Linkage of Rapid Estrogen Action to MAPK Activation by ER #945 -Shc
|
Novel Mechanisms of Estrogen Action in the Brain
Estrogen elicits a selective enhancement of the growth and differentiation of axons and dendrites (neurites) in the developing brain |
How does estrogen act as a transcription factor?
Estrogen receptors (ERs) act by regulating transcriptional processes.
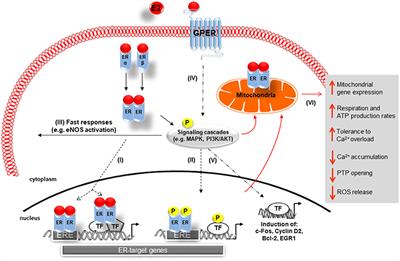
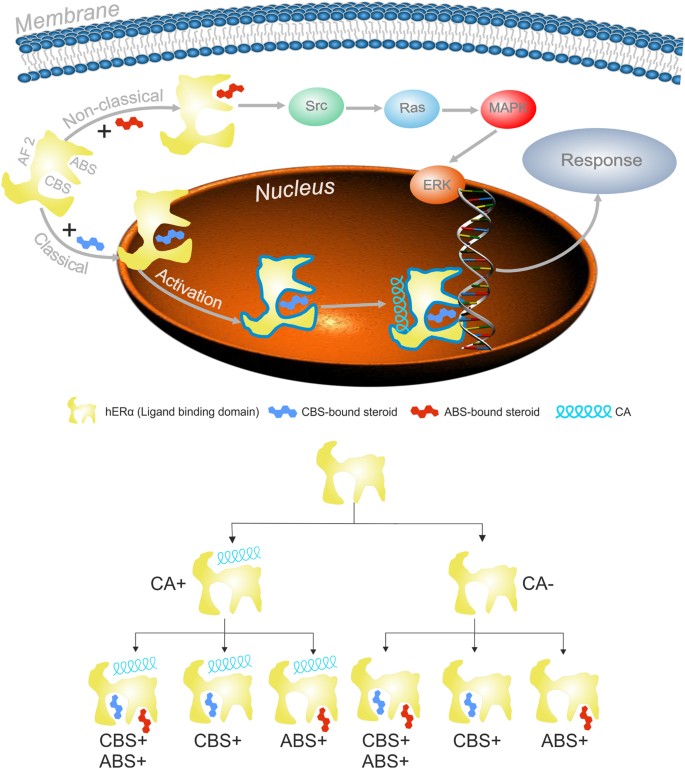
The classical mechanism of ER action involves estrogen binding to receptors in the nucleus, after which the receptors dimerize and bind to specific response elements known as estrogen response elements (EREs) located in the promoters of target genes.What does estrogen bind to?
As a steroid hormone, estrogen can enter the plasma membrane and interact with intracellular ERα and ERβ to exert direct effects by binding to DNA sequences.
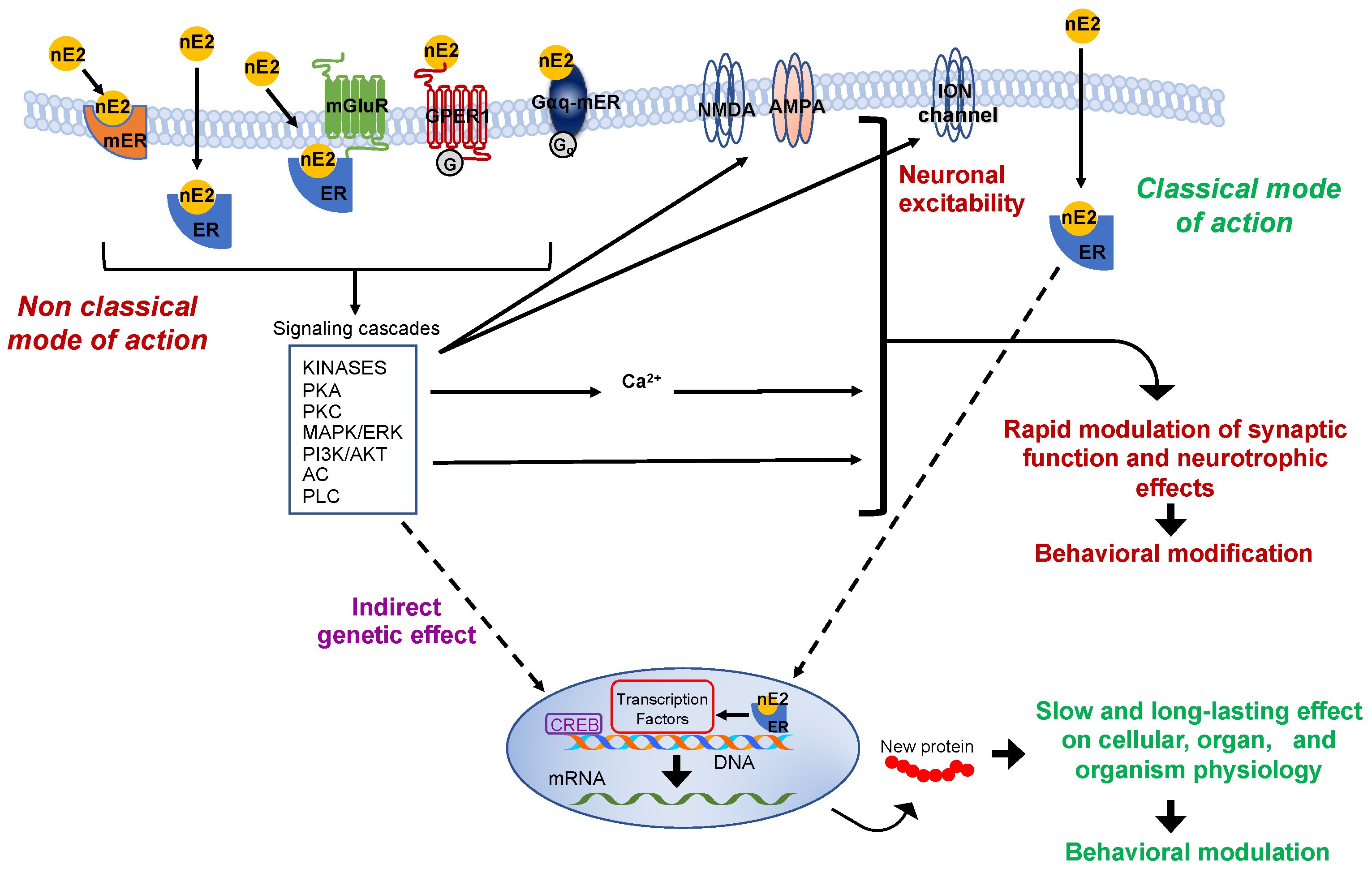
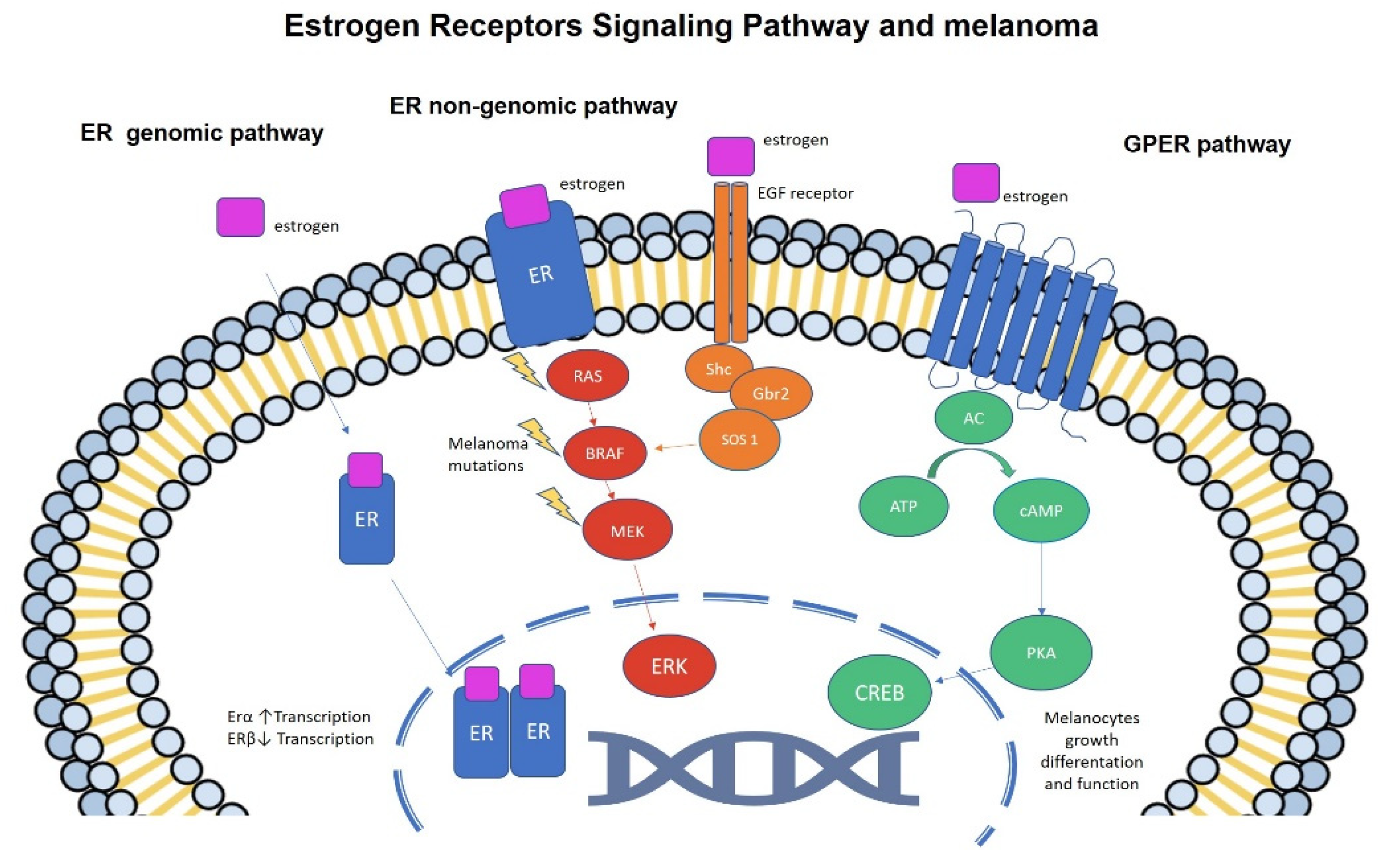
Alternatively, estrogen can activate intracellular signaling cascades via interaction with the GPER1 and/or ERα and ERβ.What does the ESR1 gene do?
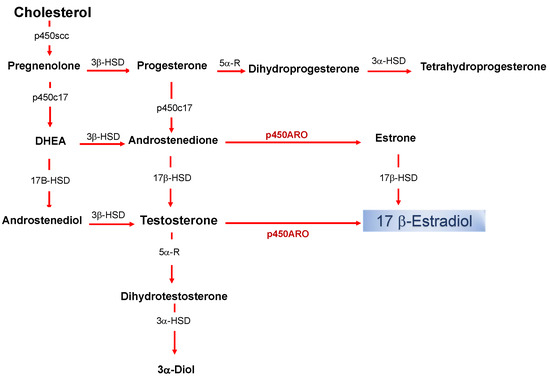
hepatic Estradiol/ESR1 signaling plays a key role in the maintenance of gluconeogenesis and lipid metabolism in males.
ESR1 inhibits chorionic gonadotropin-induced steroidogenesis and proliferation of progenitor Leydig cells in mice.
High ESR1 expression is associated with metastasis in breast Cancer.What happens when estrogen binds to its receptor?
The binding of estrogen to the ER results in a series of downstream steps that modulate transcription of genes responsible for cellular function, tumor growth, invasion, angiogenesis, and survival.
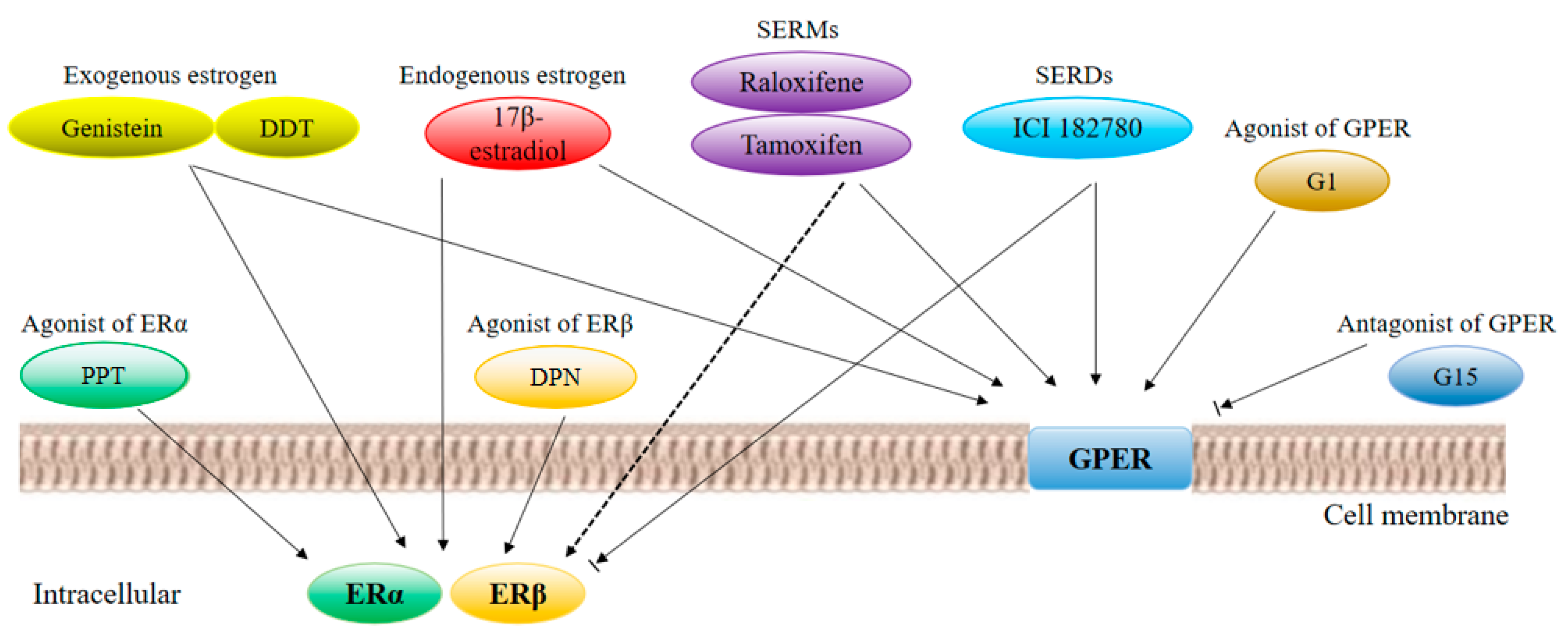
Endocrine therapy either antagonizes the ER or causes estrogen deprivation.What is the mechanism of estrogen signaling?
As a steroid hormone, estrogen can enter the plasma membrane and interact with intracellular ERα and ERβ to exert direct effects by binding to DNA sequences.
Alternatively, estrogen can activate intracellular signaling cascades via interaction with the GPER1 and/or ERα and ERβ.What is the signaling pathway of estrogen?
Estrogen mediates its cellular actions through two signaling pathways classified as "nuclear-initiated steroid signaling" and "membrane-initiated steroid signaling".
hepatic Estradiol/ESR1 signaling plays a key role in the maintenance of gluconeogenesis and lipid metabolism in males.
ESR1 inhibits chorionic gonadotropin-induced steroidogenesis and proliferation of progenitor Leydig cells in mice.
High ESR1 expression is associated with metastasis in breast Cancer.
Proposed primary target cells for estrogens in bone include growth plate chondrocytes, endosteal and trabecular lining cells/osteoblasts, osteocytes, mesenchymal cells in the bone marrow, osteoclasts, B and T lymphocytes, and megakaryocytes (6, 12–19).
Does ER play a role in MAPK activation?
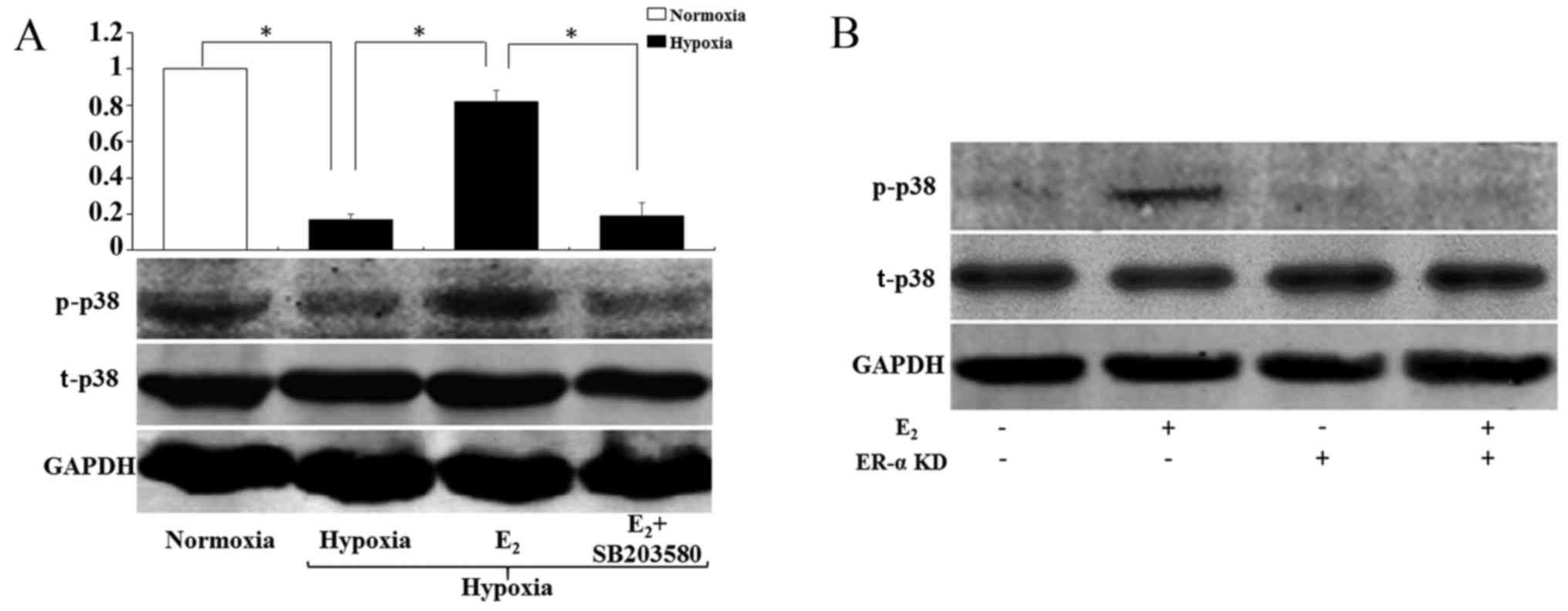
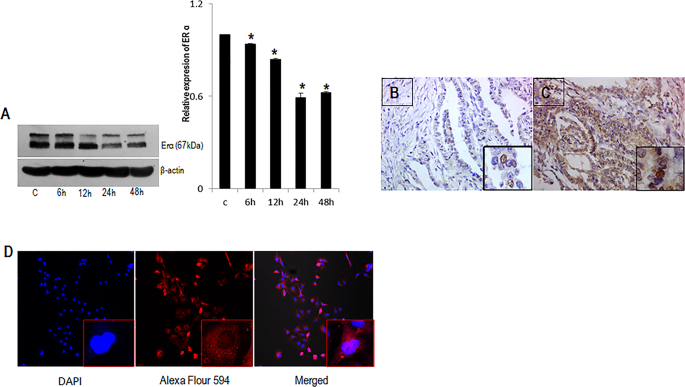
ERα-dependent MAPK activation has been reported by many laboratories using MCF-7 and other cell lines treated with E2 ( 39, 43 ). The differences regarding ERα involvement in MAPK activation under varying conditions are unknown.
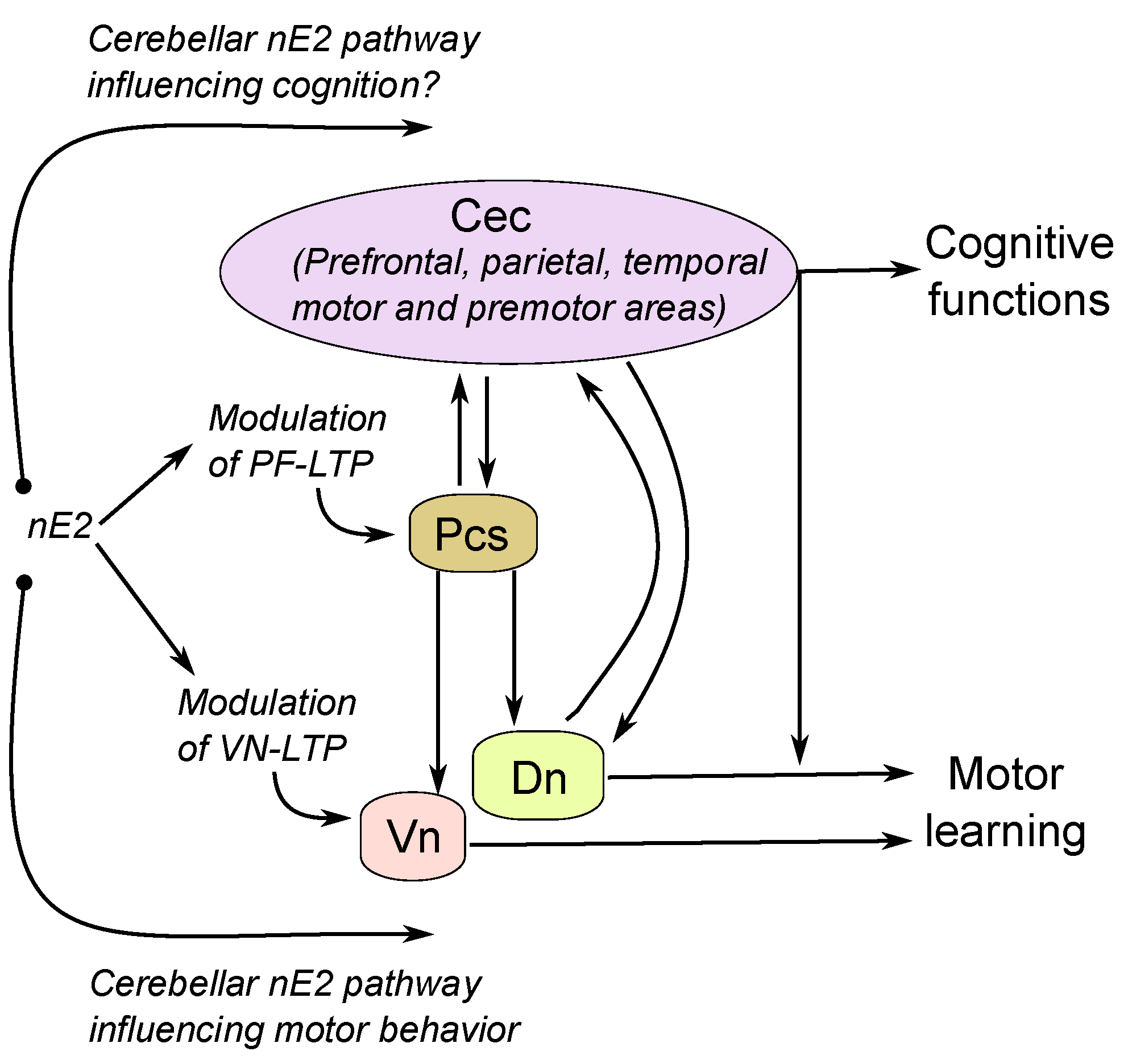
Does estrogen stimulate mitogen-activated protein kinase in rat hippocampus?
Estrogen-induced activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in the cerebral cortex of estrogen receptor-α knock-out mice. Putative membrane-bound estrogen receptors possibly stimulate mitogen-activated protein kinase in the rat hippocampus.
How does E2 affect MAPK activation?
Together, our data suggest that the nongenomic effects of E2 on Shc and MAPK activation are mediated by the classical ERα receptor, that E2 can induce an association of ERα with Shc, and that Shc appears to be a crucial step for the activation of MAPK.
How does oestradiol and progestin activate ERK-1 and erk-2?
Estrogen-induced activation of Erk-1 and Erk-2 requires the G protein-coupled receptor homolog, GPR30, and occurs via trans-activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor through release of HB-EGF. Non-transcriptional action of oestradiol and progestin triggers DNA synthesis. Constitutive phosphorylation of Shc proteins in human tumors.
|
Chrysin alleviates alteration of bone-remodeling markers in
Chrysin ovariectomized rats |
|
PROGRAM
activities as a teacher-mentor in expanding the use of PBPK dosimetry models in toxicology research and in chemical risk assessment. |
|
Society of Toxicology
Link? MRC LECTURE. 12:15 PM–1:15 PM Mode of Action in Assessing Human Relevance of ... Reactive Intermediates and Bioactivation Pathways of Xenobiotics. |
|
San Diego
Meet the Directors Session: Update of Activities Annual Meeting Message Center through a direct link from ... DAMAGE BY 17?-ESTRADIOL IN HUMAN. |
|
Program
is rapid quantitative |
|
Poster sessions
NATURAL KILLER CELL ACTIVATION AND. CYTOTOXICITY DURING LIVER REGENERATION. Nadine Graubardt1 Rene Fahrner1 |
|
Poster Sessions
ISOFORMS IN ESTRADIOL 17?-D-GLUCURONIDE- HEPATIC YB-1 ACTIVATION BY DIFFERENT ... CLINICAL RELEVANCE OF RAPID VIROLOGICAL. |
|
EstroGen metaBoLism in this issue
Oct 21 2010 hoRMoNAL ACTIvATIoN – hoRMoNES |
|
PROGRAM - Society of Toxicology
contact any member of the Annual Meeting staff They will initiate SOT's Demonstration Response Plan If you see actions that appear threatening, contact Hotel |
|
42nd Annual Meeting - Society of Toxicology
1:30 PM–4:30 PM Mode of Action in Assessing Human Relevance of Quick food service is available in the Exhibit Hall Luncheon tetrachloride that actually proved the hypothesis by linking the biological NECROSIS: ROLE OF MAPK PATHWAY V S Vaidya2, K 2:50 SYNERGISTIC ACTIVATION OF ESTROGEN |
|
Hepatology
U AASLD supports the highest attainable funding levels to rapidly advance progress throughout the NIH as envisioned by the Trans-NIH Action Plan for Liver |
![PDF] Linkage of rapid estrogen action to MAPK activation by PDF] Linkage of rapid estrogen action to MAPK activation by](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/0e830cea5499066a897999f38f124854dc0ec059/3-Figure2-1.png)
![PDF] Linkage of rapid estrogen action to MAPK activation by PDF] Linkage of rapid estrogen action to MAPK activation by](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/a417eb66d0f33bdf3dd6f0b7d99025ff530a7534/2-Figure1-1.png)
![PDF] Rapid extranuclear signaling by the estrogen receptor (ER PDF] Rapid extranuclear signaling by the estrogen receptor (ER](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/0e830cea5499066a897999f38f124854dc0ec059/6-Figure5-1.png)
![PDF] Linkage of rapid estrogen action to MAPK activation by PDF] Linkage of rapid estrogen action to MAPK activation by](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/a417eb66d0f33bdf3dd6f0b7d99025ff530a7534/6-Figure1-1.png)
![PDF] Rapid extranuclear signaling by the estrogen receptor (ER PDF] Rapid extranuclear signaling by the estrogen receptor (ER](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/a417eb66d0f33bdf3dd6f0b7d99025ff530a7534/3-Figure2-1.png)
![PDF] Rapid extranuclear signaling by the estrogen receptor (ER PDF] Rapid extranuclear signaling by the estrogen receptor (ER](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/0e830cea5499066a897999f38f124854dc0ec059/8-Figure7-1.png)
![PDF] Linkage of rapid estrogen action to MAPK activation by PDF] Linkage of rapid estrogen action to MAPK activation by](https://www.mdpi.com/ijms/ijms-21-03316/article_deploy/html/images/ijms-21-03316-g003.png)