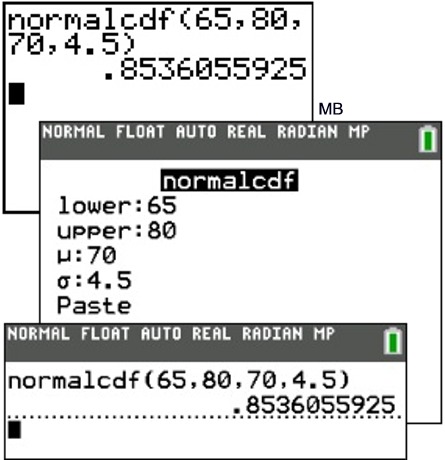
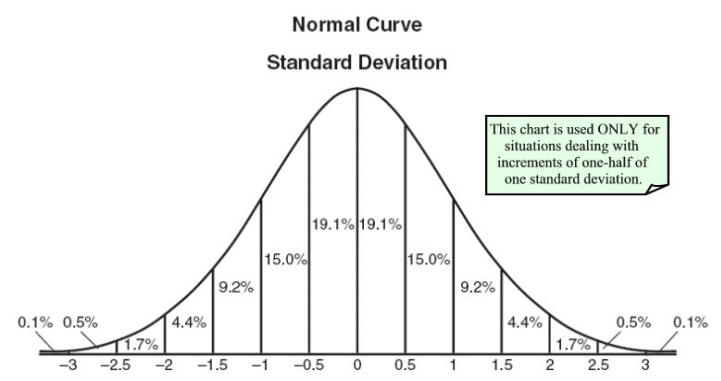
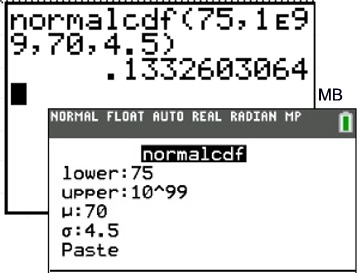
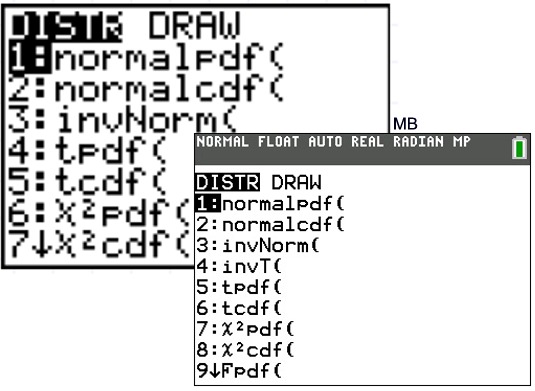
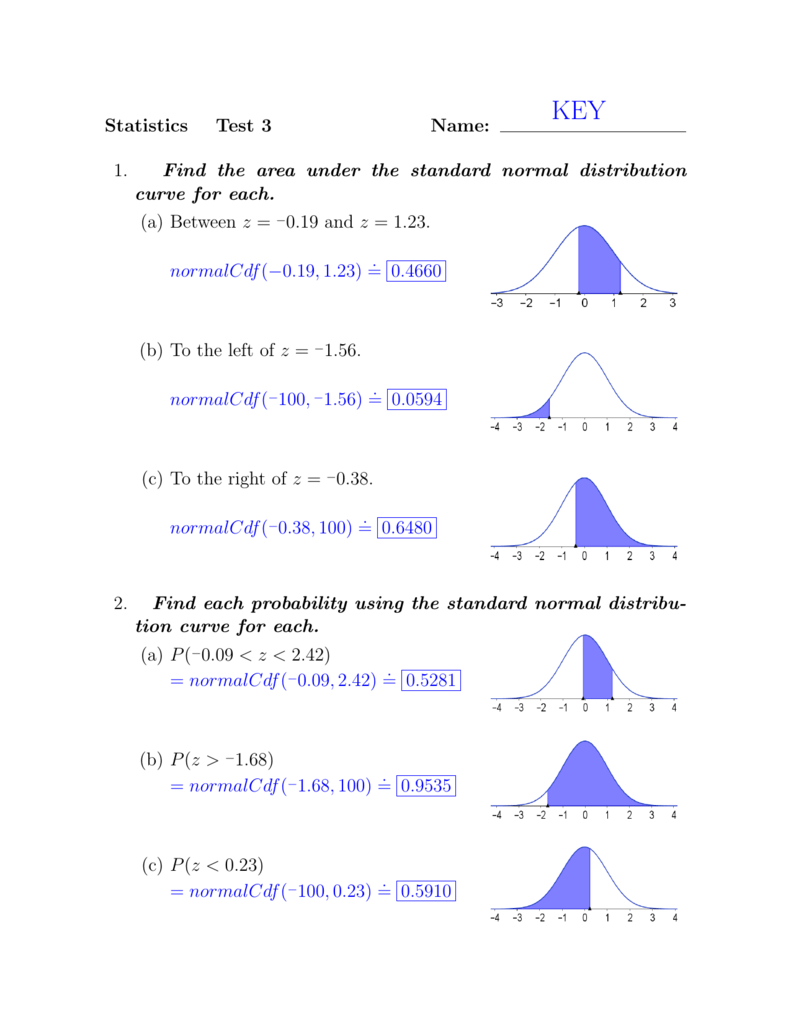
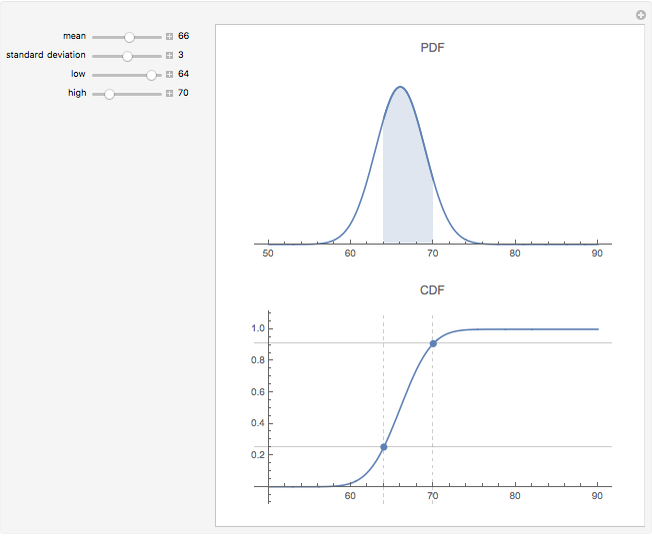
normalcdf
|
10: CDFs The Normal Distribution
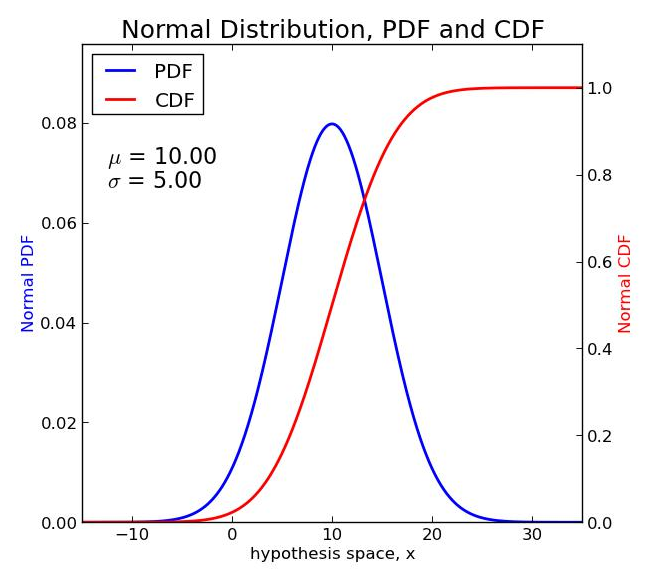
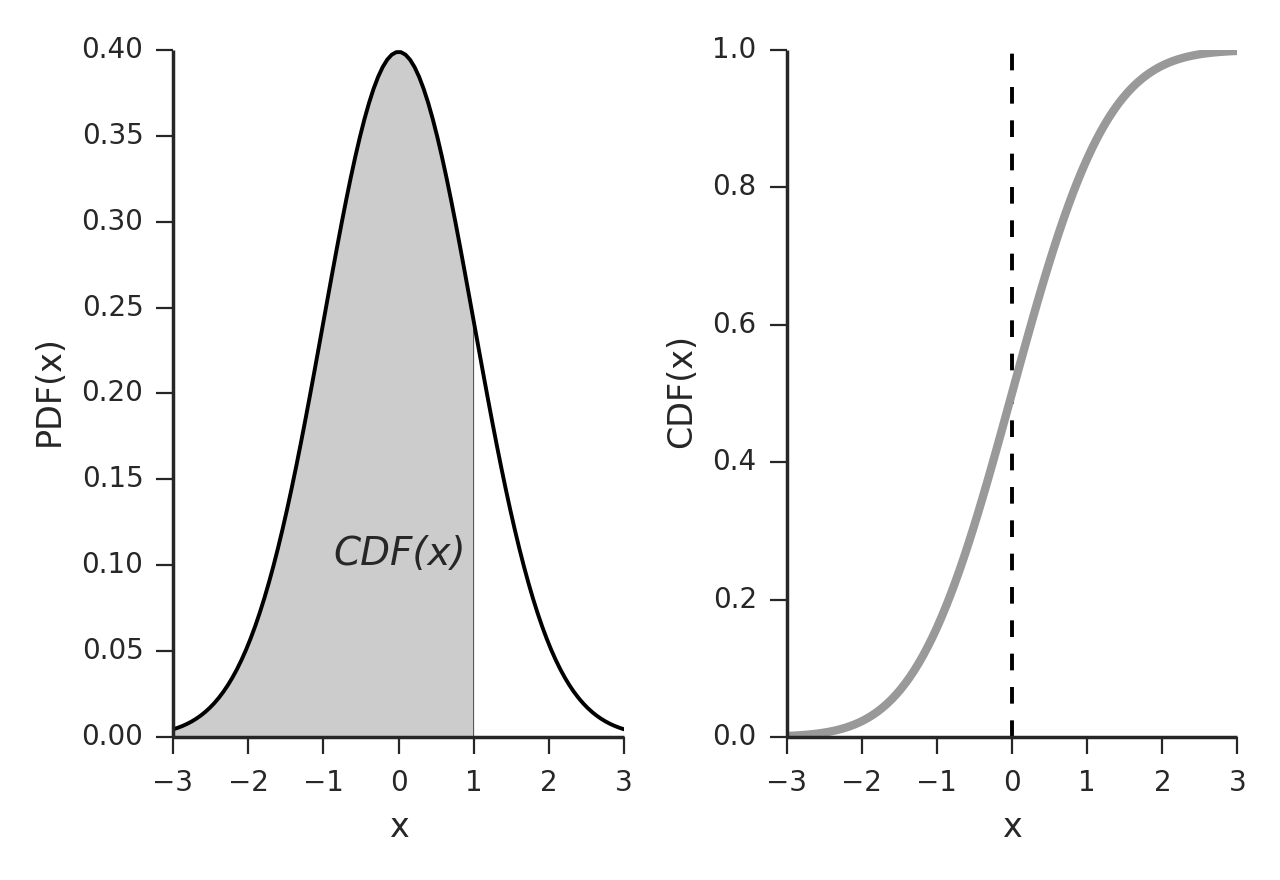
Discrete random variable Continuous random variable Probability mass function (PMF): Probability density function (PDF): To get probability: = = To get probability: ≤ ≤ = Both are measures of how likely is to take on a value |
|
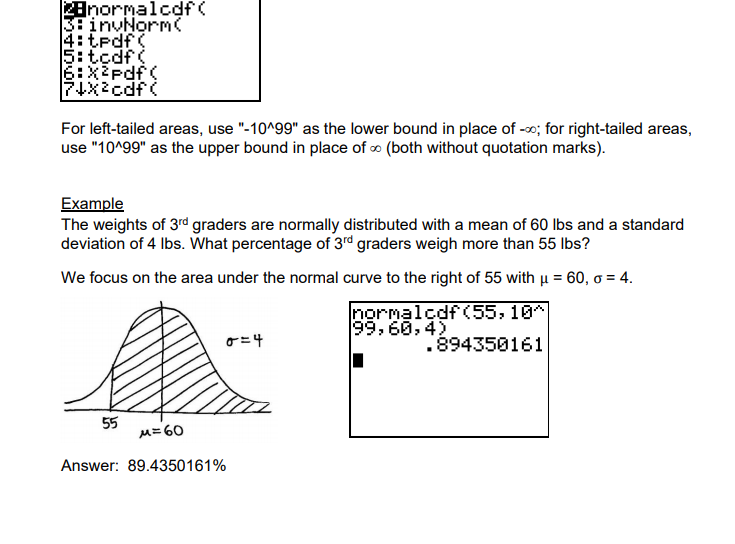
Choosing whether to use normalcdf or invNorm
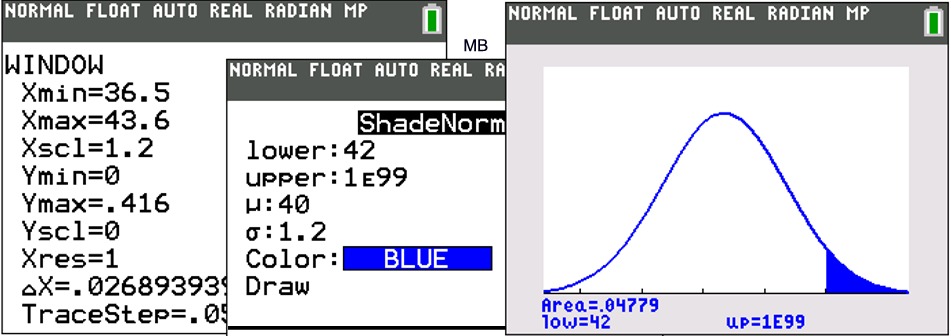
Choosing whether to use normalcdf or invNorm • The area under the normal bell curve can represent either a probability or a percentage • Use the normalcdf function to find the area under the curve when two “bounds” are known • On Texas Instrument graphing calculators press 2nd then VARS select 2:normalcdf |
|
Table 1: Table of the Standard Normal Cumulative Distribution
Table 1: Table of the Standard Normal Cumulative Distribution Function '(z)z 0 00 0 01 0 02 0 03 0 04 0 05 0 06 0 07 0 08 0 09-3 4 0 0003 0 0003 0 0003 0 0003 0 0003 |
|
Using the normalcdf function on the TI-84
Slide 1 Using the normalcdf function on the TI-84 These instructions will work for the TI-83 and TI-84 families of calculators Read the problem carefully: Consider the weights of 18 month old boys in the U S According to published growth charts the average weight is approximately 11 8 kg with standard deviation of 1 28 kg |
What is the difference between PDF and CDF?
3. PDF and CDF of The Normal Distribution The probability density function (PDF) and cumulative distribution function (CDF) help us determine probabilities and ranges of probabilities when data follows a normal distribution. The CDF is the integration, from left to right, of the PDF.
How do you know if a PDF is a normal distribution?
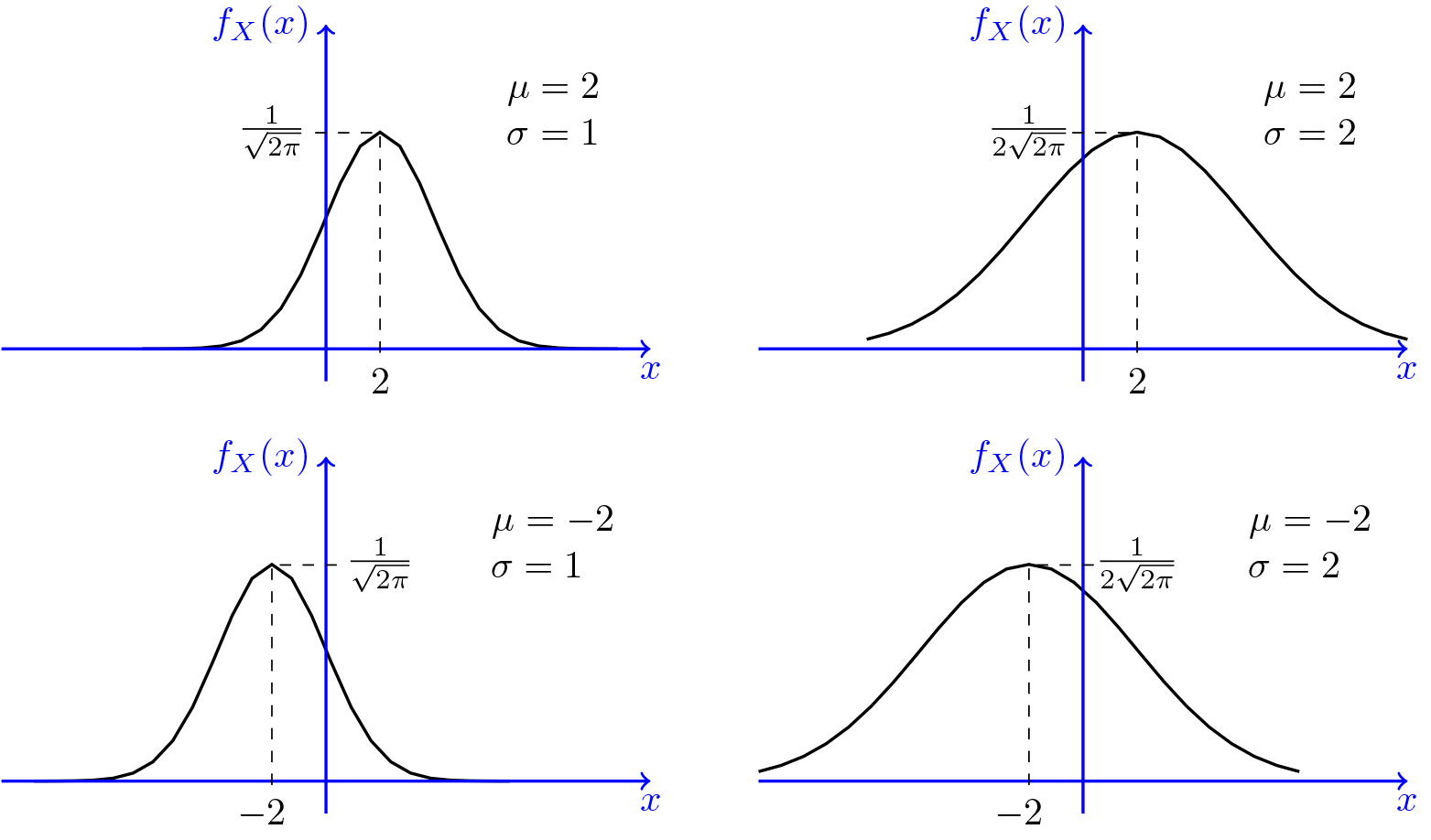
When the PDF is graphically portrayed, the area under the curve will indicate the interval in which the variable will fall. A continuous random variable X is said to follow the normal distribution if it’s probability density function (PDF) is given by: The variable µ is the mean of the data values.
How do I use normalcdf in a TI-84 calculator?
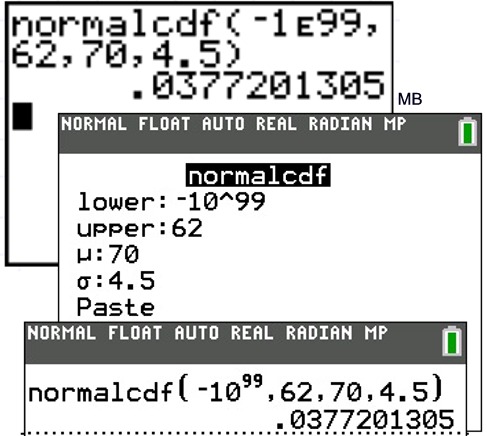
normalcdf (lower_x, upper_x, μ, σ) returns the cumulative probability associated with the normal cdf between two values. Both of these functions can be accessed on a TI-84 calculator by pressing 2nd and then pressing vars. This will take you to a DISTR screen where you can then use normalpdf () and normalcdf ():
How do you calculate CDF?
The CDF value corresponds to the sum of the area under a normal distribution curve (integration). So, we divide the whole area under the curve into small panels of a fixed width, and we add up all those individual panels to get the total area under the curve. The smaller the width of the panel, the more accurate the integration will be.
Discrete vs Continuous RVs
Discrete random variable Continuous random variable Probability mass function (PMF): Probability density function (PDF): To get probability: = = To get probability: ≤ ≤ = Both are measures of how likely is to take on a value. web.stanford.edu
Continuous RV
= = ( ) = ( ) ( ) = Both continuous and discrete RVs + = + Var( ) = ( − [ ]) = Var( + ) = − ( [ ]) Var( ) web.stanford.edu
Uniform Random Variable
def An Uniform random variable in an interval from to . takes on all values, with equal likelihood, web.stanford.edu
Exponential Random Variable
Consider an experiment that lasts a duration of time until success occurs. def An Exponential random variable is the amount of time until success. web.stanford.edu
Cumulative Distribution Function
A cumulative distribution function (CDF) is a “closed form” equation for the probability that a random variable is less than a given value. For a continuous random variable, the CDF is: = ( ≤ ) = Also written as: web.stanford.edu
Why the Normal?
Common for natural phenomena: height, weight, etc. Most noise in the world is Normal Often results from the sum of many random variables Sample means are distributed normally That’s what they want you to believe
Complexity is Tempting
This line describes this data well, but will it generalize? web.stanford.edu
Fewest Assumptions
A Gaussian maximizes entropy for a given mean and variance Fewest Assumptions A Gaussian makes the fewest assumptions after matching mean and variance web.stanford.edu
= = 0 Var = = 1
Other names: Unit Normal Note: not a new distribution; just a special case of the Normal CDF of defined as: ≤ = Φ( ) web.stanford.edu
Interval of Phi
< < ( = − ( ) ) Probabilities for a general Normal RV web.stanford.edu
|
Using the normalcdf function on the TI-84
Consider the weights of 18 month old boys in the U.S.. According to published growth charts the average weight is approximately 11.8. |
|
Choosing whether to use normalcdf or invNorm
Use the normalcdf function to find the area under the curve when two. “bounds” are known. • On Texas Instrument graphing calculators press 2nd then VARS |
|
Using the normalcdf function on the TI-89
Using the normalcdf function on the TI-89 the Normal Cdf function not the. Normal Pdf. Do not ever use normalpdf!! Highlight Normal Cdf and hit enter. |
|
Using The TI-83/84 Plus Chapter 6: Normal Distributions
normalcdf(110 1000 |
|
Calculating Normal Curve Percentiles on the TI-84
Since percentile is the area to the left of the score we use the normalcdf function to calculate the area. Page 5. Remember to enter the important numbers into |
|
Day 3 - NormalCDF and InvNorm
Day 3 NormalCDF and InvNorm. 1. WarmUp. 1. Bob is a 17 year old male who is 68 in tall. 17 year old male heights are normally distributed with mean 70 in |
|
Normal Distributions
2nd VARS ?Normalcdf(lowerupper |
|
Using a Graphing calculator to use a Z-table Finding % given z-values
to 4 (Normal Cdf). normalcdf(a b). Tells you the area of the between a and b. To find the area to the left of z=.45 for example |
| What is the difference between NormalPDF and NormalCDF? |
|
Standard Normal Distribution
Select normalcdf and click ENTER. 3. Enter the Lower bound upper bound |
|
Table of the Standard Normal Cumulative Distribution Function ?(z)
z 0 00 0 01 0 02 0 03 0 04 0 05 0 06 0 07 0 08 0 09 -3 4 0 0003 0 0003 0 0003 0 0003 0 0003 0 0003 0 0003 0 0003 0 0003 0 0002 -3 3 |
|
Normal Distribution: An Introductory Guide to PDF and CDF
1 sept 2020 · The probability density function (PDF) and cumulative distribution function (CDF) help us determine probabilities and ranges of |
|
What is the difference between NormalPDF and NormalCDF?
NormalCDF gives us the percentage of the data results that fall between a given RANGE (ex Between 50 and 100) NOTE: Really the NormalCDF calls the |
|
Normal Distributions
Normalcdf(-52 501)= 9937 The lower bound is -5 because it's the z-score of the lowest value in the given range(70-90) 2 5 |
|
Using the normalcdf function on the TI-84 - Math USU
Access the normalcdf function on the calculator by pressing 2nd Page 9 Then press VARS to access the DISTR menu |
|
Using the normalcdf function on the TI-89
IMPORTANT!! You must choose the Normal Cdf function not the Normal Pdf Do not ever use normal pdf !! Highlight Normal Cdf and hit enter |
|
Choosing whether to use normalcdf or invNorm
Use the normalcdf function to find the area under the curve when two “bounds” are known • On Texas Instrument graphing calculators press 2nd then VARS |
|
Day 3 - NormalCDF and InvNorm
Day 3 NormalCDF and InvNorm 1 WarmUp 1 Bob is a 17 year old male who is 68 in tall 17 year old male heights are normally distributed with mean 70 in |
|
Statistics - TI84 Calculator - Normal Distribution
Normalcdf: (2nd VARS (distr)) For a population that can be modelled by a Normal model centered at mean µ with standard deviation ? N(µ ?): |
|
Normal Distribution Gaussian Normal random variables PDF
We usually denote the standard normal CDF by ? The CDF of the standard normal distribution is denoted by the ? function: ?( |
| Using the normalcdf function on the TI-84 - Utah State University |
| The Normal Distribution - Mass |
| Using the normalcdf function on the TI 89 - Utah State University |
| Table 1: Table of the Standard Normal Cumulative Distribution |
| Normal Distributions - Grand Valley State University |
| How to Find normalcdf function (Section 51 Practice with |
| Searches related to normalcdf filetype:pdf |
|
Using the normalcdf function on the TI-84 - Math Usu
Access the normalcdf function on the calculator by pressing 2nd Then press VARS to access the DISTR menu ever use normal pdf Now enter the 4 important |
|
Using the normalcdf function on the TI-89 - Math Usu
Using the normalcdf function on the TI-89 the Normal Cdf function, not the Normal Pdf Do not ever use normal pdf Highlight Normal Cdf and hit enter |
|
Loi normale et calculatrice - IREM dAix-Marseille
+ DISTR b) Sélectionner normalcdf (ou normalFRép suivant les modèles) c) Compléter les paramètres |
|
15 The Standard Normal Distribution; Finding Areas Under Normal
We find areas under normal curves with the TI's normalcdf function, which is located in the Distributions menu To get to the function, press 2ND VARS, then |
|
Day 3 - NormalCDF and InvNorm
Day 3 NormalCDF and InvNorm 1 WarmUp 1 Bob is a 17 year old male who is 68 in tall 17 year old male heights are normally distributed with mean 70 in and |
|
Standard Normal Distribution
If you have TI 83, then you will have normalcdf(lower bound, upper bound, mean, standard deviation) P(Z< -1 05) = normal cdf (-1E99, -1 05, 0, 1) = 0 1469 2 |
|
Normal distributions
The normalcdf command is used for finding an area under the normal density curve This area corresponds to the probability of randomly selecting a value |
|
Using The TI-83/84 Plus Chapter 6: Normal - CosmosWeb
Probabilities with the normalcdf Function 2 For example, if IQ's are normally distributed with a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 15, what percentage of |
|
Normal Distributions - TI-NSpire APPS
Highlight 2: Normal Cdf and press · You will be prompted for the two x values that form the lower and upper boundaries of the area that you are trying to find, the |
|
Penser à régler la fenêtre daffichage a) Sélectionner le menu des
1) Pour Calculer P(a |