national debt comparison
What is government debt?
Government debt is a figure that represents the money owed by a national government. However, when a government spends more than its revenue in a year, it runs a budget deficit that fiscal year. It has to fill the funding gap with debt.
Why is the national debt so high?
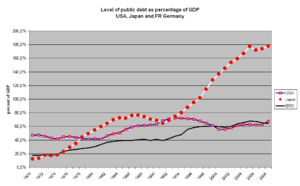
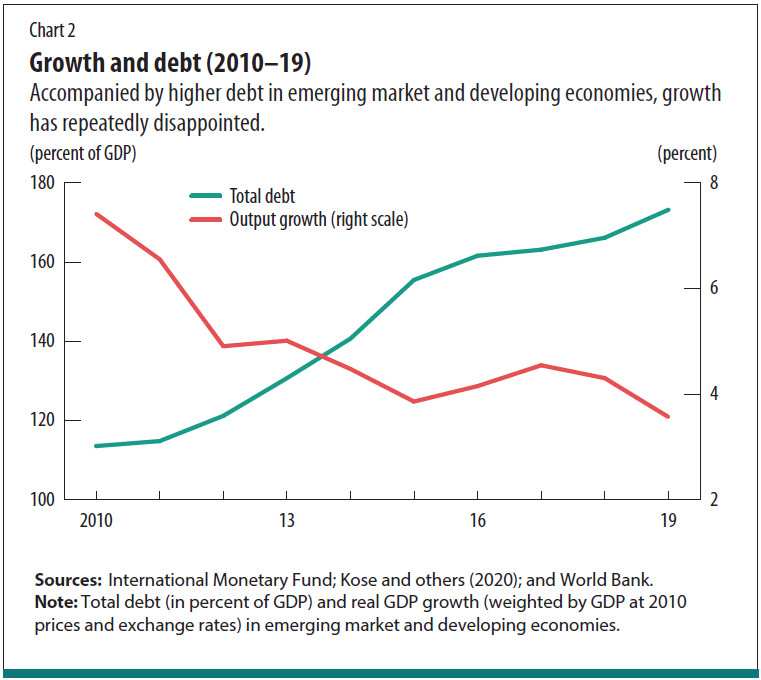
Looking at national debt in terms of debt-to-GDP ratio, the federal debt rose to an all-time high of 132.96% in the second quarter of 2020 due to the pandemic-fueled recession. The national debt is the total amount of money that a country owes to its creditors.
What is the national debt of the United States?
The national debt of the United States is what the federal government owes to its creditors. The U.S. has always carried national debt, and the majority of presidents have added to it. However, the total has been expanding rapidly since 2008 due to a combination of increased government spending and failure to raise taxes.
Which country has the highest national debt?
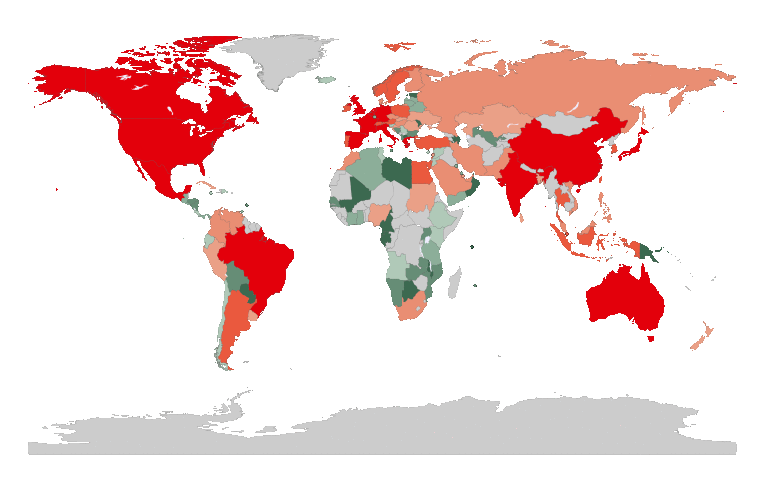
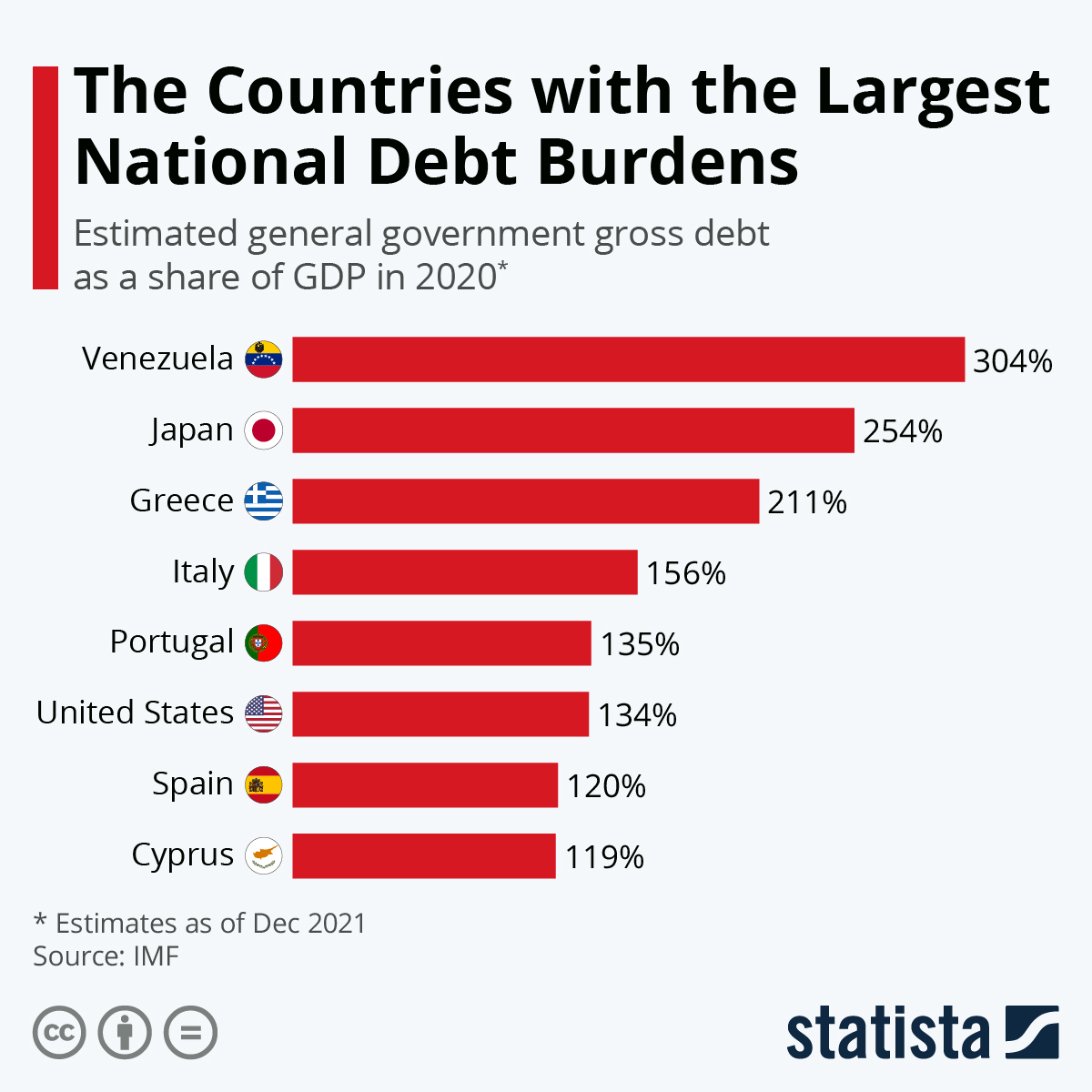
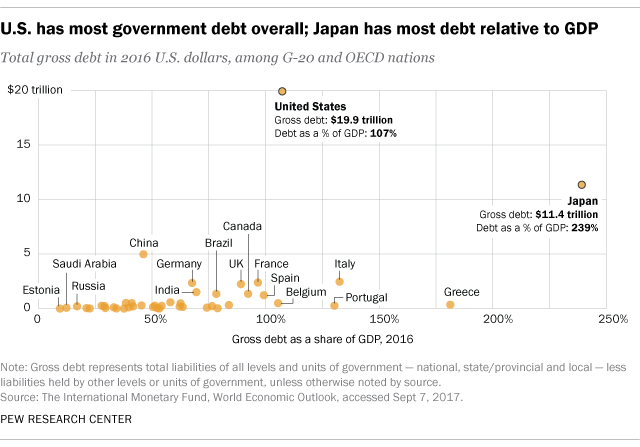
The United States has the world’s highest national debt at $31.4 trillion. Global debt currently stands at $305 trillion, $45 trillion higher than before the COVID-19 pandemic, according to the Institute of International Finance (IIF) – a global association of the financial industry.
Overview
The term national debt refers to the outstanding financial obligation of a country. The national debt of the United States is what the federal government owes to its creditors. The U.S. has always carried , and the majority of presidents have added to it. However, the total has been expanding rapidly since 2008 due to a combination of increased government spending and failure to raise taxes. The U.S. national debt passed $33.99 trillion in January 2024. Tax cuts, stimulus programs, and increased government spending on defense can cause the national debt to rise sharply. Looking at the debt-to-gross-national-product ratio of a country shows whether the nation can pay back its debt. investopedia.com
Understanding National Debt
The federal government borrows money to cover outstanding expenses that accumulate over time. Funds for federal spending are mainly generated by collecting taxes on personal and corporate income, payroll earnings, and borrowing. The government then spends this money on programs such as Social Security, healthcare, education, infrastructure, and national defense. When the government spends less than the revenue collected through taxes, there is a When government spending exceeds its revenue, the result is a To pay for this deficit, the borrows money by issuing Treasury bills, notes, and bonds. These can be purchased by investors, financial institutions such as banks and insurers, the , and other foreign central banks. investopedia.com
The Growing National Debt
The U.S. has carried debt since it was founded. In fact, the U.S. accumulated more than $75 million in debt during the Revolutionary War, and that increased to greater than $2 billion by the end of the Civil War in 1865. Major economic and political events usually trigger an increase in the national debt. Recent events causing a spike in debt levels include the wars in Afghanistan and Iraq, the , and the COVID-19 pandemic. Military spending reached record levels of more than $600 billion during the wars in Afghanistan and Iraq. Government spending on relief measures during times of economic turmoil, such as the Great Recession and COVID-19, also causes an increase in the national debt. For example, then-President Barack Obama’s American Recovery and Reinvestment Act (ARRA) was an $831 billion fiscal stimulus aimed at restoring jobs during the 2008 recession. investopedia.com
Debt-to-GDP Ratio
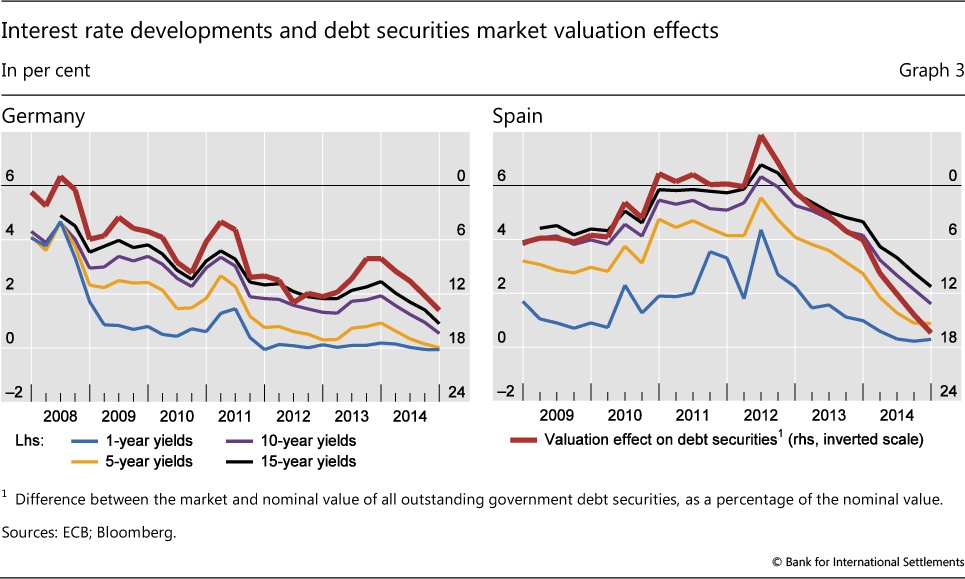
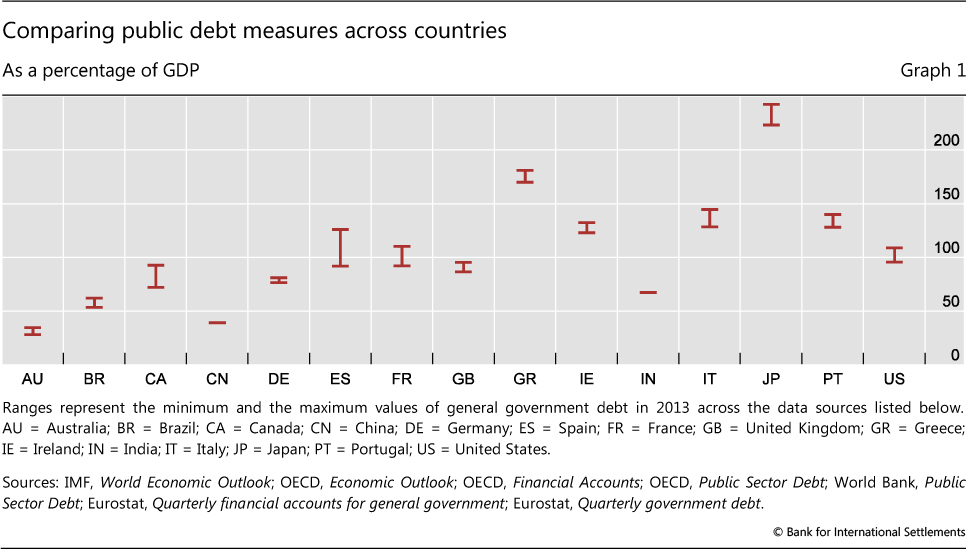
is the ratio of a country’s public debt to its Looking at a country’s debt compared with its GDP is similar to a lender looking at someone’s credit history—it reveals how likely the country is to pay back its debt. The debt-to-GDP ratio is usually expressed as a percentage and is used as a reliable indicator of a country’s economic situation, because it compares what the country owes to what it produces, in turn showing its ability to repay the debt. The higher a country’s debt-to-GDP ratio, the less likely the country is to pay off its debt. This also puts the country at higher risk of , which is concerning to investors as it could cause financial panic in domestic and international markets. According to a study by the , countries with a debt-to-GDP ratio above 77% for a prolonged period experience significant slowdowns in economic growth. As of the third quarter of 2023, the U.S. debt-to-GDP ratio was 120.13%. The U.S. debt-to-GDP ratio has been above 77% since 2009, following the financial crisis that started in 2007. investopedia.com
Types of Debt Included in the National Debt
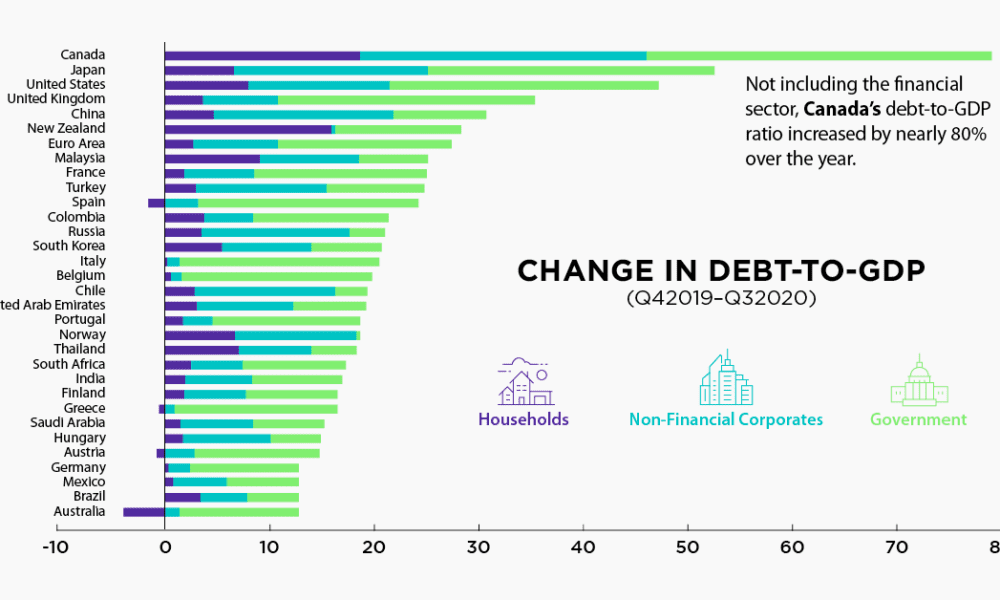
There are different types of debt that comprise the national debt. We've highlighted some of them below. such as Treasury bills, bonds, notes, and can be traded on the secondary market, and their ownership can be transferred from one person or entity to another. , which include savings bonds, government account series, and state and local government series, can’t be sold to other investors. The U.S. federal debt is mainly held by the American public, followed by foreign governments, U.S. banks, and investors. This portion of the debt held by the public doesn’t include U.S. debt held by the federal government or intragovernmental debt. Debt held by the public includes individuals, corporations, state or local governments, Federal Reserve banks, foreign investors and governments, and other entities outside the U.S. government. The increase in the U.S. national debt since 2013. One of the main causes of the jump in publicly held federal debt was the increased funding of programs and services during the COVID-19 pandemic. investopedia.com
Tracking, Maintaining, and Managing the National Debt
Bureau of the Fiscal Service provides accounting and reporting services for the government and manages all federal payments and collections. One of the Fiscal Service’s main roles is to track and report the national debt. Like the rest of us, the federal government is also charged interest for borrowing money. How much interest the government pays depends on the total national debt and the interest rates of different securities. When the target range for the federal funds rate (fed rate) Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) , carrying debt becomes more expensive for the government, too. investopedia.com
The Debt Ceiling
, or debt limit, is the maximum amount that the U.S. government can borrow by issuing bonds. When the debt ceiling is reached, the Treasury must find other ways to pay expenses. If what the federal government owes reaches the debt limit, and that limit is not raised, there is a risk that the U.S. will default on its debt. This sounds alarm bells for investors because that could have severe consequences for national and global markets. To avoid the risk of default, the debt ceiling needs to be raised by Congress, which has been done many times. In January 2023, U.S. Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen that the U.S. government hit its debt ceiling. Yellen said the U.S. government would take “extraordinary measures” to prevent a , which could come in mid-2023 if the debt ceiling isn’t raised or abolished altogether. Extraordinary measures authorized by Congress would temporarily suspend certain intragovernmental debt, allowing the Treasury to borrow more money for a limited amount of time. The investopedia.com
How Much Does the Pay on Its Debt Every Year?
Paying down, or servicing, the national debt is one of the federal government’s biggest expenses. According to the Congressional Budget Office, net interest payments on the federal debt were $475 billion in 2022, and are projected to rise to $640 billion in 2023. investopedia.com
What Is the Current Debt?
As of January 2024, the U.S. national debt was over $33.99 trillion. investopedia.com
When Was the National Debt the Highest?
Looking at national debt in terms of debt-to-GDP ratio, the federal debt rose to an all-time high of 132.96% in the second quarter of 2020 due to the pandemic-fueled recession. investopedia.com
|
Fourth quarter of 2021 - Government debt down to 95.6% of GDP in
22 avr. 2022 Compared with the fourth quarter of 2020 the government debt to GDP ... system of national and regional accounts in the European Union. |
|
Do Fundamentals Explain Differences between Euro Area
Keywords: interest rates sovereign bond spreads |
|
BIS debt securities statistics: a comparison of nationality data with
2 The DDS and TDS statistics are from national sources and compiled on a residence basis. The IDS statistics are based on security-by-security information. |
|
First quarter of 2021 - Government debt up to 100.5% of GDP in euro
22 juil. 2021 Compared with the first quarter of 2020 the government debt to GDP ratio ... system of national and regional accounts in the European Union. |
|
National Debt in a Neoclassical Growth Model
A relationship between changes in the size of the national debt and changes in problem of initial conditions not just as a comparison of Golden Age. |
|
First quarter of 2022 - Government debt down to 95.6% of GDP in
21 juil. 2022 Compared with the first quarter of. 2021 the government debt to GDP ratio decreased more strongly in both the euro area (from 100.0% to 95.6%). |
|
First quarter of 2022 - Government debt down to 95.6% of GDP in
21 juil. 2022 Compared with the first quarter of. 2021 the government debt to GDP ratio decreased more strongly in both the euro area (from 100.0% to 95.6%). |
|
“Comparative analysis of internal and external national debt of
5 avr. 2017 Internal national debt consists of the loans of the Government of Ukraine and loans given with unconditional guarantees for financing of ... |
|
Third quarter of 2021 - Government debt down to 97.7% of GDP in
21 janv. 2022 Compared with the third quarter of 2020 the government debt to GDP ratio rose in both the euro area (from 96.6% to 97.7%) and the EU (from. |
|
Third quarter of 2021 - Government debt down to 97.7% of GDP in
21 janv. 2022 Compared with the third quarter of 2020 the government debt to GDP ratio rose in both the euro area (from 96.6% to 97.7%) and the EU (from. |
|
CHAPTER 31: DEFICITS AND DEBT
What is the difference between the deficit and the national debt? How are they related? 2 “The national debt is a huge burden on our economy ” How would you |
|
“Comparative analysis of internal and external national debt of
With the help of correlation analysis, strength of correlation and directions of influence of different types of debts on the national budget of Ukraine in 2006- 2015 |
|
Public Debt and Demography - An International Comparison Using
it debt or budget deficits, Generational Accounting merous indicators to compare the fiscal situation tor as stated in their national accounts in a base year, |
|
High public debt in euro- area countries: comparing - CORE
sentiment than Belgium, especially when the sovereign debt crisis spread from Greece to other euro-area countries Italy responded to the onslaught of markets |
|
Government Debt - Harvard University
U S federal debt as a percentage of gross national product over the past 200 years 1 differences, timing conventions, and some shifting of items between the |
|
Public finances in Euro Area Member States - European Parliament
of total government debt 20191 Yield on sovereign bonds (10 years) The budget surplus (+)/deficit (-) is the difference between the General Government's |
|
A comparison of 28 countries budget deficit levels and the
International public debt review: a comparison of 28 countries As the global economy dependent on payments by the national oil company (which currently |
|
Addressing the Long-Run Deficit: A Comparison of Approaches
14 mai 2019 · This report examines alternative approaches to reducing annual budget deficits and decisions about how to bring the national debt under control |
|
Public Debt and Deficits: - Deloitte
Public debt (alternatively, national debt or sovereign debt) is debt comparison misses the point which we have been trying to make; it is not just the debt level |




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/us-deficit-by-year-3306306_final-6fe17db00c73413eb26c0888ba0b5952.png)