non negativity constraints lagrangian
|
Applications of Lagrangian: Kuhn Tucker Conditions
Figure 1: We require that therefore either λ1(B − Pxx − Pyy) = 0 λ1 = 0 or B − Pxx − Pyy = 0 If we interpret λ1as the marginal utility of the budget (Income) then if the budget constraint is not met the marginal utility of additional B is zero (λ1 = 0) (2) Similarly for the ration constraint either x − x = 0 or λ2 = 0 |
|
Constrained Optimization Using Lagrange Multipliers
Jul 10 2020 · The negative value of λ∗ indicates that the constraint does not affect the optimal solution and λ∗ should therefore be set to zero Setting λ∗ = 0 JA(x λ) is minimized at x∗ = 0 Figure 2(a) plots JA(x λ) for a few negative values of λ and Figure 2(b) plots contours of JA(x λ) 12 |
|
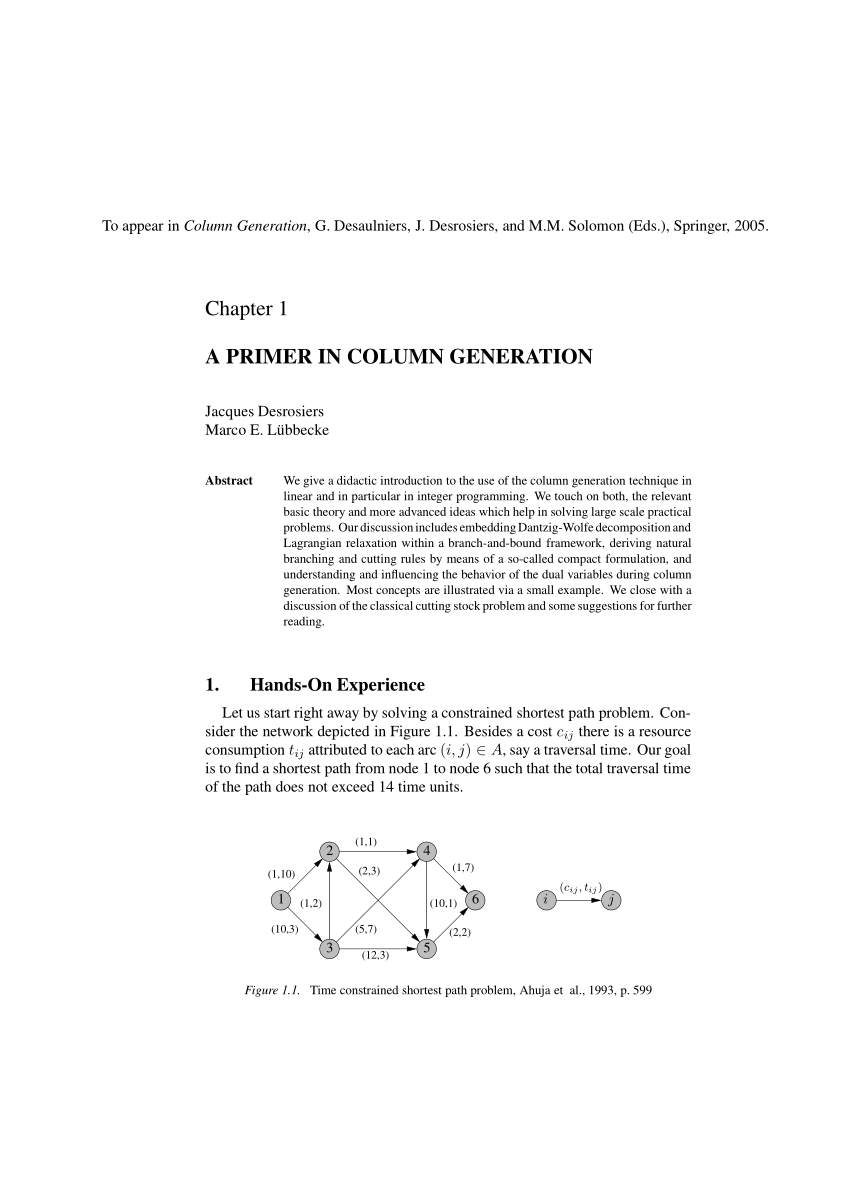
1403/14003 Fall 2016 Lecture 4 Notes
consumer would prefer to choose a bundle with negative quantities of xand positive quantities of y That’s not feasible in the real world So to solve the problem using theLagrangianmethodweimposethesenon-negativityconstraintstopreventanon-sensicalsolution Anothertypeof“corner”solutioncanresultfromindivisibilitiesthebundle(oftencalled |
How to solve a non sensical problem using the Lagrangian method?
That’s not feasible in the real world. So to solve the problem using the Lagrangian method, we impose these non-negativity constraints to prevent a non- sensical solution. Another type of “corner” solution can result from indivisibilities the bundle (often called integer constraints).
Why do we impose non-negativity constraints in the Lagrangian method?
The consumer would prefer to choose a bundle with negative quantities of x and positive quantities of y. That’s not feasible in the real world. So to solve the problem using the Lagrangian method, we impose these non-negativity constraints to prevent a non- sensical solution.
Which equality constraints should be included in a Lagrangian function?
Since equality constraints always have to be active at the constrained optimum, they are all required to be included in the Lagrangian function with an associated non-zero Lagrangian multiplier denoted λ9, λ10, λ11, λ12, λ13, λ14, λ15 ≠ 0. We are now ready to form our Lagrangian function of the general form below.
How to assign zero Lagrange multipliers to inactive constraints?
Assigning zero Lagrange multipliers to the inactive constraints, we obtain ∇f(x ∗) + r ∑ j = 1μ ∗ j ∇gj(x ∗) = 0 with μ ∗ j = 0 ∀j ∉ A(x ∗).
|
Non-negativity constraints on the variables over which you are
You could include each of the non-negativity constraints explicitly adding each as a constraint in the Lagrangian with an associated. Lagrange multiplier. |
|
System identification under non-negativity constraints - Applications
Feb 28 2014 1.1.2 Non-negativity constraints in system identification . ... where ? is the vector of non-negative Lagrange multipliers. The Karush-Kuhn-. |
|
1 Constrained Optimization
A constrained optimization problem (with two unknowns) consists of. - an objective function there are non-negative Lagrangian multipliers ?1?2 |
|
Constrained Optimization
Aug 13 2013 Consider the following general constrained optimization problem: ... Now consider the Lagrangian without the nonnegativity constraints |
|
Non-negativity constraints on the pre-image for pattern recognition
Dec 26 2018 nonlinear pattern recognition under non-negativity constraints. ... where µ represents the vector of non-negative Lagrange multipliers. |
|
Kuhn Tucker Conditions
Univariate function f with non-negativity constraint. We find for the maximum x? of f: (new non-negativity constraint). Lagrange function:. |
|
Constrained Optimization Using Lagrange Multipliers
augmented by the constraint equations through a set of non-negative multiplicative Lagrange multipliers ?j ? 0. The augmented objective function |
|
A fast non-negativity-constrained least squares algorithm
true least squares non-negativity-constrained models is typically many times longer than equal to s (step B5) and a new set of Lagrange multipliers w is ... |
|
Applications of Lagrangian: Kuhn Tucker Conditions
Lagrange method easily allows us to set up this problem by adding the second constraint in in addition the non-negativity constraint x ? 0 and y ? 0. |
|
A fully Lagrangian non-parametric bias model for dark matter halos
We present a non-parametric Lagrangian biasing model and fit the ratio of the halo 3.4 Effects of the non-negativity and normalization constraints. |
|
Non-negativity constraints on the variables over - Nolan H Miller
You could include each of the non-negativity constraints explicitly, adding each as a constraint in the Lagrangian with an associated Lagrange multiplier |
|
Constrained Optimization
13 août 2013 · unconstrained optimization problem, not a constrained one Now consider the Lagrangian without the nonnegativity constraints, and call it |
|
1 Constrained Optimization - peopleexeteracuk - University of Exeter
If the k-the constraint is not binding, then it is superfluous in the sense that we could leave it out from there are non-negative Lagrangian multipliers λ1,λ2, λK |
|
Kuhn Tucker Conditions - Mathematical Methods - Foundations of
Non-Negativity Constraint ▶ x∗ is an interior point of the feasible region: x∗ > 0 and f (x∗) = 0; or ▶ x∗ is a boundary point of the feasible region: x∗ = 0 and f (x∗) ≤ 0 |
|
Constrained Optimization Using Lagrange Multipliers - Duke People
augmented by the constraint equations through a set of non-negative multiplicative Lagrange multipliers, λj ≥ 0 The augmented objective function, JA( x), is a |
|
Applications of Lagrangian: Kuhn Tucker Conditions
Lagrange method easily allows us to set up this problem by adding the The Lagrange becomes in addition, the non-negativity constraint x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0 |
|
Nonnegativity Constraints in Numerical Analysis - Wake Forest
Key Words: nonnegativity constraints, nonnegative least squares, matrix and tensor fac- torizations is a generalization of the method of Lagrange multipliers |
|
Kuhn-Tucker-Lagrange conditions: basics
the fact that the constraints are formulated as inequalities, Lagrange multipliers will be non-negative Kuhn- Tucker conditions, henceforth KT, are the necessary |
|
CONSTRAINED OPTIMIZATION
Let us define Lagrange multipliers ρ1, ρ2, , ρn corresponding to the non- negativity constraints Then in the K-K-T conditions we have via complementary |
|
Lagrange multipliers and optimization problems - csail
We will denote the Lagrange multiplier by α to be consistent with the SVM problem Finding the smallest (non-negative) α for which the constraint is satisfied |