3-Les muscles
|
THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM MANUAL
All features of the 3rd edition have been preserved; the 4th edition of The Muscular System Manual has many new features: Evidence-based full referencing for all joint actions of the muscles Expanded coverage of muscle function to address the oblique plane motion patterns of the muscles |
|
THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM
The body has 3 main types of muscle tissue 1)Skeletal 2) Smooth and 3) Cardiac SKELETAL MUSCLE SMOOTH MUSCLE CARDIAC MUSCLE Skeletal muscles attach to and move bones by contracting and relaxing in response to voluntary messages from the nervous system |
|
The Muscular System
Scanning electron micrograph of motor neurons terminating at muscle fibers A muscle fiber receives the stimulus to contract at a neuromuscular junction |
|
The Muscular System
Differentiate the three major muscle types Explain the difference between voluntary and involuntary muscles Explain the types of skeletal muscle movement and the relationship between muscles Review movement terminology Identify and explain the components of a muscle cell Describe the cellular activities required for muscle movement |
|
Anatomy (Structures) of the Muscular System
Anatomy (Structures) of the Muscular System Muscle is one of the four primary tissue types of the body and it is made up of specialized cells called fibers The body contains three types of muscle tissue: skeletal muscle cardiac muscle and smooth muscle The Three Types of Muscle Tissue |
|
ANATOMY OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM
individual muscle fibers (b) surrounds groups of skeletal muscle fibers (fascicles) and (c) covers the muscle as a whole 2 Name the tough connective tissue cord that serves to attach a muscle to a bone 3 Name three types of fiber arrangements seen in skeletal muscle |
c h a p t e r
Scanning electron micrograph of motor neurons terminating at muscle fibers. A muscle fiber receives the stimulus to contract at a neuromuscular junction. highered.mheducation.com
7.6 Homeostasis (p. 136)
Describe how the muscular system works with other systems of the body to maintain homeostasis. Describe some common muscle disorders and some of the serious diseases that can affect muscles. highered.mheducation.com
Smooth Muscle
Smooth muscle is located in the walls of hollow internal or-gans, and its involuntary contraction moves materials through an organ. Smooth muscle fibers are spindle-shaped cells, each with a single nucleus (uninucleated). The cells are usually arranged in parallel lines, forming sheets. Smooth muscle does not have the striations (bands of light and
Cardiac Muscle
Cardiac muscle forms the heart wall. Its fibers are uninucle-ated, striated, tubular, and branched, which allows the fibers to interlock at intercalated disks. Intercalated disks permit contractions to spread quickly throughout the heart. Cardiac fibers relax completely between contractions, which prevents fatigue. Contraction of cardiac muscle fib
Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal muscle fibers are tubular, multinucleated, and stri-ated. They make up the skeletal muscles attached to the skele-ton. Skeletal muscle fibers can run the length of a muscle and therefore can be quite long. Skeletal muscle is voluntary be-cause its contraction is always stimulated and controlled by the nervous system. In this chapter, we wi
Smooth muscle
has spindle-shaped, nonstriated, uninucleated fibers. occurs in walls of internal organs. is involuntary. highered.mheducation.com
Cardiac muscle
has striated, tubular, branched, uninucleated fibers. occurs in walls of heart. is involuntary. highered.mheducation.com
Skeletal muscle
has striated, tubular, multinucleated fibers. is usually attached to skeleton. is voluntary. muscle itself is covered by a connective tissue layer called the epimysium. The epimysium becomes a part of the fascia, a layer of fibrous tissue that separates muscles from each other (deep fascia) and from the skin (superficial fascia). Collagen fiber
Functions of Skeletal Muscles
This chapter concerns the skeletal muscles, and therefore it is fitting to consider their functions independent of the other types of muscles: Skeletal muscles support the body. Skeletal muscle contraction opposes the force of gravity and allows us to remain upright. Some skeletal muscles are serving this purpose even when you think you are relaxed
Medial
skin superficial fascia (adipose tissue) nerve humerus vein artery deep fascia individual muscle fascicles b. endomysium perimysium periosteum (cut) a. muscle fiber, c.s. fascicle, c.s. fascicle, l.s. c. highered.mheducation.com
7.2 MicroscopicAnatomyand Contraction ofSkeletalMuscle
We have already examined the structure of skeletal muscle as seen with the light microscope. As you know, skeletal muscle tissue has alternating light and dark bands, giving it a striated appearance. The electron microscope shows that these bands are due to the arrangement of myofilaments in a muscle fiber. highered.mheducation.com
Function
Sarcolemma Sarcoplasm Glycogen Myoglobin T tubule Sarcoplasmic reticulum Myofibril Myofilament Plasma membrane of a muscle fiber that forms T tubules Cytoplasm of a muscle fiber that contains organelles, including myofibrils polysaccharide that stores energy for muscle contraction red pigment that stores oxygen for muscle contraction Extension of t
Myofibrils and Sarcomeres
Myofibrils are cylindrical in shape and run the length of the muscle fiber. The striations of skeletal muscle fibers are formed by the placement of myofilaments within units of myofibrils called sarcomeres. A sarcomere extends between two dark lines called the Z lines. A sarcomere contains two types of protein myofilaments. The thick filaments are
Myofilaments
The thick and thin filaments differ in the following ways: Thick Filaments A thick filament is composed of several hundred molecules of the protein myosin. Each myosin mol-ecule is shaped like a golf club, with the straight portion of the molecule ending in a double globular head, or cross-bridge. Cross-bridges are slanted away from the middle of a
Skeletal Muscle Contraction
Muscle fibers are innervated—that is, they are stimulated to contract by motor neurons whose axons are found in nerves. The axon of one motor neuron has several branches and can stimulate from a few to several muscle fibers of a particular muscle. Each branch of the axon ends in an axon terminal that lies in close proximity to the sarcolemma of a m
The Role of Actin and Myosin
Figure 7.5 shows the placement of two other proteins associ-ated with an actin filament, which you will recall is com-posed of a double row of twisted actin molecules. Threads of tropomyosin wind about an actin filament, and troponin oc-curs at intervals along the threads. Calcium ions (Ca2 ) that have been released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Creatine Phosphate Breakdown
products (carbon dioxide and water) are usually no prob-lem. Carbon dioxide leaves the body at the lungs, and water simply enters the extracellular space. The by-product, heat, keeps the entire body warm. highered.mheducation.com
Fermentation
Fermentation, like creatine phosphate breakdown, supplies ATP without consuming oxygen. During fermentation, glu-cose is broken down to lactate (lactic acid): Creatine phosphate is a high-energy compound built up when a muscle is resting. Creatine phosphate cannot partici-pate directly in muscle contraction. Instead, it can regenerate ADP ATP ATP b
Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration completed in mitochondria usually pro-vides most of a muscle’s ATP. Glycogen and fat are stored in muscle cells. Therefore, a muscle cell can use glucose from glycogen and fatty acids from fat as fuel to produce ATP if oxy-gen is available: ADP ATP glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + water Myoglobin, an oxygen carrier similar to
Oxygen Deficit
When a muscle uses fermentation to supply its energy needs, it incurs an oxygen deficit. Oxygen deficit is obvious when a person continues to breathe heavily after exercising. The ability to run up an oxygen deficit is one of muscle tissue’s greatest assets. Brain tissue cannot last nearly as long with-out oxygen as muscles can. Repaying an oxygen
7.3 Muscle Responses
Muscles can be studied in the laboratory in an effort to un-derstand how they respond when in the body. highered.mheducation.com
In the Laboratory
When a muscle fiber is isolated, placed on a microscope slide, and provided with ATP plus the various electrolytes it requires, it contracts completely along its entire length. This observation has resulted in the all-or-none law: A muscle fiber contracts completely or not at all. In contrast, a whole muscle shows degrees of contraction. To study w
Naming Muscles
When learning the names of muscles, considering what the name means will help you remember it. The names of the various skeletal muscles are often combinations of the fol-lowing terms used to characterize muscles: Size. For example, the gluteus maximus is the largest muscle that makes up the buttocks. The gluteus minimus is the smallest of the glut
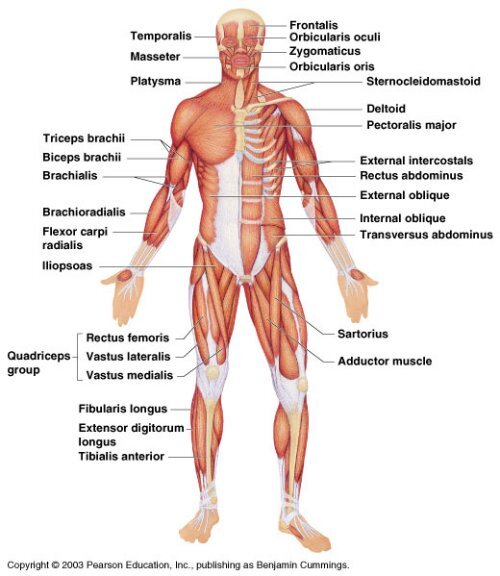
Muscles of Facial Expression
The muscles of facial expression are located on the scalp and face. These muscles are unusual in that they insert into and move the skin. Therefore, we expect them to move the skin and not a bone. The use of these muscles communicates to others whether we are surprised, angry, fearful, happy, and so forth. Frontalis lies over the frontal bone; it r
Function
Muscles of Facial Expression Frontalis (frun-ta lis) Orbicularis oculi (or-bik yu-la-ris ok yu-li) Orbicularis oris (or-bik yu-la-ris o ris) Buccinator (buk si-na tor) Zygomaticus (zi go-mat ik-us) highered.mheducation.com
Origin/Insertion
Raises eyebrows Closes eye Closes and protrudes lips Compresses cheeks inward Raises corner of mouth Muscles of Mastication Masseter (mas-se ter) Temporalis (tem-po-ra lis) Closes jaw Closes jaw Muscles That Move the Head Sternocleidomastoid (ster no-kli do-mas toid) Trapezius (truh-pe ze-us) Cranial fascia/skin and muscles around eye Maxillary and
Muscles That Move the Scapula
Deltoid Origin/Insertion Depresses scapula and pulls it forward; elevates arm above horizontal Abducts arm to horizontal Pectoralis major Flexes and adducts arm Latissmus dorsi Rotator cuff Upper nine ribs/vertebral border of scapula Extends or adducts arm Angular and rotational movements of arm Muscles That Move the Forearm Biceps brachii Triceps
|
Anatomie du périnée féminin
Les muscles ischio-caverneux sont innervés par un rameau périnéal du nerf pudendal. III.4.2 Muscle bulbo-caverneux (muscle bulbo-spongieux). C'est un muscle |
|
Le muscle squelettique
Les muscles striés squelettiques sont constitués de cellules allongées : les fibres musculaires. Associées en faisceaux ces fibres sont rendues solidaires par |
|
Corrigé Fiches dactivités Biologie et physiopathologie humaines 1
Faisceau de fibres musculaires. 3. Os. 6. Fibre ou cellule musculaire. 9. Vaisseaux sanguins. ?. |
|
OPTION E
DONC IL FAUT S'ECHAUFFER POUR : 1) augmenter en profondeur la plasticité des masses musculaires qui vont travailler intensément. 2) irriguer les muscles et |
|
CREATINE-KINASE ET ISOENZYMES
Elle est présente dans de nombreux tissus de l'organisme: majoritairement dans les muscles squelettiques et le muscle cardiaque. On la trouve aussi dans d' |
|
Les affections de lappareil locomoteur ? Partie 3 : les atteintes
Les muscles sont reliés aux os par les tendons. Une articulation mobile est composée d'os de surfaces articulaires cartilagineuses |
|
Chapitre 8 : Evolution des somites : Formation du squelette et des
squelette et des muscles DÉVELOPPEMENT DES MUSCLES DE LA TETE ET DU COU ... Figure 3 : Les cellules du sclérotome et leur migration. |
|
Lintérêt du renforcement des muscles cervicaux dans les
21 mars 2018 Le système musculaire du rachis cervical doit assurer la mobilité et la stabilité segmentaire (46). On peut distinguer les muscles postérieurs ... |
|
Guide de promotion consultation et prescription médicale dactivité
Elle a plusieurs dimensions : la capacité cardio-respiratoire (appelée aussi endurance) ; les capacités ou aptitudes musculaires (la force musculaire l' |
|
BIOMECANIQUE DU RACHIS CERVICAL
3- MUSCLES MOTEURS. 4- CONTRAINTES MECANIQUES 3- l'articulation occipito-axoïdienne ... 3- les muscles de la nuque en 4 plans ... |
|
Le système musculaire squelettique
La contraction des muscles lisses est indépendante de la volonté Le muscle strié constitue les muscles squelettiques qui assurent, sous le contrôle du système |
|
Le muscle squelettique
Les muscles striés squelettiques sont constitués de cellules allongées : les fibres musculaires Associées en faisceaux, ces fibres sont rendues solidaires par |
|
Généralités sur les muscles
Un muscle squelettique est entouré de plusieurs couches de tissu conjonctif : • L' endomysisum entoure chaque fibre musculaire; • Le périmysium assemble les |
|
Les muscles - Infirmierscom
o Les muscles annulaires : corps charnu circulaire entourant un orifice creux : bouche, yeux ou viscère creux : sphincter Les muscles lisses : la contraction ne |
|
Le système musculaire - IFSI DIJON
Fonction muscle = contraction – Raccourcissement → mouvement – Mobilisation coordonnée de plusieurs muscles • Contribution la + importante au poids |
|
Les muscles
Outre la force musculaire, la capacité d'étirement du muscle est également un élément clé pour un mouve ment efficace Les muscles monoarticulaires doivent |
|
PHYSIOLOGIE MUSCULAIRE
La troponine est une protéine régulatrice de l'interaction actine/myosine dans le muscle strié NB : les filaments fins sont structuralement polarisés : , |
|
Le tissu musculaire
Les muscles striés sont formés de cellules musculaires juxtaposées parallèlement, organisées en faisceaux Le muscle est entouré de tissu conjonctif vasculaire |
|
Anatomie musculaire du sourire - Actualités Odonto
Rappelons que les muscles faciaux, dérivés du deuxième arc branchial, reçoivent leur innervation motrice du nerf facial (VII), et possèdent une inser- tion cutanée |
|
Les muscles respiratoires Anatomie, physiologie - Edimark
Comme tout muscle squelettique, les muscles respiratoires contiennent plusieurs types de fibres musculaires organisées en unités motrices innervées chacune |








![Download PDF] Anatomy of the Moving Body Second Edition: A Basic Download PDF] Anatomy of the Moving Body Second Edition: A Basic](https://www.coursehero.com/doc-asset/bg/e32153d1ad7069b20139369625bfe570bf2d42fe/splits/v9.2.qiv2.clean/split-0-page-1-html-bg-unsplit.png)


![PDF] The Concise Book of Muscles Online PDF] The Concise Book of Muscles Online](https://etude-az.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/les-muscles-du-corps-humain-schema-1-300x225.jpg)
