intel core i9
|
12th Generation Intel® Core™ Processors
The processor families do not retain any end-user data when powered down and/or when the processor is physically removed NOTE Powered down refers to the state which all processor power rails are off |
|
8th and 9th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor Families
Datasheet Volume 1 of 2 Supporting 8th Generation Intel®Core™ Processor Families Intel®Pentium® Processors Intel®Celeron®Processors for U/H/S Platforms formerly known as Coffee Lake Supporting 9th Generation Intel®Core™ Processor Families H/S Platforms formerly known as Coffee Lake Refresh July 2020 Revision 006 |
|
Intel® Core™ i9 Desktop Processors Comparison Chart
Intel® Core™ i9 Desktop Processors Comparison Chart INSTRUCTIONS Ordering Package Specification Security & Reliability Processors Number Collection Box Order Number (Click to link to Compatible Motherboards) Launch Year Processor Socket Processor Base Frequency (GHz) Max Turbo Frequency Intel® Turbo Boost Max Technology 3 0 Frequency |
|
Intel® Core™ i9 X-series processor
Intel Corporation 2200 Mission College Blvd Santa Clara CA 95054-1549 USA EU Single Point of Contact: Intel Corporation (UK) Ltd Attn: Corp Quality |
Which Intel® CoreTM processors are included in the technical resources list?
These documents apply to 5th Generation Intel® Core™ processors i7-xxxxC, i7-xxxxR, i5-xxxxC, i5-xxxxR Intel® Core™ processors technical resources list includes applications notes, datasheets, packing information, product briefs, and more.
Which processor families are supported by Intel® CoreTM processor families?
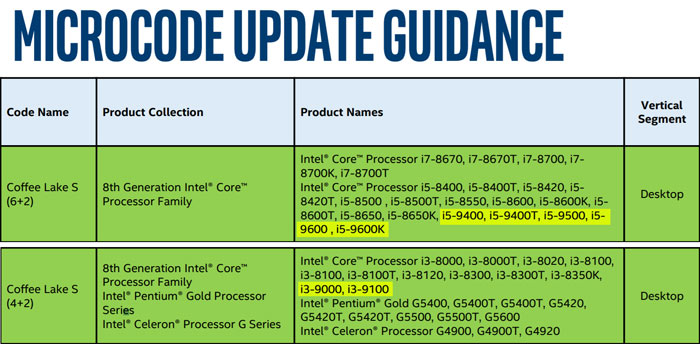
Supporting 13th Generation Intel® Core™ processor families and Intel® Core™ processor (14th Gen) for desktop platform, formerly known as Raptor Lake Supporting 12th Generation Intel® Core™ processor families for desktop platform, formerly known as Alder Lake Intel® 600 Series Chipset Family Platform Controller Hub (PCH)
What is a processor IA core?
The processor IA core will scale the operating points such that: The voltage will be optimized according to the temperature, the processor IA core bus ratio and the number of processor IA cores in deep C-states. The processor IA core power and temperature are reduced while minimizing performance degradation.
1.1 Processor Volatility Statement
The processor families do not retain any end-user data when powered down and/or when the processor is physically removed. NOTE Powered down refers to the state which all processor power rails are off. cdrdv2-public.intel.com
Graphics Core Power Savings Technologies
Graphics Dynamic Frequency Intel® Graphics Render Standby Technology (Intel® GRST) Dynamic FPS (DFPS) cdrdv2-public.intel.com
2.0 Technologies
This chapter provides a high-level description of Intel technologies implemented in the processor. The implementation of the features may vary between the processor SKUs. Details on the different technologies of Intel processors and other relevant external notes are located at the Intel technology web site: http://www.intel.com/technology/ NOTE The
2.1 Platform Environmental Control Interface
Platform Environmental Control Interface (PECI) is an Intel proprietary interface that provides a communication channel between Intel processors and external components such as Super IO (SIO) and Embedded Controllers (EC) to provide processor temperature, Turbo, Assured Power (cTDP), and Memory Throttling Control mechanisms and many other services
Key Features
The processor supports the following added new Intel® VT-x features: Mode-based Execute Control for EPT (MBEC) - A mode of EPT operation which enables different controls for executability of Guest Physical Address (GPA) based on Guest specified mode (User/ Supervisor) of linear address translating to the GPA. When the mode is enabled, the executabi
Intel® VT-d Objectives
The key Intel® Virtualization Technology (Intel® VT) for Directed I/O (Intel® VT-d) objectives are domain-based isolation and hardware-based virtualization. A domain can be abstractly defined as an isolated environment in a platform to which a subset of host physical memory is allocated. Intel® VT-d provides accelerated I/O performance for a Virtua
Context entry 0
Context entry Table For bus 0 Address Translation Structures for Domain B Intel® VT-d functionality often referred to as an Intel® VT-d Engine, has typically been implemented at or near a PCI Express* host bridge component of a computer system. This might be in a chipset component or in the PCI Express functionality of a processor with integrated I
2.2.3 Intel® APIC Virtualization Technology (Intel® APICv)
APIC virtualization is a collection of features that can be used to support the virtualization of interrupts and the Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller (APIC). When APIC virtualization is enabled, the processor emulates many accesses to the APIC, tracks the state of the virtual APIC, and delivers virtual interrupts — all in VMX non-root ope
2.2.4 Hypervisor-Managed Linear Address Translation
Hypervisor-Managed Linear Address Translation (HLAT) is active when the “enable HLAT” VM-execution control is 1. The processor looks up the HLAT if, during a guest linear address translation, the guest linear address matches the Protected Linear Range. The lookup from guest linear addresses to the guest physical address and attributes is determined
2.3.1 Intel® Trusted Execution Technology
Intel® Trusted Execution Technology (Intel® TXT) defines platform-level enhancements that provide the building blocks for creating trusted platforms. The Intel® TXT platform helps to provide the authenticity of the controlling environment such that those wishing to rely on the platform can make an appropriate trust decision. The Intel® TXT platform
2.3.2 Intel® Advanced Encryption Standard New Instructions
The processor supports Intel® Advanced Encryption Standard New Instructions (Intel® AES-NI) that are a set of Single Instruction Multiple Data (SIMD) instructions that enable fast and secure data encryption and decryption based on the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). Intel® AES-NI is valuable for a wide range of cryptographic applications, such
2.3.5 Execute Disable Bit
The Execute Disable Bit allows memory to be marked as non-executable when combined with a supporting operating system. If code attempts to run in non-executable memory, the processor raises an error to the operating system. This feature can prevent some classes of viruses or worms that exploit buffer overrun vulnerabilities and can, thus, help impr
2.3.6 Boot Guard Technology
Boot Guard technology is a part of boot integrity protection technology. Boot Guard can help protect the platform boot integrity by preventing the execution of unauthorized boot blocks. With Boot Guard, platform manufacturers can create boot policies such that invocation of an unauthorized (or untrusted) boot block will trigger the platform protect
2.3.9 Intel® Secure Hash Algorithm Extensions
The Intel® Secure Hash Algorithm Extensions (Intel® SHA Extensions) is one of the most commonly employed cryptographic algorithms. Primary usages of SHA include data integrity, message authentication, digital signatures, and data de-duplication. As the pervasive use of security solutions continues to grow, SHA can be seen in more applications now t
2.3.12 Intel® Total Memory Encryption - Multi-Key
This technology encrypts the platform's entire memory with multiple encryption keys. Intel® Total Memory Encryption (Intel® TME), when enabled via BIOS configuration, ensures that all memory accessed from the Intel processor is encrypted. Intel TME encrypts memory accesses using the AES XTS algorithm with 128-bit keys. The global encryption key use
Shadow Stack
A shadow stack is a second stack for the program that is used exclusively for control transfer operations. This stack is separate from the data stack and can be enabled for operation individually in user mode or supervisor mode. The shadow stack is protected from tamper through the page table protections such that regular store instructions cannot
2.3.14 KeyLocker Technology
A method to make long-term keys short-lived without exposing them. This protects against vulnerabilities when keys can be exploited and used to attack encrypted data such as disk drives. An instruction (LOADIWKEY) allows the OS to load a random wrapping value (IWKey). The IWKey can be backed up and restored by the OS to/from the PCH in a secure man
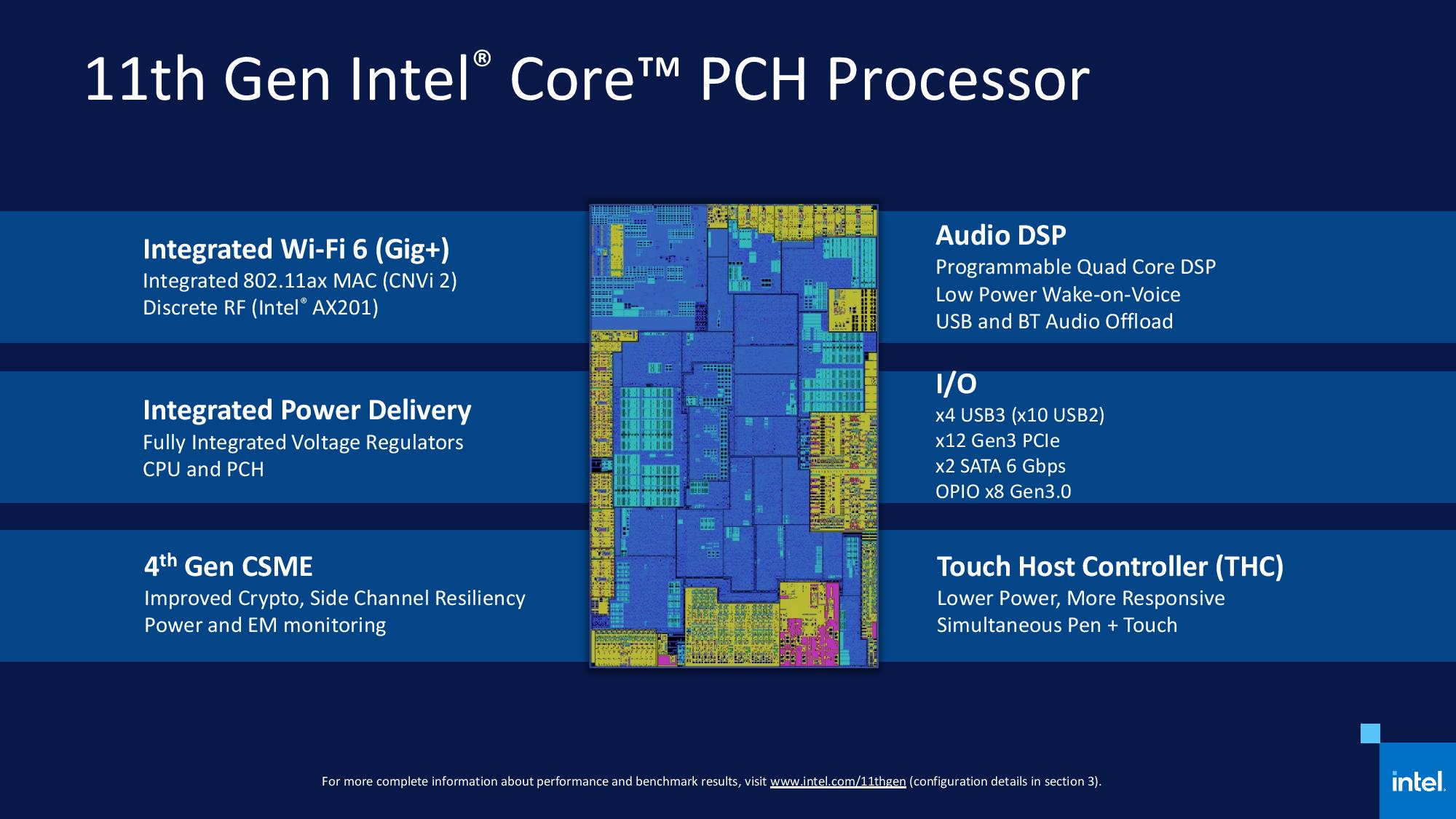
2.4.3 Ring Interconnect
The Ring is a high speed, wide interconnect that links the processor cores, processor graphics and the System Agent. The Ring shares frequency and voltage with the Last Level Cache (LLC). The Ring's frequency dynamically changes. Its frequency is relative to both processor cores and processor graphics frequencies. cdrdv2-public.intel.com
2.4.4 Intel® Performance Hybrid Architecture
The processor contains two types of cores, denoted as P-Cores and E-Cores (P core is a Performance core and E core is efficient core ). The P-Cores and E-Cores share the same instruction set. The available instruction sets, when hybrid computing is enabled, is limited compared to the instruction sets available to P-Cores. P core and E core frequenc
2.4.6 Intel® Hyper-Threading Technology
The processor supports Intel® Hyper-Threading Technology (Intel® HT Technology) that allows an execution processor IA core to function as two logical processors. While some execution resources such as caches, execution units, and buses are shared, each logical processor has its own architectural state with its own set of general-purpose registers a
2.4.7.1 Intel® Turbo Boost Technology 2.0 Power Monitoring
When operating in turbo mode, the processor monitors its own power and adjusts the processor and graphics frequencies to maintain the average power within limits over a thermally significant time period. The processor estimates the package power for all components on the package. In the event that a workload causes the temperature to exceed program
2.4.8 Enhanced Intel SpeedStep® Technology
Enhanced Intel SpeedStep® Technology enables OS to control and select P-state. The following are the key features of Enhanced Intel SpeedStep® Technology: Multiple frequencies and voltage points for optimal performance and power efficiency. These operating points are known as P-states. Frequency selection is software controlled by writing to proces
2.4.10 Intel® Speed Shift Technology
Intel® Speed Shift Technology is an energy efficient method of frequency control by the hardware rather than relying on OS control. OS is aware of available hardware P-states and requests the desired P-state or it can let the hardware determine the P-state. The OS request is based on its workload requirements and awareness of processor capabilities
2.4.12 Intel® 64 Architecture x2APIC
The x2APIC architecture extends the xAPIC architecture that provides key mechanisms for interrupt delivery. This extension is primarily intended to increase processor addressability. Specifically, x2APIC: Retains all key elements of compatibility to the xAPIC architecture: — Delivery modes — Interrupt and processor priorities — Interrupt sources —
2.4.13 Intel® Dynamic Tuning Technology
Intel® Dynamic Tuning (Intel® DTT) consists of a set of software drivers and applications that allow a system manufacturer to optimize system performance and usability by: Dynamically optimize turbo settings of IA processors, power and thermal states of the platform for optimal performance Dynamically adjust the processor’s peak power based on the
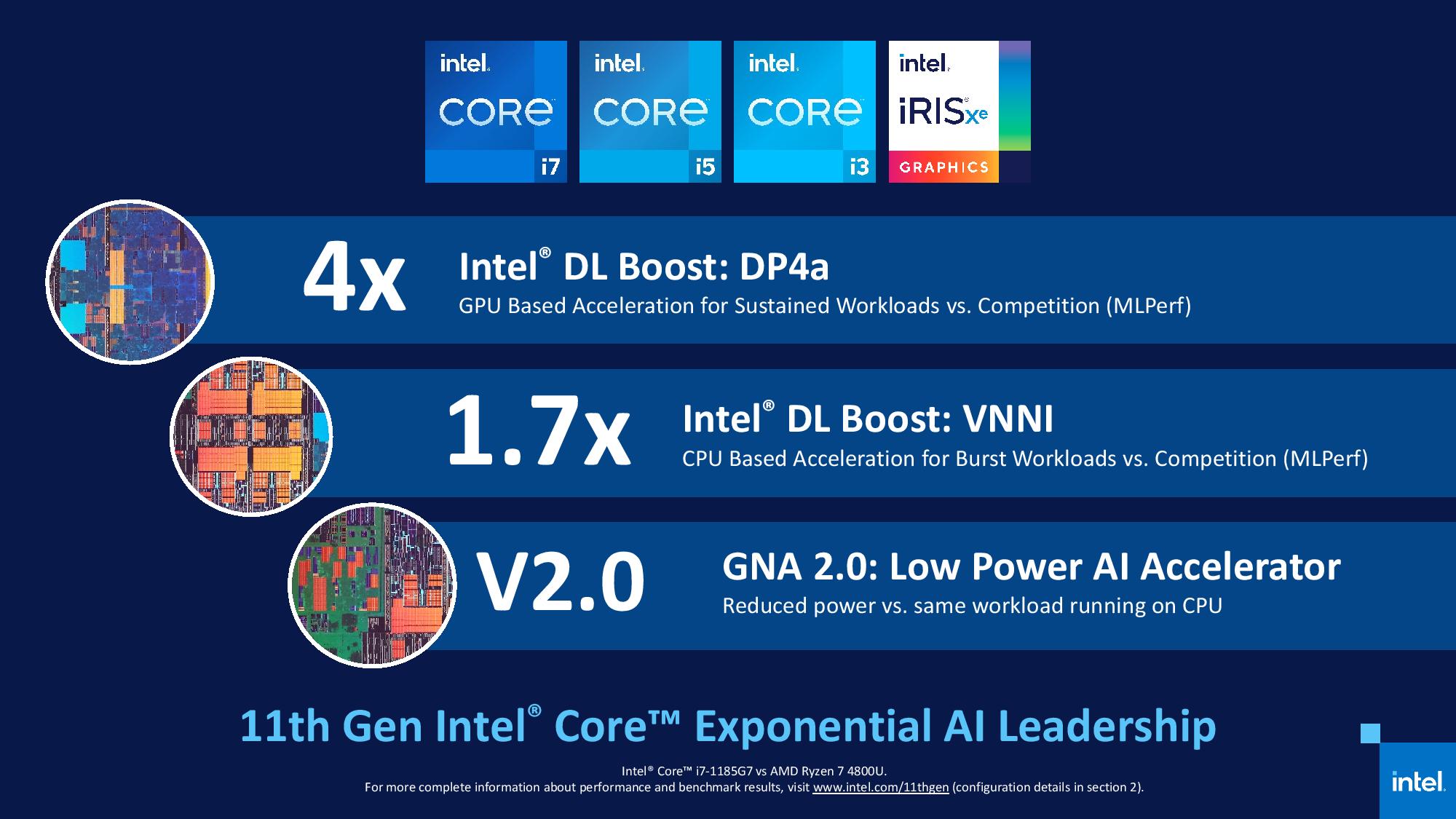
2.4.14 Intel® GMM and Neural Network Accelerator
GNA stands for Gaussian Mixture Model and Neural Network Accelerator. The GNA is used to process speech recognition without user training sequence. The GNA is designed to unload the processor cores and the system memory with complex speech recognition tasks and improve the speech recognition accuracy. The GNA is designed to compute millions of Gaus
2.4.16 Remote Action Request
PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com PECI Ground Minimum Hysteresis Valid Input Signal Range cdrdv2-public.intel.com
|
13th Gen Intel Core Desktop Media Presentation
27 sept. 2022 7 2022. Intel Core i9-13900K is the world's fastest desktop processor at 5.8 GHz. World's Best Gaming Experience based on performance and ... |
|
8th and 9th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor Families Datasheet
Intel Intel Core |
|
13th Gen Intel Core Mobile
1 At 5.6GHz 13th Gen Intel Core i9-13980HX is the fastest mobile processor as of December 2022. 2 .Based on unique features and superior in-game benchmark mode |
|
12th Gen Intel® Core™ Desktop Processors
2x16GB G.Skill TridentZ 3200Mhz CL14 RAM System. B: Core i9-12900K on Asus Z690 Prime-P DDR5 Motherboard. 2x16GB SK.Hynix 4400Mhz CL40 RAM |
|
Intel® Core™ i9 Desktop Processors Comparison Chart
Core™ X-series. BX80673I97900X. Q2'17. LGA2066. 3.30. 4.30. 4.50. 13.75. 10/20. Yes. 140. No. N/A. Yes. 2. Yes. Yes. 4. 2666/ NA. Intel® Core™ i9 Processor Top |
|
APP-for-Intel-Core-Processors.pdf
i9-7940X. 1075.2. 0.032256. Intel® Core™ i9-7920X X-series Processor (16.50M Cache up to 4.30 GHz) i9-7920X. 844.8. 0.025344. Intel® Core™ i9-7900X X-series |
|
Intel® Core™ 14th Gen S-series Processors
16 oct. 2023 Based on performance of the Intel Core 14thGen i9-14900K. For all workload and configuration seewww.intel.com/PerformanceIndex. Results may vary ... |
|
13th Gen Intel® Core™ i9-13900KS Processor Sales Brief
Select 13th Gen Intel Core processors do not have performance hybrid architecture only P-cores |
|
Product Change Notification
7 dec. 2020 Intel® Core™ i9-9900KF Processor. CM8068403873928 S RG1A 999H3C. R0. Intel® Core™ i9-9900T Processor. CM8068403874122 S RG1B 999H3D. R0. Page 3 ... |
|
Product Brief: Intel® Core™ 14th Gen Desktop Processors
With up to 24 cores (8 Performance-cores and 16 Efficient-cores) and up to 32 threads. The Intel® Core i9 processor P-cores are capable of reaching 6.0Ghz with |
|
8th and 9th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor Families Datasheet
Intel Intel Core |
|
Intel® Core™ i9 Desktop Processors Comparison Chart
Intel® Core™ i9 Desktop Processors Comparison Chart. INSTRUCTIONS. Ordering. Package. Specification. Security &. Reliability. Processors Number. Collection. |
|
12th Gen Intel® Core™ Desktop Processors
The 12th Gen Intel® Core™ desktop processor redefines x86 architecture performance. B: Core i9-12900K on Asus Z690 Prime-P DDR5 Motherboard. 2x16GB SK. |
| PC gaming processor study: Intel Core i9-9900K processor vs |
|
Introducing Intels First-ever Core™ i9 Mobile Processor
the latest generation of Intel Core processors. For the enthusiast the fully-unlocked 8th Generation Intel® Core™ i9-8950HK processor. |
|
HP EliteDesk 800 G6 Tower PC
GHz base frequency up to 5.1 GHz with Intel® Turbo Boost Technology |
|
ADL-HX Northstar Claims
1 – Source: Intel. Based on performance estimated with measurements on 12th Gen Intel Core i9-12900HX with RTX 3080Ti against Intel Core i9-11980HK with. |
|
Intel-ces-2022-press-deck.pdf
The Fastest Mobile Processor. Ever. 12th Gen Intel® Core™ H-series Processors. Intel Core i9-12900HK. M1 |
|
HP Z4 G4 Workstation
05-Feb-2018 Intel® Core TM i9 Extreme Edition processor. 5. 2 PCIe G3 x16 2 PCIe G3 x4 |
|
I9-10900K i9-10900KF i9-10900 i9-10900F i7-10700K i7-10700KF
ALL CORE TURBO. FREQUENCY (GHZ)?. INTEL® ALL. CORE TURBO. FREQUENCY i9-10900K ... Intel® processor numbers are not a measure of performance. |
|
PRÉSENTATION DE LA NOUVELLE FAMILLE DE - Intel
ESSEUR INTEL® CORE™ i9 EXTREME EDITION Une nouvelle race de processeurs |
|
Familles de processeurs Intel® hautes performances
solution-briefsPDF |
|
Intel® Core™ i9 Desktop Processors Comparison Chart
KS 9th Gen BX80684I99900KS Q4'19 LGA1151 4 00 5 00 N/A 16 8/ 16 Yes 127 Yes |
|
Powerhouse Performance with Intel® Core™ i9 Mobile Processor
product-briefsPDF |
|
9th Generation Intel® Core™ Desktop Processors
st Intel® Core™ i9 desktop processor for the mainstream users Best in class, the i9-9900K with |
|
9th Gen Intel® Core™ Mobile Processors (H-Series) Product Brief
pdf DocsPDF |
|
Product Brief: Intel® Core™ X-Series Processor Family
el® Core™ I9 exTreme edITIon proCessor The dawn of a new breed of extreme desktop |
|
Intel® Core™ i9-9960X X-series Processor
Core™ i9-9960X X-series Processor 22M Cache, up to 4 50 GHz Add to Compare |