antibodies are produced by what cells
Are antibodies heterogeneous?
In a normal individual, antibodies are extremely heterogeneous. Heterogeneity of antibodies makes sequencing impossible (each B cell clone produces a unique version of antibody). Multiple myeloma: cancer derived from an antibody producing cells (plasma B cell).
Why are antibodies produced in secondary lymphoid organs?
Antibodies are produced primarily to mediate the immune response towards foreign pathogens, as part of the adaptive immune response. Pathogen recognition by B cells in secondary lymphoid organs allows differentiation into memory B cells and plasma cells.
How are antibodies produced?
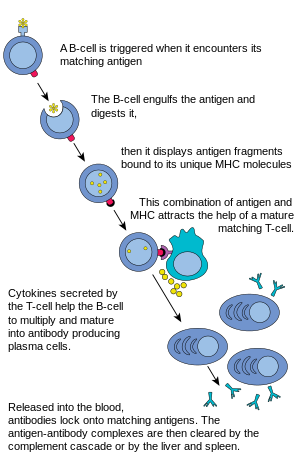
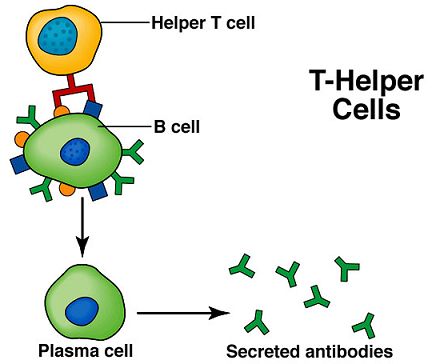
Antibodies are produced by specialized white blood cells called B lymphocytes (or B cells ). When an antigen binds to the B-cell surface, it stimulates the B cell to divide and mature into a group of identical cells called a clone. The mature B cells, called plasma cells, secrete millions of antibodies into the bloodstream and lymphatic system.
Overview
antibody, a protective protein produced by the immune system in response to the presence of a foreign substance, called an antigen. Antibodies recognize and latch onto antigens in order to remove them from the body. A wide range of substances are regarded by the body as antigens, including disease-causing organisms and toxic materials such as insec
How antibodies work
When an alien substance enters the body, the immune system is able to recognize it as foreign because molecules on the surface of the antigen differ from those found in the body. To eliminate the invader, the immune system calls on a number of mechanisms, including one of the most important—antibody production. Antibodies are produced by specialized white blood cells called B lymphocytes (or B cells). When an antigen binds to the B-cell surface, it stimulates the B cell to divide and mature into a group of identical cells called a clone. The mature B cells, called plasma cells, secrete millions of antibodies into the bloodstream and lymphatic system. As antibodies circulate, they attack and neutralize antigens that are identical to the one that triggered the immune response. Antibodies attack antigens by binding to them. The binding of an antibody to a toxin, for example, can neutralize the poison simply by changing its chemical composition; such antibodies are called antitoxins. By attaching themselves to some invading microbes, other antibodies can render such microorganisms immobile or prevent them from penetrating body cells. In other cases the antibody-coated antigen is subject to a chemical chain reaction with complement, which is a series of proteins found in the blood. The complement reaction either can trigger the lysis (bursting) of the invading microbe or can attract microbe-killing scavenger cells that ingest, or phagocytose, the invader. Once begun, antibody production continues for several days until all antigen molecules are removed. Antibodies remain in circulation for several months, providing extended immunity against that particular antigen. britannica.com
Antibodies and B cells
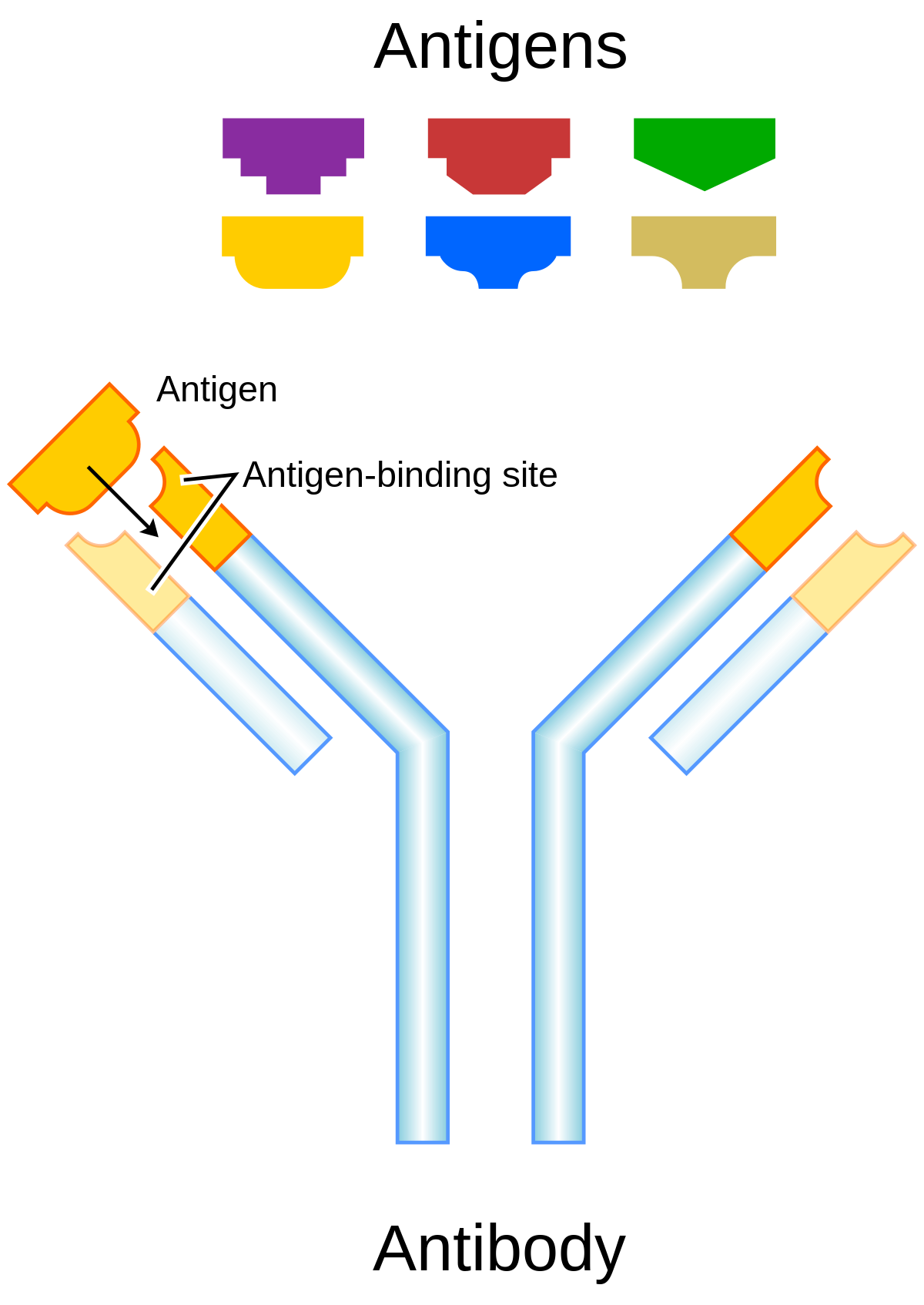
B cells and antibodies together provide one of the most important functions of immunity, which is to recognize an invading antigen and to produce a tremendous number of protective proteins that scour the body to remove all traces of that antigen. Collectively B cells recognize an almost limitless number of antigens; however, individually each B cell can bind to only one type of antigen. B cells distinguish antigens through proteins, called antigen receptors, found on their surfaces. An antigen receptor is basically an antibody protein that is not secreted but is anchored to the B-cell membrane. Britannica Quiz Medical Terms and Pioneers Quiz All antigen receptors found on a particular B cell are identical, but receptors located on other B cells differ. Although their general structure is similar, the variation lies in the area that interacts with the antigen—the antigen-binding, or antibody-combining, site. This structural variation among antigen-binding sites allows different B cells to recognize different antigens. The antigen receptor does not actually recognize the entire antigen; instead it binds to only a portion of the antigen’s surface, an area called the antigenic determinant or epitope. Binding between the receptor and epitope occurs only if their structures are complementary. If they are, epitope and receptor fit together like two pieces of a puzzle, an event that is necessary to activate B-cell production of antibodies. britannica.com

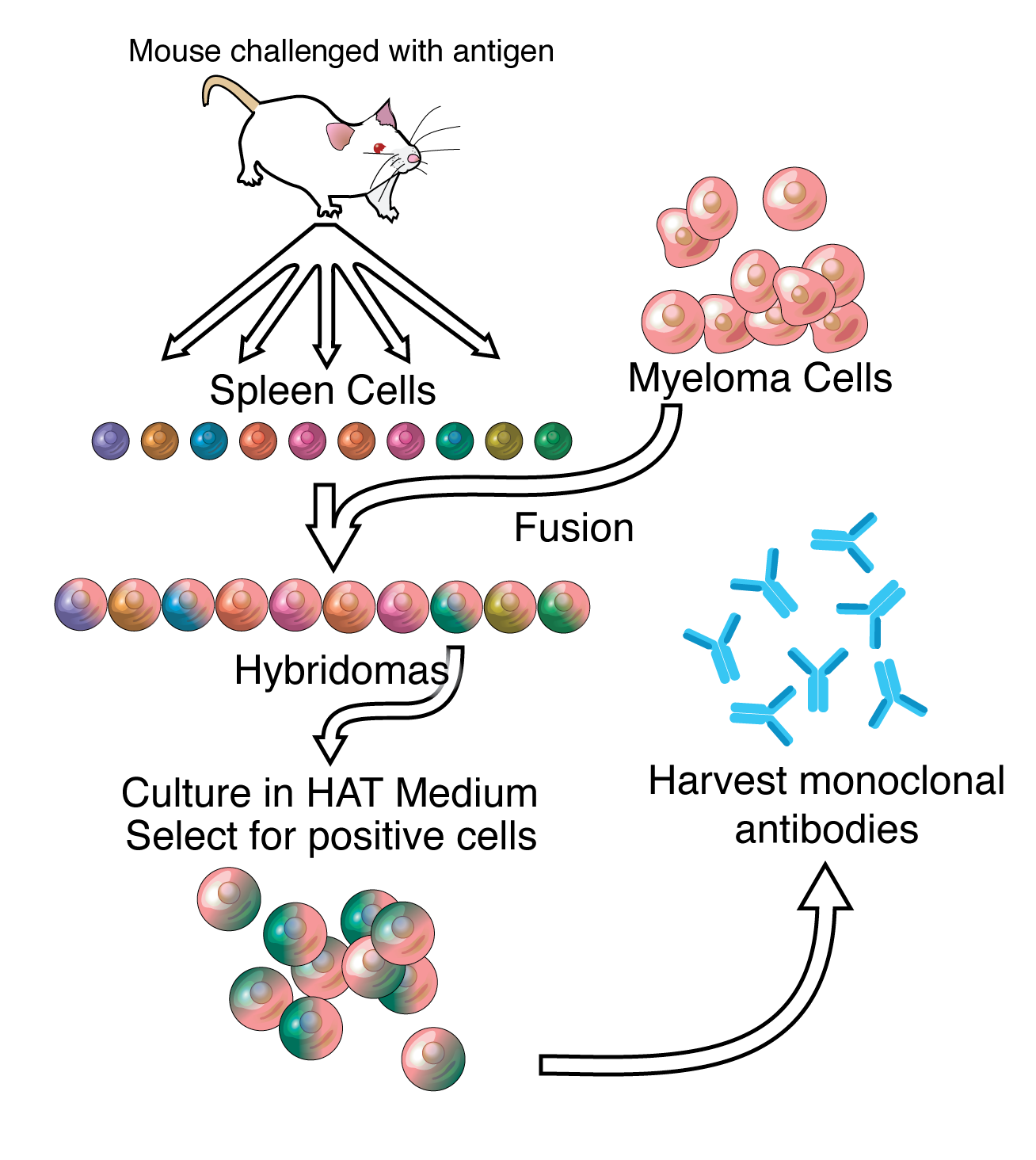
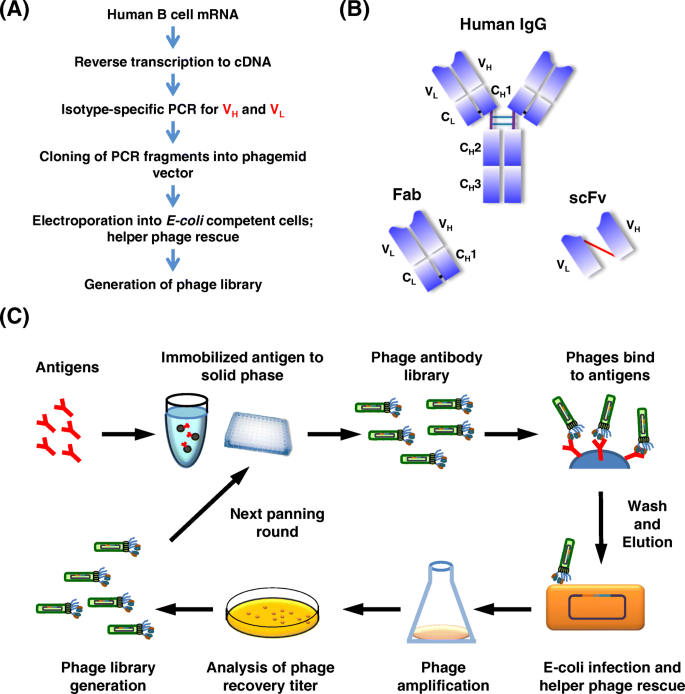
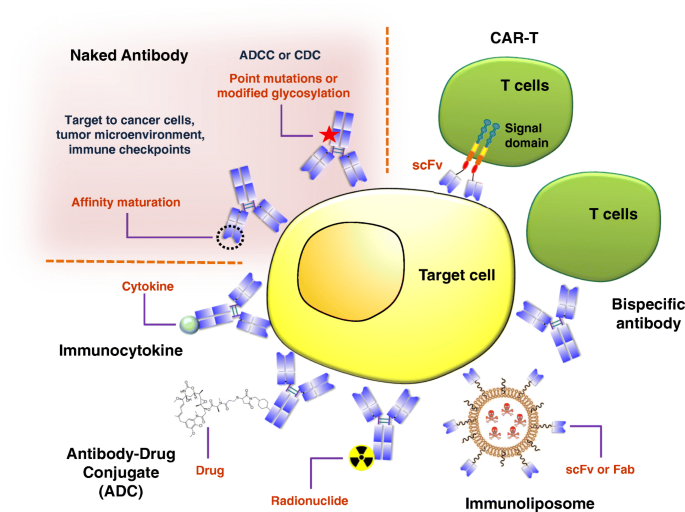
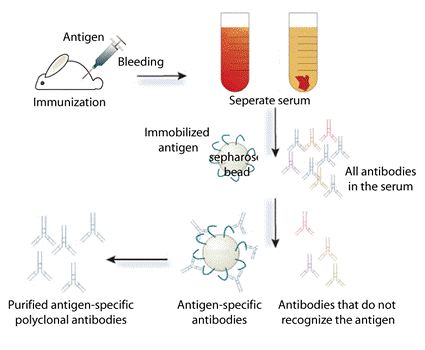
Monoclonal Antibodies and its Production

Antibody structure and function Immunoglobulin

GCSE Biology
|
MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY PRODUCTION 1999
Committee on Methods of Producing Monoclonal Antibodies. Institute for Laboratory Animal Research These antibodies are produced by cell. |
|
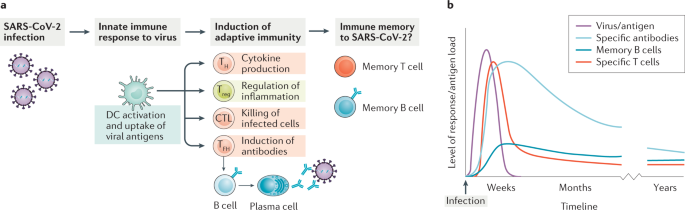
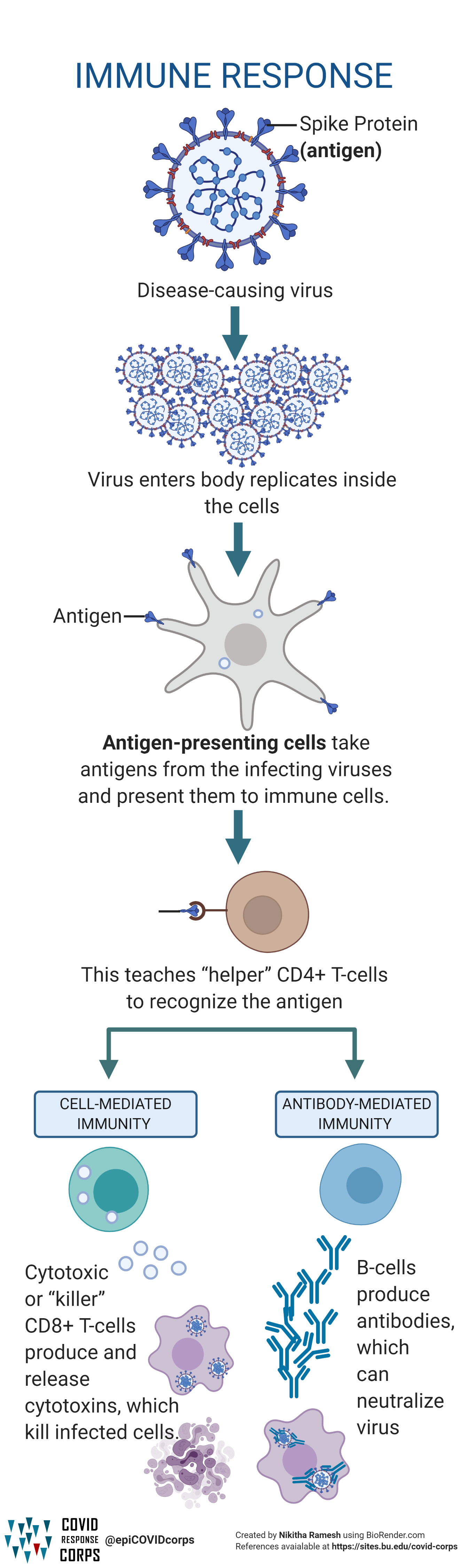
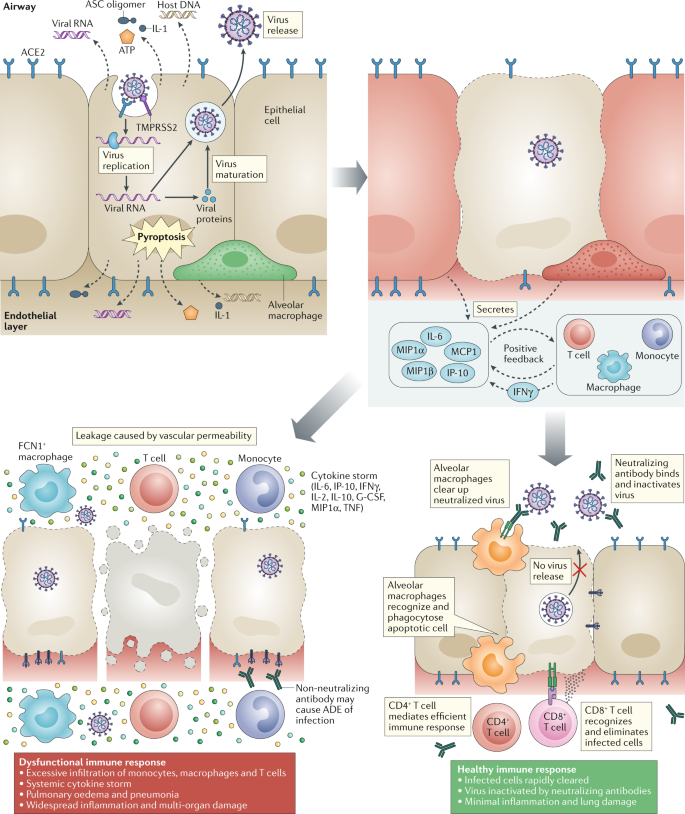
COVID-19 immune response
2 août 2020 B CELLS (Antibody response). • produce antibodies that are specific to that virus. • IgM antibodies are produced first and disappear after a ... |
|
London 18 December 2008 EMEA/CHMP/BWP/157653/2007
18 déc. 2008 antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC). Monoclonal antibodies may be generated by ... |
|
An outlook on bispecific antibodies: Methods of production and
The therapeutic use of monoclonal antibodies consists in activation of antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) complement-dependent cytotoxicity ( |
|
PRODUCTION AND QUALITY CONTROL OF MONOCLONAL
Murine monoclonal antibodies are almost always prepared using cell lines (hybridomas) made by fusion of lymphocytes from an immunised donor with myeloma cells. |
|
Chapter 1: Principles Vaccination; Epidemiology and Prevention of
interacting cells called the immune system. Since most organisms (e.g. bacteria |
|
An outlook on bispecific antibodies: Methods of production and
The therapeutic use of monoclonal antibodies consists in activation of antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) complement-dependent cytotoxicity ( |
|
Blood Groups and Red Cell Antibodies in Pregnancy
How red cell antibodies are formed during pregnancy. Mother's red blood cells. Baby's red blood cells. Mother's antibody. A. This baby has a different blood. |
|
Human-human hybridomas producing monoclonal antibodies of
they are foreign proteins. Chimeric hybridomas have been generated by fusing mouse myeloma cells with human im- munoglobulin-producing cells (3); however |
|
Theories of Antibodies Production ppt
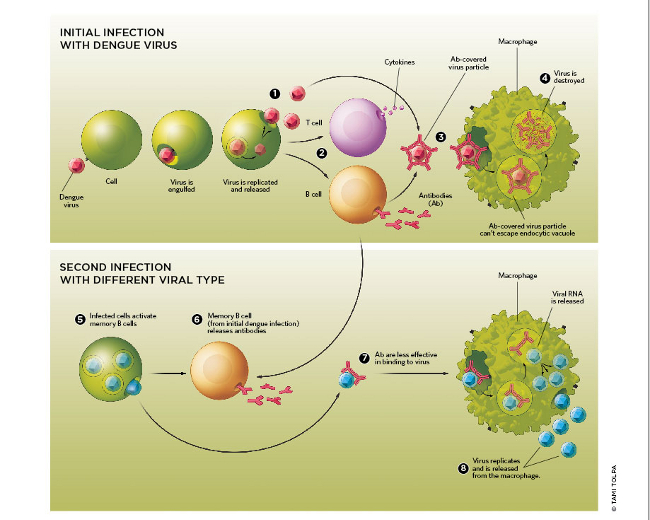
In the secondary immune response, memory cells are activated by a second exposure to the same antigen, which initiates a rapid and anamnestic response 3 Random somatic hypermutations during clonal expansion cause the production of B cells with increased antibody-binding affinity for their antigens |
|
Man-made antibodies - Nature
2) Antibodies kill cells by triggering the complement cascade at the cell surface, with consequent lysis, or by binding to receptors on the |
|
PRODUCTION AND QUALITY CONTROL OF MONOCLONAL
Humanised antibodies contain a minimum of rodent sequence Suitable cells for expression of the rDNA monoclonal antibody genes are mammalian cell lines |
|
Amc technical briefs - The Royal Society of Chemistry
In mammals, the antibodies are produced by a subclass of white blood cells known as the B lymphocytes which develop in adult bone marrow or foetal liver |
|
MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY PRODUCTION 1999
mouse, the hybridoma cells multiply and produce fluid (ascites) in its abdomen; this fluid contains a high concentration These antibodies are produced by cell |
|
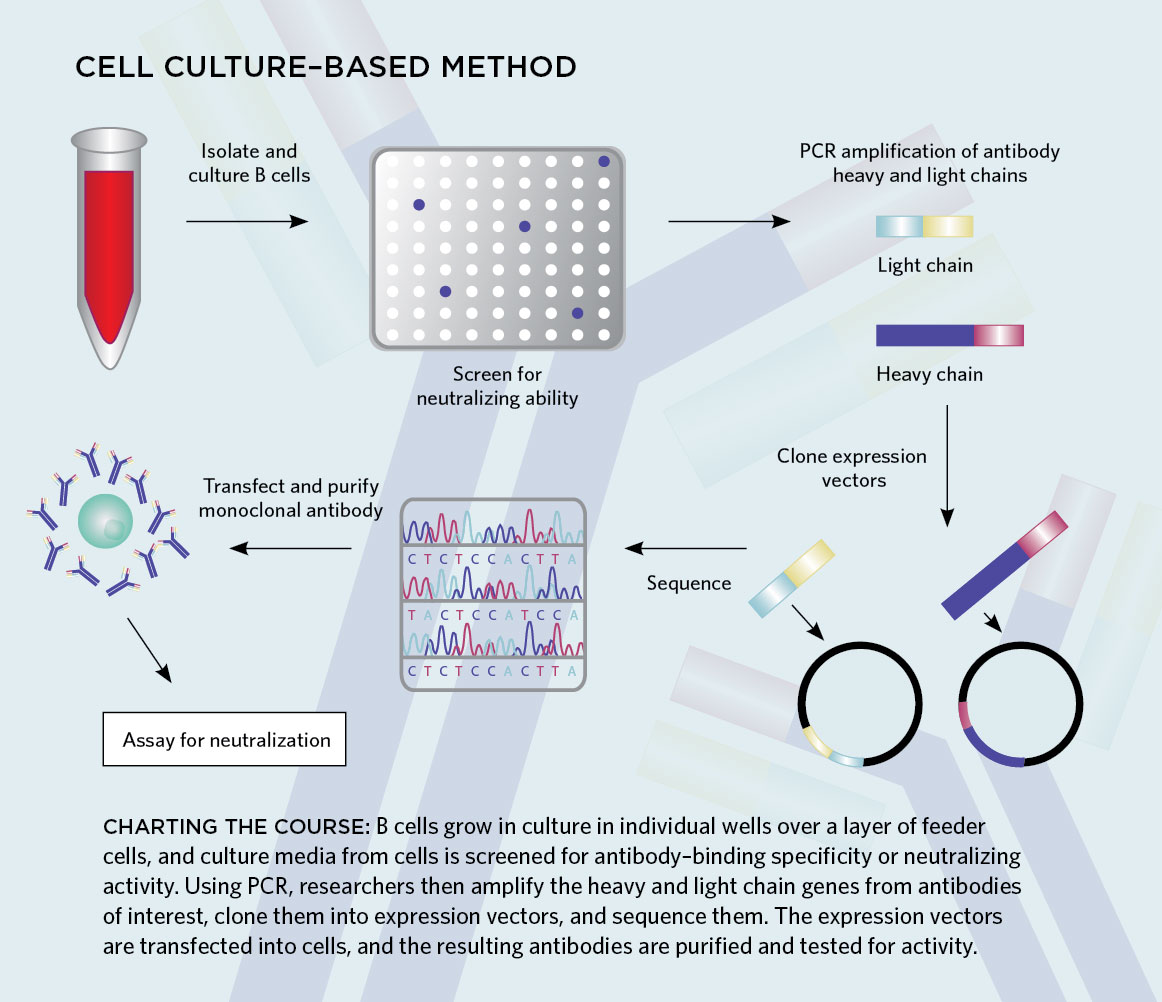
Human monoclonal antibodies produced by primary in vitro - PNAS
Human monoclonal antibodies produced by primary in vitro immunization of peripheral blood lymphocytes (hybridoma/T-cell-dependent antigen/ lysosomotropic |
|
Vaccine Immunology - WHO World Health Organization
Processes through which antigen-specific B cells undergo somatic hypermutation and affinity-based selection, resulting in B cells that produce antibodies with |
|
Production of Monoclonal Antibodies In Vitro Immunization - CORE
Following immunization, cells were fused with mouse myeloma cells (SP2/0, Ag 8 653) and cultured for 2-3 wk before initial screening for antibody In five |


















-Flow%20Cytometry-NBP2-00814-img0002.jpg)



-Flow%20Cytometry-NBP2-00814-img0001.jpg)


![Monoclonal antibodies in immunoassays - [PDF Document] Monoclonal antibodies in immunoassays - [PDF Document]](https://cdn.britannica.com/33/94933-004-7EE5BA10/cells-antibodies-antigens-B.jpg)