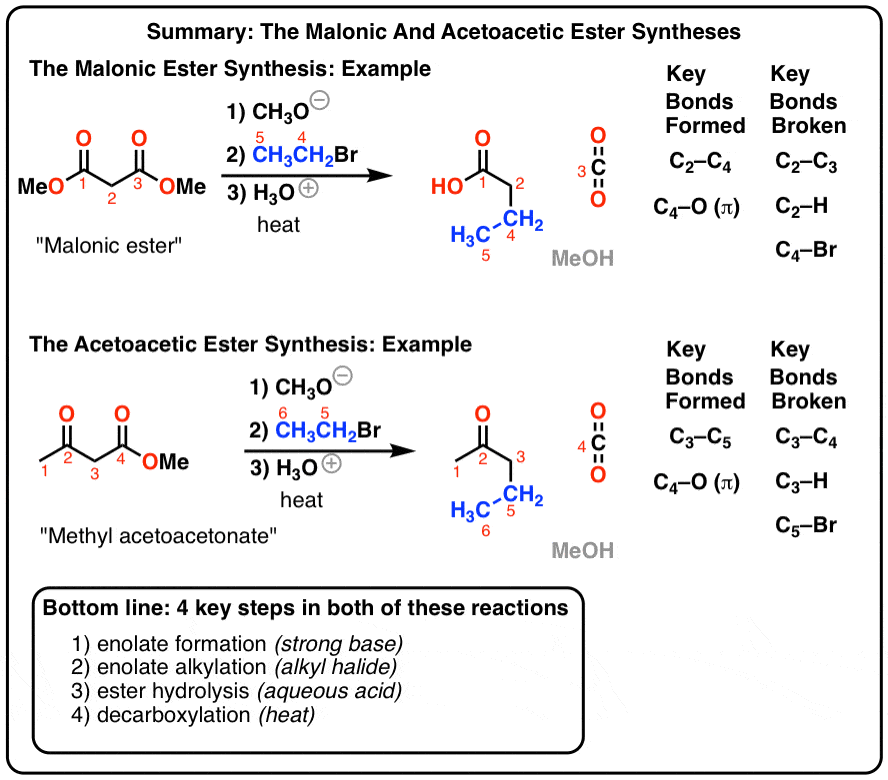
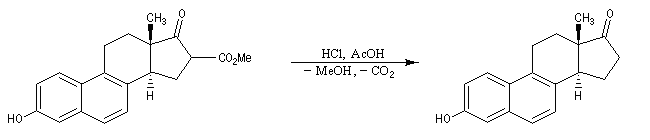saponification of cyclic esters
How are esters cleaved back into a carboxylic acid?
Esters can be cleaved back into a carboxylic acid and an alcohol by reaction with water and a base. The reaction is called a saponification from the Latin sapo which means soap. The name comes from the fact that soap used to be made by the ester hydrolysis of fats. Due to the basic conditions a carboxylate ion is made rather than a carboxylic acid.
What are acyclic and cyclic ester reactions?
All their reactions are applicable to both acyclic and cyclic esters, called lactones. An ester is hydrolyzed, either by aqueous base or aqueous acid, to yield a carboxylic acid plus an alcohol. Ester hydrolysis in basic solution is called saponification, after the Latin word sapo, meaning “soap.”
What is a saponification reaction?
The reaction is called a saponification from the Latin sapo which means soap. The name comes from the fact that soap used to be made by the ester hydrolysis of fats. Due to the basic conditions a carboxylate ion is made rather than a carboxylic acid. Esters can be cleaved back into a carboxylic acid and an alcohol by reaction with water and a base.
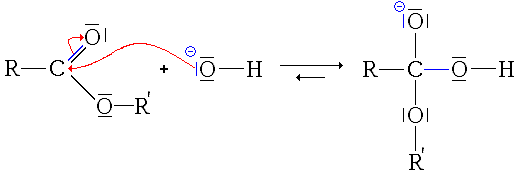
What is the mechanism of ester saponification?
The mechanism of ester saponification begins with the nucleophilic addition of a hydroxide ion at the carbonyl carbon to give a tetrahedral alkoxide intermediate. The carbonyl bond is reformed along with the elimination of an alkoxide (-OR) leaving group yielding a carboxylic acid.
Basic Hydrolysis of Esters
When esters are treated with hydroxide ion, followed by neutralization with acid, they are converted into carboxylic acids. This process is called basic hydrolysis of esters. Another name for it is saponification, since the carboxylate salts initially formed through hydrolysis are often used as soaps (sapon = soap in Latin). Many different hydroxid
The Mechanism For Basic Hydrolysis
The first step in saponification is nucleophilic addition of the hydroxide ion to the carbonyl carbon of the ester to form a tetrahedral intermediate. (See post: Nucleophilic Addition) This is followed by elimination of alkoxide (RO–) from the tetrahedral intermediate to give a carboxylic acid. This two step addition-elimination process is an examp
Saponification Is Irreversible Under Basic Conditions
If we can obtain carboxylic acids from esters under basic conditions, it’s worth asking if can we go in the opposite direction and obtain esters from carboxylic acids by using an alkoxide(RO(-) ? The answer is no. Saponification of an ester with HO(-) is irreversible. Getting the ester back is highly unfavorable under basic conditions.(Note 1– it c
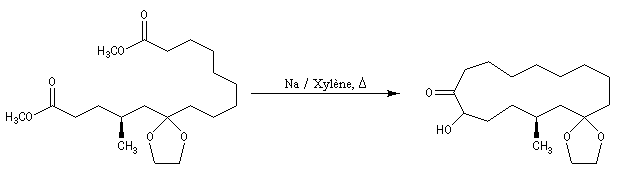
Basic Hydrolysis of Lactones
Any time you learn a new reaction it is worth the time to explore the intramolecular version. It involves no new concepts, but it looks weird, and for this reason intramolecular reactions make for good exam problems. In this case a cyclic ester, called a lactone, can be converted into an acyclic hydroxy-acid (Note 2) through addition of hydroxide i
Saponification of Fats
The origin of the term saponification comes from the Latin sapofor soap. Fatscontain a molecule of glycerol attached to three long-chain carboxylic acids via ester linkages. At some point in human history, some bright spark it discovered that lye (essentially NaOH) undergoes reaction with fats to give molecules that can act as detergents and soaps
Notes
Note 1. The Fischer esterification is the conversion of a carboxylic acid to an ester under acidic conditions (See post: The Fischer Esterification) Note 2. Sometimes called a “seco-acid” from the Latin seco, secaris, secare“to cut, sever”. masterorganicchemistry.com
References and Further Reading
On the mechanism of hydrolysis. The alkaline saponifications of amyl acetate Polanyi and A. L. Szabo Trans. Faraday Soc., 1934, 30, 508-512DOI: 10.1039/TF9343000508 One of the first mechanistic stu

Saponification

Fischer Esterification and Saponification

Saponification (Hydrolysis of Esters with OH-)
|
Mechanisms of Lactone Hydrolysis in Acidic Conditions
3 jui 2013 · ABSTRACT: The acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of linear esters and lactones was studied using a hybrid supermolecule−polarizable continuum |
|
217 HYDROLYSIS OF CARBOXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVES
The mechanism of ester saponification involves the reaction of the nucleophilic hydroxide ion at the carbonyl carbon to give a tetrahedral addition intermediate from which an alkoxide ion is expelled The alkoxide ion, after expulsion as a leaving group (methoxide in Eq |
|
HYDROLYSIS
In the C-O cleavage reaction, the mechanism is also a direct displacement SN2 reaction, where the phosphate ester anion is acting as the leaving group |
|
Ester Chemistry Tutorial
aromatic or cyclic (called "lactones") as illustrated by the examples below: ( hydrolysis) yielding an acid and alcohol product if the nucleophile is water (or an |
|
Mechanisms of Lactone Hydrolysis in Neutral and Alkaline Conditions
11 jui 2013 · A parallel work addresses the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of lactones 1 INTRODUCTION The hydrolysis of carboxylic acid esters is one of the |