convection. Tp. Tm. Fluide. Paroi. ??=?= ?. S ... 6. Transfert thermique Isolation. ? Les matériaux. |
|
FA2 : correction II/ Origine du flux thermique et transfert dénergie 1
énergie considérable s'est -Par conduction c'est un transfert de chaleur de proche en proche sans mouvement de ... La convection est donc un moyen très. |
|
Chapitre 16 Transferts thermiques et bilans dénergie
surfaces sont séparées par un milieu dans lequel un transfert thermique s'effectue par convection et/ou conduction. Le flux thermique phi majuscule (?) à |
|
TRANSFERTS THERMIQUES
La convection est un mode de transfert de chaleur qui met en jeu en plus de la conduction |
|
TP T1 : CONDUCTION THERMIQUE : ETUDE DE LA
Le but de ce TP est de déterminer expérimentalement la conductivité thermique du cuivre. Pour cela on opérera de la manière suivante : • On s'intéressera |
|
TP DOPTIQUE
Élaborer une séquence pédagogique associant les parties du programme : Propriétés des ondes : diffraction et Image numérique stockage optique. Terminale S. |
|
Liste matériel terminale S
Liste de matériel pour la classe de Terminale S (enseignement spécifique et spécialité) établie par le groupe salle de TP au moins ... conduction par. |
|
Thermiquepdf
Cours Transferts thermiques 2ème année Ecole des Mines Nancy 6 NOMENCLATURE Coefficient de transfert de chaleur par convection (W m-2 °C-1) Tp |
|
TP quantifier un transfert thermique - Physique et Chimie
conduction convection rayonnement Compétences attendues Associer l'échauffement d'un système à l'énergie reçue stockée sous forme d'énergie interne |
|
Transferts thermiques - Labo TP
Les trois types de transferts thermiques Conduction Convection Rayonnement Q1 Associer à chacun des schémas 1 et 2 le type de transferts thermiques |
|
Transmission de la chaleur 1- Les transferts thermiques - Bac STI 2D
Il existe 3 modes de transferts thermiques : la conduction la convection et le rayonnement Analysons ces modes de transfert de chaleur dans l'habitat : |
|
Transferts thermiques - Prof-TC
Terminale S - Spécifique - Page 1/6 1er mode : par conduction La convection est un transfert porté par un mouvement de matière Elle ne se produit |
|
TP Conduction PDF Transfert thermique - Scribd
Avis 10 |
|
Transfertdechaleur-vol2pdf
Ex-3 4(S) Conduction avec génération de chaleur (à l'examen final 1991) température T4 et le coefficient de convection à la surface de l'ailette est h |
|
COURS DE TRANSFERTS THERMIQUES Philippe Marty 2012-2013
En convection on caractérise le flux de chaleur ? qui est extrait par le fluide de température T0 d'une paroi de surface S `a la température TP par : |
|
Chapitre 16 Transferts thermiques et bilans dénergie
surfaces sont séparées par un milieu dans lequel un transfert thermique s'effectue par convection et/ou conduction Le flux thermique phi majuscule (?) à |
|
TS 20 Les transferts thermiques dans un bâtiment
Transferts thermiques : conduction convection rayonnement Flux thermique Résistance thermique Compétences exigibles du programme de Term S |
| Convection Conduction & Radiation |
| Heat Transfer: Conduction Convection and Radiation |
| Conduction Convection and Radiation - Vanderbilt University |
| Steady Heat Transfer with Conduction and Convection |
| Heat Transfer: Conduction Convection and Latent Heat In |
| Searches related to tp conduction convection terminale s filetype:pdf |
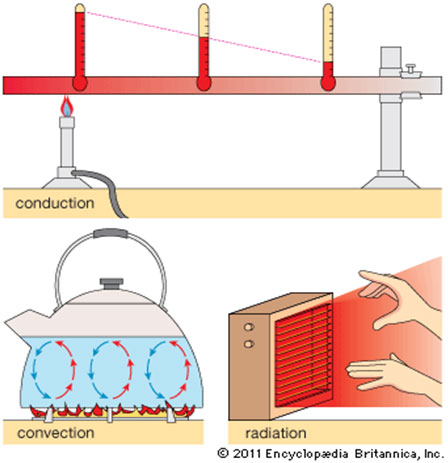
What is the difference between conduction and convection?
- Conduction is how heat travels between objects that are touching.
. Conduction travels fastest through solids, but liquids and gases can also conduct heat.
. Some materials, like metal, can conduct heat very quickly, while other materials (like plastic or wood) conduct heat very slowly.
. Convection is how heat travels through fluids – liquids and gases.
What are the characteristics of steady heat transfer?
- • In steady heat transfer the temperature and heat flux at any coordinate point do not change with time • Both temperature and heat transfer can change with spatial locations, but not with time • Steady energy balance (first law of thermodynamics) means that heat in plus heat generated equals heat out 8 Rectangular Steady Conduction
How does conduction heat through a wall work for energy conservation?
- Energy conservation requires that conduction heat through wall equals the heat leaving the wall by convection and radiation Q&1 =Q&2+Q&3 Figure 1-18 from Çengel, Heat and Mass Transfer 12 Where Does the Heat Go? II Figure 1-18 from Çengel, Heat and Mass Transfer Figure 3-5 from Çengel, Heat and Mass Transfer Steady Heat Transfer February 14, 2007
What is conduction and how does it work?
- Conduction is how heat transfers through direct contact with objects that are touching.
. Any time that two objects or substances touch, the hotter object passes heat to the cooler object. (That hot sand passed the heat energy right into my poor feet) Think of a row of dominoes that are all lined up.
|
Bilans thermiques - Physique terminale S
30 août 2013 · échange par conduction : échange par contact sans déplacement de matière l' air et par convection avec le ventilateur situé à côté |
|
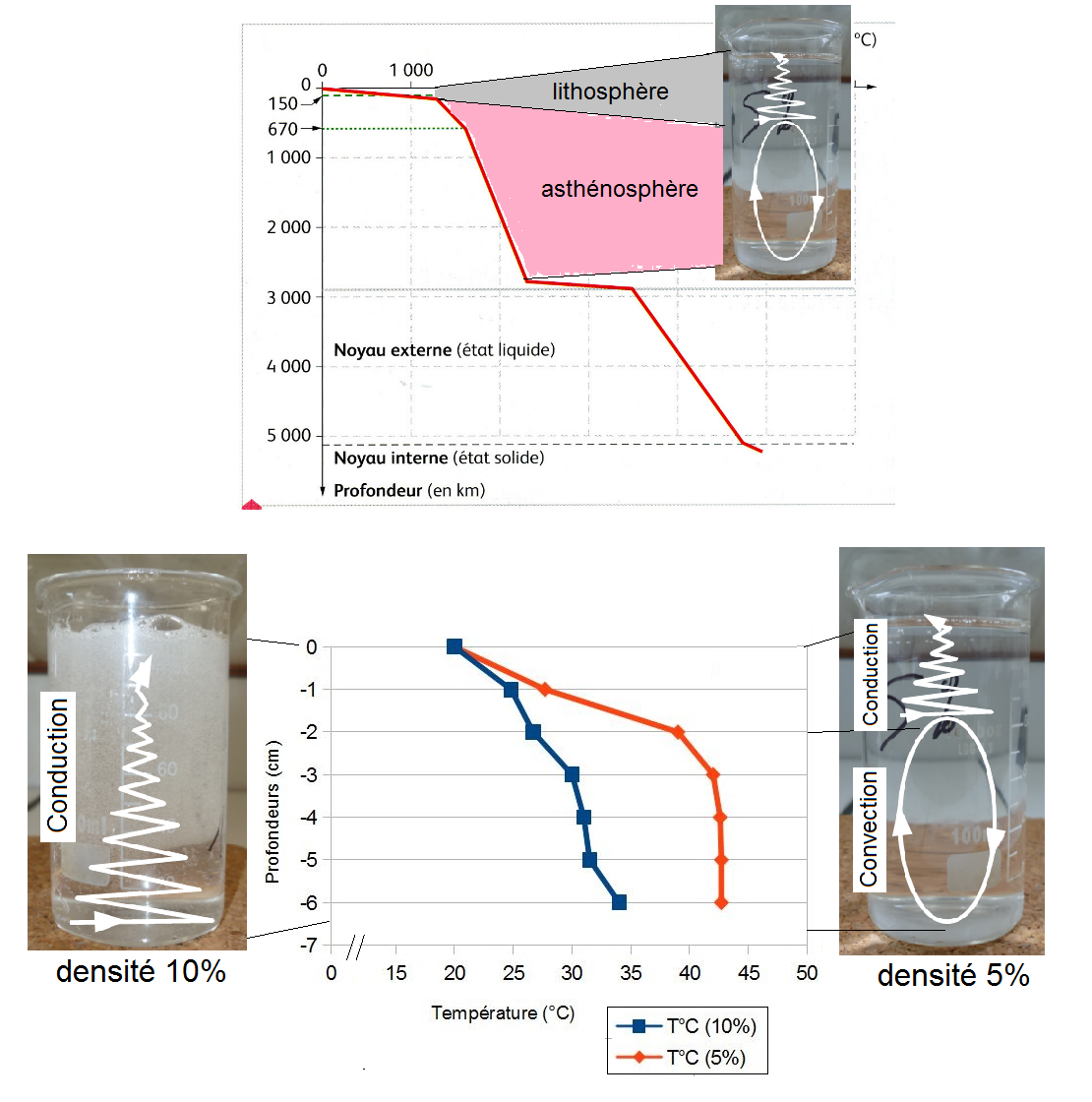
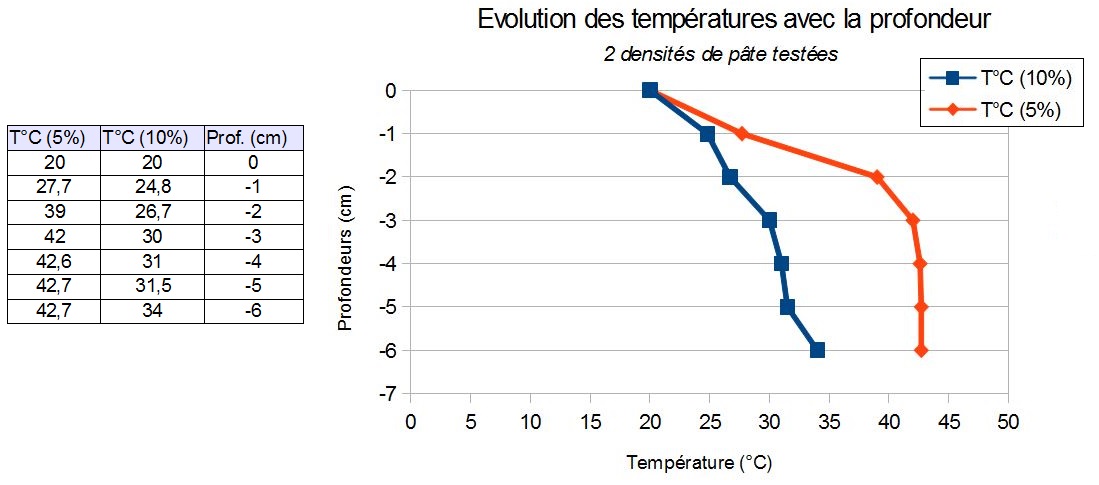
Géothermie et propriétés thermiques de la Terre - Lycée dAdultes
par conduction et convection 35 - 1ère série de mesures : pas de déplacement du liquide au sein du bécher Les transferts de chaleur se font par conduction |
|
Physique, Chapitre 10 Terminale S TRANSFERT THERMIQUE D
la convection ✓ le rayonnement 2) Trois modes de transfert a) conduction Dans ce type de transfert, nécessitant un milieu matériel, l'énergie est transportée |
|
TP 5 Convection – Conduction et modélisation des flux - Jeulin
Problématique scientifique Dans la terre, cohabite deux mécanismes de flux thermiques d'efficacité dif- férente : la conduction et la convection Peut on mettre |
|
TS 20 Les transferts thermiques dans un bâtiment
Transferts thermiques : conduction, convection, rayonnement deux faces Compétences du préambule du cycle terminal du programme de Terminale S |
|
TS21 Chauffer Isoler
de Terminale S Transferts thermiques : conduction, convection, rayonnement Flux thermique Résistance thermique Compétences exigibles du programme de |
|
EXERCICES CORRIGES p : 365 n°14 – 15 – 16 – 18 Ch14
par convection ; par rayonnement a Il y a des transferts thermiques par conduction entre la piscine et le sol qui l'entoure, entre l |
|
PDF 5 - Transferts thermiques
La propagation de la chaleur par conduction à l'intérieur d'un corps s'effectue selon Remarque : La valeur du coefficient de transfert de chaleur par convection h est fonction de la nature du fluide, la partie terminale de l' échangeur |
|
Transferts thermiques Cours et exercices corriges - Dunod
Les différents modes de transfert, par conduction, rayon- nement et convection thermiques, sont progressivement introduits en privilégiant une approche physique |
|
TP 3 : La convection et la conduction Situation initiale : Lénergie
– Quel modèle représente la conduction/ la convection – Définir ces termes – Ces deux processus sont responsables de quoi ? – Des deux modes de dissipation |