antibodies are produced by which line of defense
|
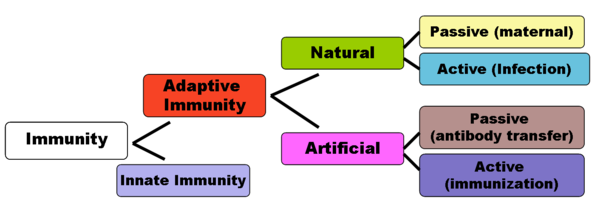
Immunity First Line of Defense
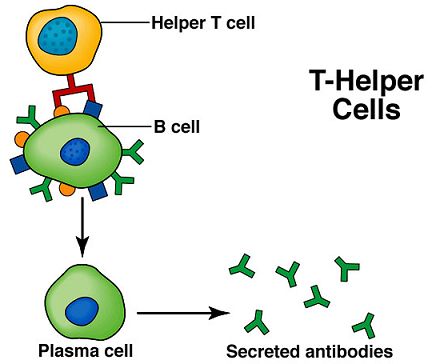
Antibodies •Also called immunoglobulins (Ig) •Produced by plasma cells (mature B cells) in response to exposure to antigen •Classes of antibody – IgG - most abundant class (80-85 ) •major antibody found in fetus & newborn – IgA – found in blood and secretions – IgM – largest produced 1st in initial response to antigen |
How do activated B cells protect against pathogens?
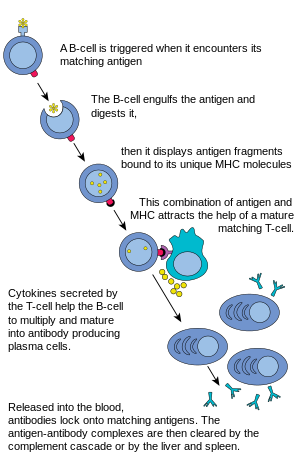
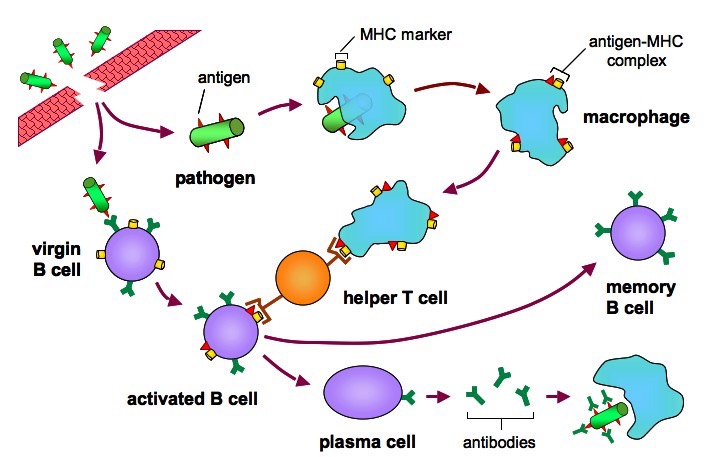
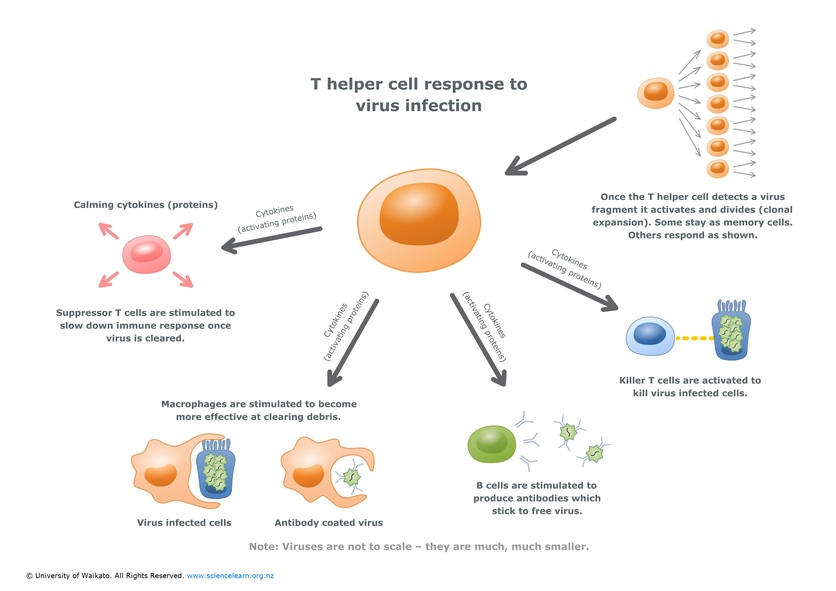
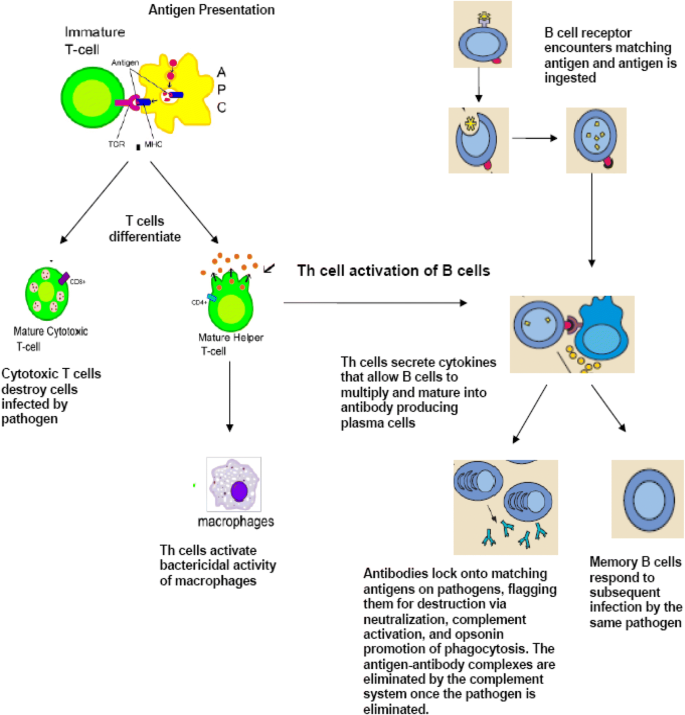
Activated B cells grow rapidly, producing plasma cells, which release antibodies into the bloodstream, and memory B cells, which store information about the pathogen in order to provide future immunity. Antibodies alone are often not enough to protect the body against pathogens.
How do B cells recognize antigens?
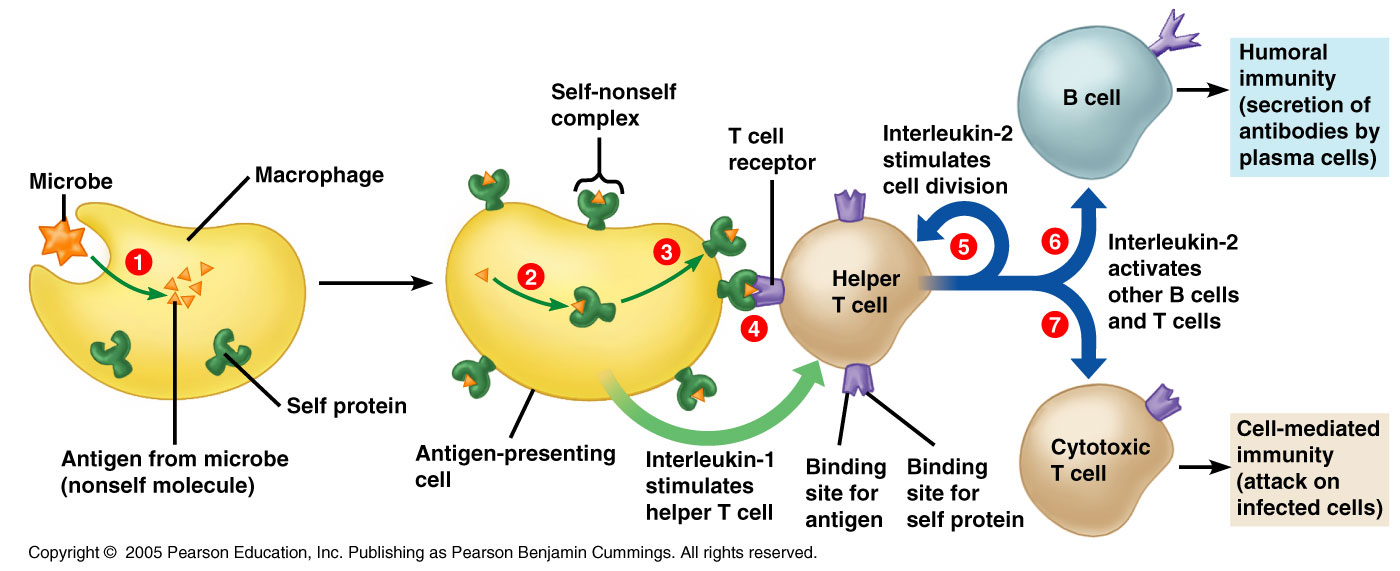
B cells arise from hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow and, following maturation, leave the marrow expressing a unique antigen-binding receptor on their membrane. Unlike T cells, B cells can recognize antigens directly, without the need for APCs, through unique antibodies expressed on their cell surface.
Why are antibodies important in preventing bacterial toxins from entering cells?
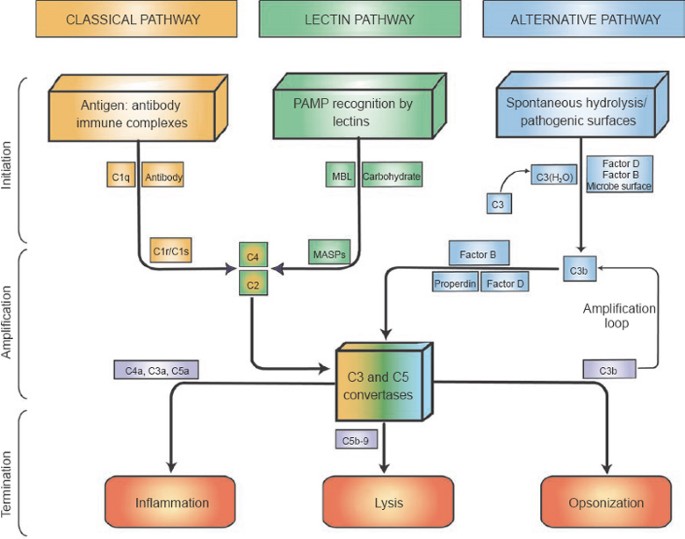
Neutralization by antibodies is also important in preventing bacterial toxins from entering cells. Antibodies protect against bacteria that multiply outside cells mainly by facilitating uptake of the pathogen by phagocytic cells that are specialized to destroy ingested bacteria. Antibodies do this in either of two ways.
How are antibodies produced?
Antibodies are produced by B cells (specialized white blood cells ). When an antigen comes into contact with a B cell, it causes the B cell to divide and clone. These cloned B cells — or plasma cells — release millions of antibodies into your bloodstream and lymph system.
Overview
Antibodies are protective proteins produced by your immune system. They attach to antigens (foreign substances) — such as bacteria, fungi, viruses and toxins — and remove them from your body. Contents Arrow Down OverviewFunctionAnatomyConditions and Disorders Contents Arrow Down my.clevelandclinic.org
Function
What are the 5 types of antibodies and their function? Antibodies are categorized into five classes according to their location. Each one is labeled by a letter, which is attached to an abbreviation of the term “immunoglobulin” (Ig): \tAntibody Type\tFunction IgA\tFound in saliva, tears, mucus, breast milk and intestinal fluid, IgA protects against ingested and inhaled pathogens.\t IgD\tThis antibody is found on the surface of your B cells. Though its exact function is unclear, experts think that IgD supports B cell maturation and activation.\t IgE\tFound mainly in your skin, lungs and mucus membranes, IgE antibodies cause your mast cells (a type of white blood cell) to release histamine and other chemicals into your bloodstream. IgE antibodies can cause allergic reactions.\t IgG\tThis is the most common antibody, making up approximately 70% to 75% of all immunoglobulins in your body. It’s found mainly in blood and tissue fluids. IgG antibodies help protect your body from viral and bacterial infections.\t IgM\tFound in your blood and lymph system, IgM antibodies act as the first line of defense against infections. They also play a large role in immune regulation.\t \tAntibody Type IgA\t Function\t Found in saliva, tears, mucus, breast milk and intestinal fluid, IgA protects against ingested and inhaled pathogens.\t IgD\t Function\t This antibody is found on the surface of your B cells. Though its exact function is unclear, experts think that IgD supports B cell maturation and activation.\t IgE\t Function\t Found mainly in your skin, lungs and mucus membranes, IgE antibodies cause your mast cells (a type of white blood cell) to release histamine and other chemicals into your bloodstream. IgE antibodies can cause allergic reactions.\t IgG\t Function\t This is the most common antibody, making up approximately 70% to 75% of all immunoglobulins in your body. It’s found mainly in blood and tissue fluids. IgG antibodies help protect your body from viral and bacterial infections.\t IgM\t Function\t Found in your blood and lymph system, IgM antibodies act as the first line of defense against infections. They also play a large role in immune regulation.\t Advertisement my.clevelandclinic.org
Anatomy
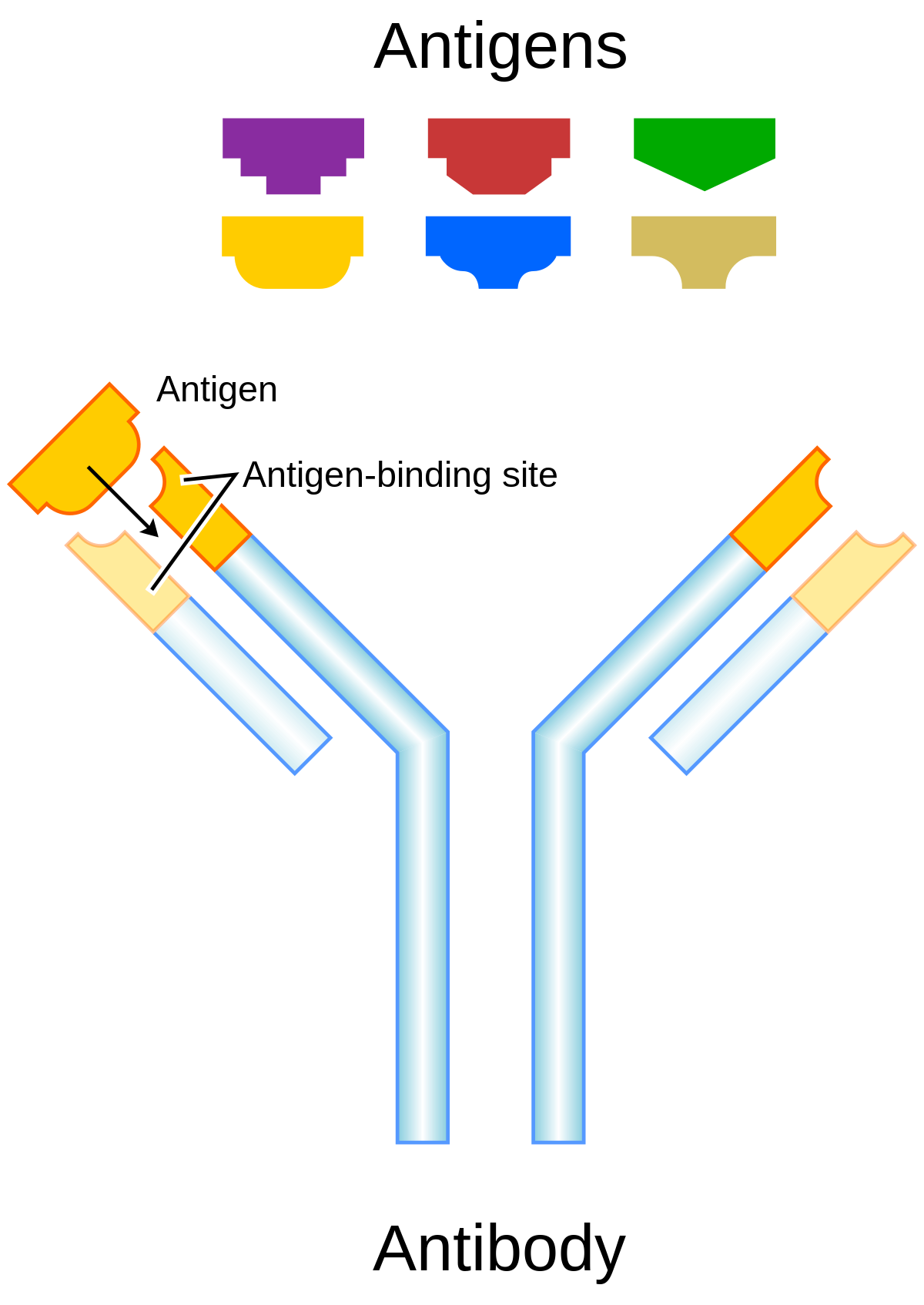
What are antibodies made of? Antibodies are proteins. Each antibody has four polypeptides (peptides that consist of two or more amino acids), including two heavy chains and two light chains. What do antibodies look like? Each antibody structure consists of two heavy chains and two light chains, which join to form a Y-shaped molecule. Each type of antibody has a different amino acid sequence at the tips of the “Y” which is why each antibody is shaped differently. my.clevelandclinic.org
Conditions and Disorders
What conditions can monoclonal antibodies treat? Each type of monoclonal antibody targets a specific antigen. As a result, monoclonal antibodies can treat a number of health conditions, including: Cancer. Rheumatoid arthritis. Heart disease. Multiple sclerosis (MS). Ulcerative colitis. Lupus. Crohn’s disease. Psoriasis. Organ transplant rejection. What are COVID antibodies? Antibodies to the virus that causes COVID-19 can be found in the blood of people who have recovered from the infection or those who have received the COVID-19 vaccine. If you’ve already had COVID-19, getting the vaccine increases your body’s antibody response and improves your protection against the virus. What are thyroglobulin antibodies? Thyroglobulin antibodies are often found in people who have thyroid problems, such as hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism. These antibodies target thyroglobulin proteins (precursors of thyroid hormones) and can potentially destroy the thyroid gland. my.clevelandclinic.org
|
21-1248 ELISA Simulation Kit
The body possesses several lines of defense against infection by A secondary antibody that recognizes antibodies produced by humans (anti-human. |
|
Communicable Disease Control Manual Chapter 2: Immunization
Adaptive immunity is the second line of defense against anything recognized as Antibodies produced are of the IgM class and immunologic memory is not. |
|
Spending the Best but Banking the Rest
Nov 25 2020 produce protective antibodies as a first line of defense against reinfection |
|
Chapter 17: Specific Host Defenses: The Immune Response The
Immune Response: Third line of defense. Involves production of antibodies and generation of specialized lymphocytes against specific antigens. Antigen: |
|
COVID-19 immune response
Aug 2 2020 produce antibodies that are specific to that virus. • IgM antibodies are produced first and disappear after a few weeks. • IgG antibodies are ... |
|
COVID-19 Neutralizing Antibodies in Breast Milk of Mothers
Apr 18 2022 antibodies and a first line of defense against infections for neonates ... a higher antibody production that is transferable to the infant. |
|
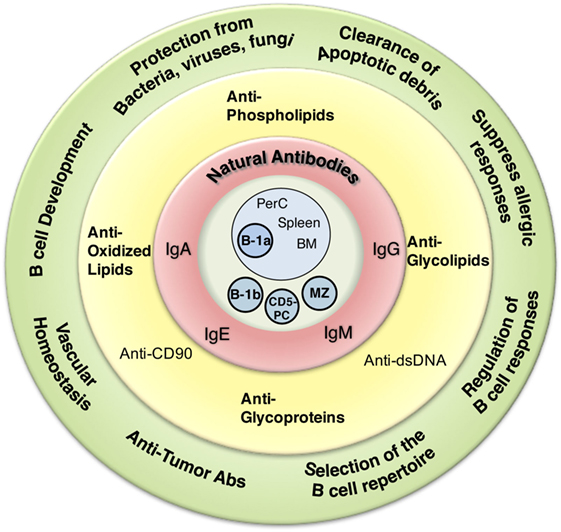
Natural Antibodies: from first line defense against pathogens to
Oct 23 2019 Subsequently |
|
Immunology Made Simple Ms. Ashleigh Freeman Princeton Senior
Natural immunity the first line of defense against foreign White blood cells that produce antibodies and aid in immune response memory are called… |
|
Defining Natural Antibodies
Jul 1 2017 present prior to the body encountering cognate antigen |
|
Human Defense Mechanisms First Line of Defense First Line of
Defense. – Chapter 8: Stress and Disease. 1. Innate Immunity: Second line of defense. – Inflammation ... Antibodies are produced by. A. B cells. |
|
Human Defense Mechanisms First Line of Defense First Line of
Defense – Chapter 8: Stress and Disease 1 Innate Immunity: Inflammation Wound Healing Chapter Second line of defense Antibodies are produced by |
|
Chapter 16/17: Immune system
Formed elements Second line of defense Complement system Chapter 17: Specific defenses Antibodies Humoral response Cellular response Lab |
|
Natural Antibodies: from first line defense against pathogens to
23 oct 2019 · These are divided into five classes/isotypes, namely IgG, IgM, IgA, IgE, and IgD [4 ] Antibody production is the main function of differentiated B |
|
1 The Immune System 2 Types of Defense Mechanisms Lines of
the production of antibodies by inactivating Specific Defenses • 1st 2nd line defenses - Can not discriminate between invaders • 3rd line defense - specific |
|
IMMUNE SYSTEM
Second line of defense – phagocytic white blood cells, antimicrobial proteins, and other cells • Inflammatory The plasma cells produce antibodies also called |
|
Acting Out the Immune Response - The American Association of
invading pathogen The topics to be covered in this activity are: the first line of defense Antibodies are produced by white blood cells called B lymphocytes |
|
76 The immune system - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
Inflammation and phagocytosis are your body's first line of defence if B lymphocytes produce antibodies to kill pathogens or destroy the toxins they produce |
|
Chapter 14 Topics - Defense Mechanisms - Non-specific immunity
specific (Third line) immune defense systems • White blood cells Components Hemopoiesis • Production of blood antibodies Lymphatic system • Fluids |
|
Principles of Immunology - BC Centre for Disease Control
Adaptive immunity is the second line of defense against anything recognized as The antibodies produced in response to T cell-dependent antigens are |