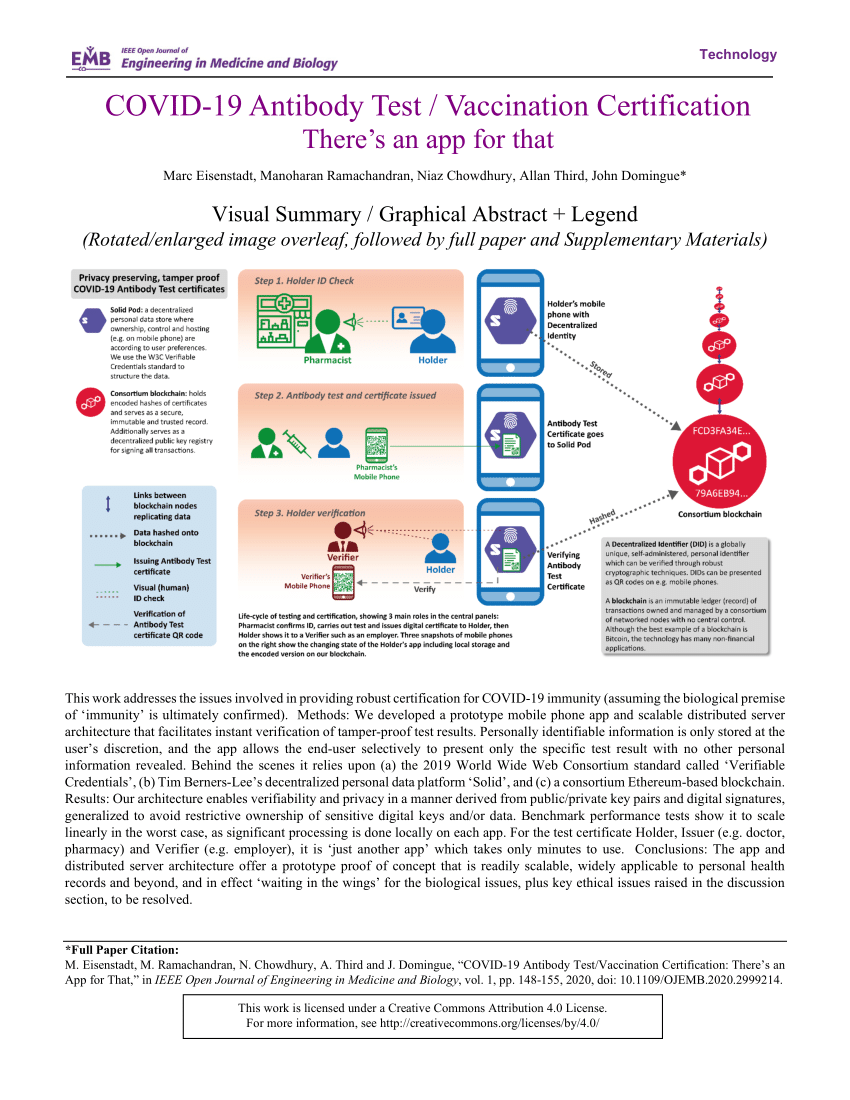
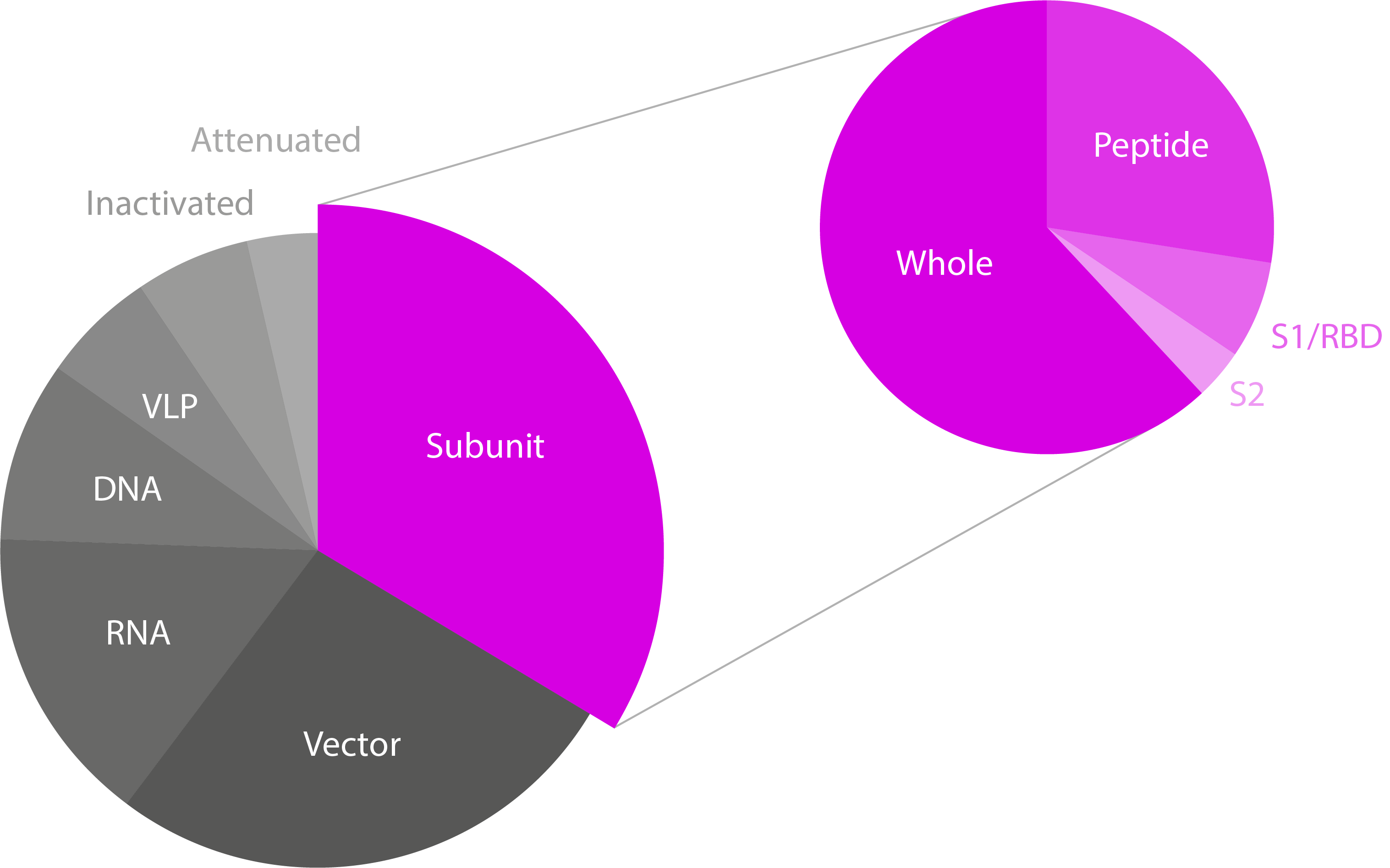
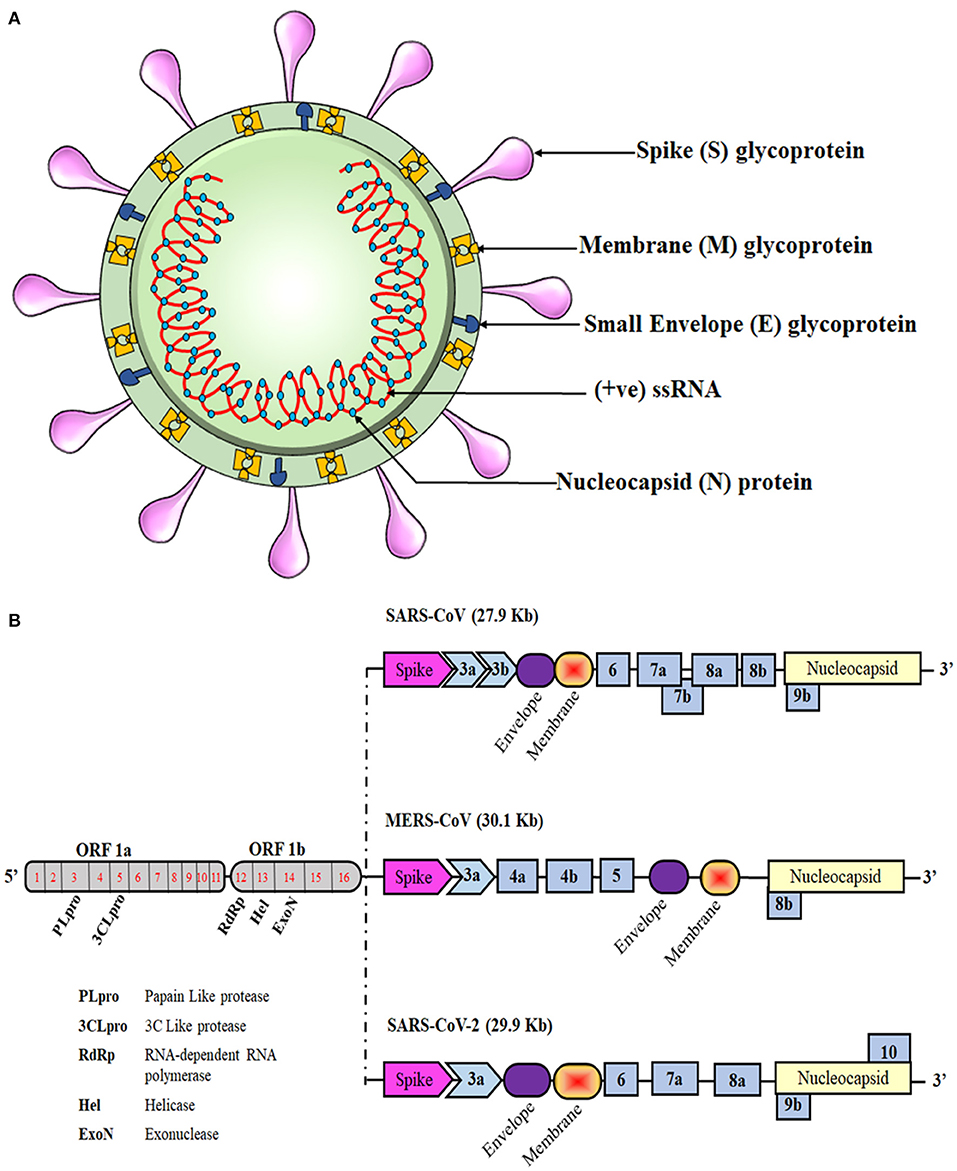
antibody vaccine examples
|
EpiVac Pink Book Web-on-Demand Series Principles of
May 18 2020 · Antibodies attaching to antigens Antibody is specific to a single antigen or closely related group of antigens Used for diagnosis of and therapy for certain cancers and autoimmune and infectious diseases as well as prevention of transplant rejection |
|
Immunology and Vaccine-Preventable Diseases
Homologous pooled human antibody also known as immune globulin is produced by combining the antibody fraction specifically the class of antibody referred to as IgG from the blood of thousands of adult donors Because it comes from many different donors it contains antibody to many different antigens |
|
Use and interpretation of diagnostic vaccination in primary
variable immunodeficiency specific antibody deficiency The majority of patients given a diagnosis of primary immu-nodeficiency disease (PIDD) have some impairment of humoral immunity These most typically include quantitative deficiencies of antibodies qualitative deficiencies of antibodies or both |
|
Principles of Vaccination
1 Immunity Immunity Self vs “nonself” Protection from infectious diseases Usually indicated by the presence of antibody Generally specific to a single organism Antigen Live or inactivated substances (e g viruses bacteria toxins) Capable of stimulating an immune response Antigen = antibody generator Antibody Protein molecules (immunoglobulins) |
Vaccines contribute to active immunity by providing us with a controlled way to create an immune response.
When a vaccine is introduced, our immune system treats it like any other exposure.
What type of immunity is an antibody injection?
Passive immunity can occur naturally, such as when an infant receives a mother's antibodies through the placenta or breast milk, or artificially, such as when a person receives antibodies in the form of an injection (gamma globulin injection).
What is an antibody vaccine?
An antibody is a Y-shaped protein produced by B cells, which are part of the immune system.
There are several different kinds of antibodies, and typically vaccines are designed to produce the antibodies that recognize and “tag” viruses as foreign invaders by binding to unique parts of a virus.
What are antigens in vaccines?
Vaccines contain killed, weakened, or synthetically manufactured versions of the disease-causing germ or parts of the germ called antigens.
Some newer vaccines (e.g., COVID-19 mRNA vaccines) contain instructions for producing antigens rather than the antigen itself.
|
CDC
Immunology and Vaccine-Preventable Diseases. To understand how vaccines work and polyclonal containing many types of antibodies in lesser quantities. |
|
COVID-19 vaccines & immune response
8 mar. 2021 EXAMPLE OF VACCINES. Inactivated virus. Inactivated dead virus. Induces strong antibody response. Requires large quantities of virus. |
|
MRNA Booster Vaccination Enhances Antibody Responses against
30 jun. 2022 Vaccination Enhances Antibody. Responses against SARS-CoV2. Omicron Variant in Individuals. Primed with mRNA or Inactivated. Virus Vaccines. |
|
General Best Practice for Immunization; Epidemiology and
Inactivated vaccines can be administered before after |
|
MRNA Booster Vaccination Enhances Antibody Responses against
30 jun. 2022 Vaccination Enhances Antibody. Responses against SARS-CoV2. Omicron Variant in Individuals. Primed with mRNA or Inactivated. Virus Vaccines. |
|
Inactivated and live-attenuated seasonal influenza vaccines boost
3 feb. 2022 evaluate vaccine-elicited broadly neutralizing antibody (bNAb) responses against group 1 influenza A viruses in children. Repeated seasonal. |
|
Long-Term Immunity and Antibody Response: Challenges for
12 may. 2022 Antibodies 2022 11 |
|
Kinetics of the Neutralizing and Spike SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies
27 may. 2022 Inactivated virus vaccines may also carry a greater risk of post-vaccination breakthrough infection than mRNA vaccines [10]. In this study in ... |
|
Communicable Disease Control Manual Chapter 2: Immunization
3.5 Factors that Influence the Vaccine Immune Response . Examples of passive immunity are maternal antibodies (trans-placental and breast milk) and. |
|
Safety and Immunogenicity of Inactivated Bacillus subtilis Spores as
24 jun. 2022 Spores as a Heterologous Antibody Booster for. COVID-19 Vaccines ... For example a third dose of 30 µg homologous mRNA vaccine BNT162b2. |
|
Live attenuated vaccines - CDC
Hyperimmune globulins are used for postexposure prophylaxis for several diseases, including hepatitis B, rabies, tetanus, and varicella Heterologous hyperimmune serum is also known as antitoxin This product is produced in animals, usually horses (equine), and contains antibodies against only one antigen |
|
Understanding How Vaccines Work - CDC
antigens as dangerous and stimulates antibodies to attack them • B-lymphocytes are Examples of live, attenuated vaccines include measles, mumps, and |
|
Vaccine Immunology - WHO World Health Organization
monia21 in addition to invasive diseases Under most circumstances, inactivated vaccines do not elicit sufficiently high and sustained antibody titers on mucosal |
|
Immunity and How Vaccines Work - HSE
Anything that can be bound by an antibody • Fragments of Vaccines work by making us produce antibodies inactivated/conjugate/recombinant/subunit |
|
Principles of Immunology - BC Centre for Disease Control
3 2 Antibody Response to a Non-Replicating Vaccine Examples of passive immunity are maternal antibodies (trans-placental and breast milk) and injected |
|
Vaccine antigens - CORE
inactivated whole-pathogen vaccines, pioneered by the work of Louis Pasteur and concept of antigens ('antibody generators') as the ligands of antibodies |
|
Antibody Testing vs Vaccination Applications in Clinical - Biogal
or perform antibody testing on individual patients for the core vaccine- Exposure For example, a “positive” antibody test result for canine parvovirus correlates |
|
Greenbook chapter 1 immunity and how vaccines work - Govuk
antibodies or a combination acting against one or more antigens on the infecting The newest types of vaccine use the pathogen's genetic code as the vaccine; |