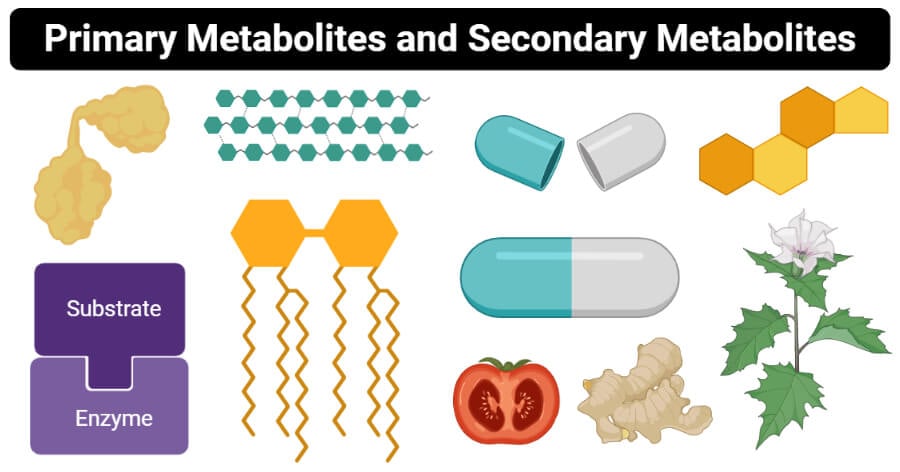
biochemical pathways examples
How are biological pathways discovered?
Researchers have discovered many important biological pathways through laboratory studies of cultured cells, bacteria, fruit flies, mice and other organisms. Many of the pathways identified in these model systems are the same as, or are similar to, counterparts in humans. Still, many biological pathways remain to be discovered.
Which is an example of a cyclic pathway?
The Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle is an example of a cyclic pathway. Spiral pathway- The same set of enzymes catalyze a progressive lengthening of an acetyl chain.
What are biochemical pathways?
Biochemical pathways are synonymous with metabolic pathways. The word metabolism comes from a Greek word “metabole” which means change referring to all the chemical reactions that occur inside the organism’s body. These pathways are necessary for maintaining the homeostasis of the organism and to keep it alive.
What is metabolic pathway example?
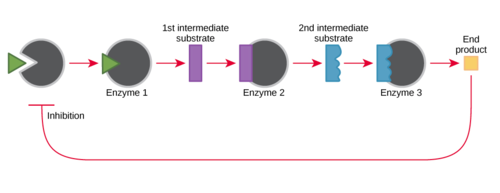
A metabolic pathway is a step-by-step series of interconnected biochemical reactions that convert a substrate molecule or molecules through a series of metabolic intermediates, eventually yielding a final product or products. For example, one metabolic pathway for carbohydrates breaks large molecules down into glucose.
Overview
Overview of metabolic pathways, energy flow in a cell, and anabolism and catabolism. khanacademy.org
Introduction
What’s going on in your body right now? Your first answer might be that you’re hungry, or that your muscles are sore from a run, or that you feel tired. But let’s go even deeper, moving past the layer of your consciousness and looking at what’s going in your cells. If you could peek inside of any cell in your body, you’d find that it was a remarkable hub of activity, more like a busy open-air market than a quiet room. Whether you are awake or sleeping, running or watching TV, energy is being transformed inside your cells, changing forms as molecules undergo the connected chemical reactions that keep you alive and functional. khanacademy.org
Overview of metabolism
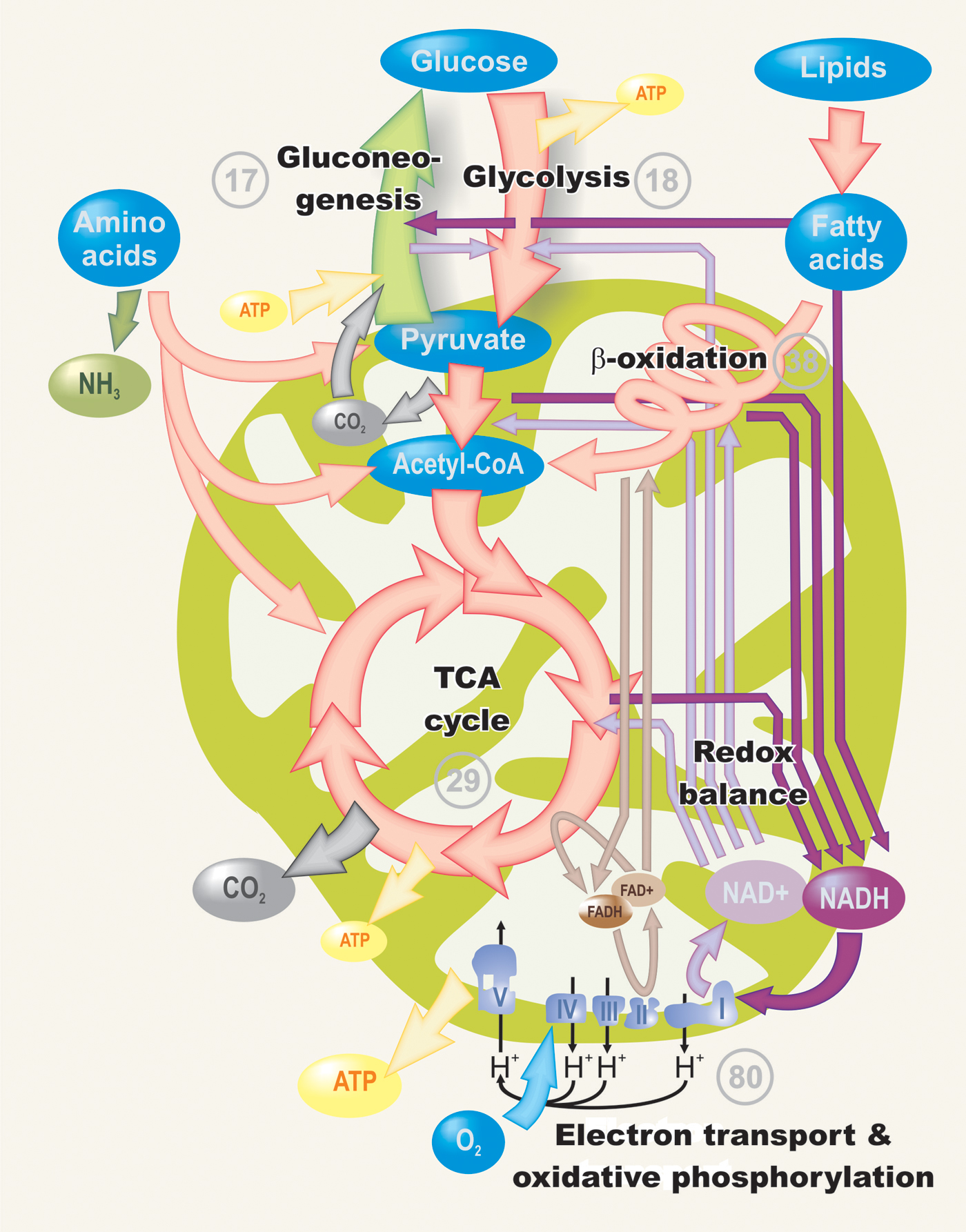
Cells are constantly carrying out thousands of chemical reactions needed to keep the cell, and your body as a whole, alive and healthy. These chemical reactions are often linked together in chains, or pathways. All of the chemical reactions that take place inside of a cell are collectively called the cell’s metabolism. To get a sense of the complexity of metabolism, let's take a look at the metabolic diagram below. To me, this mess of lines looks like a map of a very large subway system, or possibly a fancy circuit board. In fact, it's a diagram of the core metabolic pathways in a eukaryotic cell, such as the cells that make up the human body. Each line is a reaction, and each circle is a reactant or product. In the metabolic web of the cell, some of the chemical reactions release energy and can happen spontaneously (without energy input). However, others need added energy in order to take place. Just as you must continually eat food to replace what your body uses, so cells need a continual inflow of energy to power their energy-requiring chemical reactions. In fact, the food you eat is the source of the energy used by your cells To make the idea of metabolism more concrete, let's look at two metabolic processes that are crucial to life on earth: those that build sugars, and those that break them down. khanacademy.org
Breaking down glucose: Cellular respiration
As an example of an energy-releasing pathway, let’s see how one of your cells might break down a sugar molecule (say, from that candy you had for dessert). Many cells, including most of the cells in your body, get energy from glucose (C6H12O6 ) in a process called cellular respiration. During this process, a glucose molecule is broken down gradually, in many small steps. However, the process has an overall reaction of: C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy Breaking down glucose releases energy, which is captured by the cell in the form of adenosine triphosphate, or ATP. ATP is a small molecule that gives cells a convenient way to briefly store energy. khanacademy.org
Building up glucose: Photosynthesis
As an example of an energy-requiring metabolic pathway, let's flip that last example around and see how a sugar molecule is built. Sugars like glucose are made by plants in a process called photosynthesis. In photosynthesis, plants use the energy of sunlight to convert carbon dioxide gas into sugar molecules. Photosynthesis takes place in many small steps, but its overall reaction is just the cellular respiration reaction flipped backwards: 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2 Like us, plants need energy to power their cellular processes, so some of the sugars are used by the plant itself. They can also provide a food source for animals that eat the plant, like the squirrel below. In both cases, the glucose will be broken down through cellular respiration, generating ATP to keep cells running. khanacademy.org
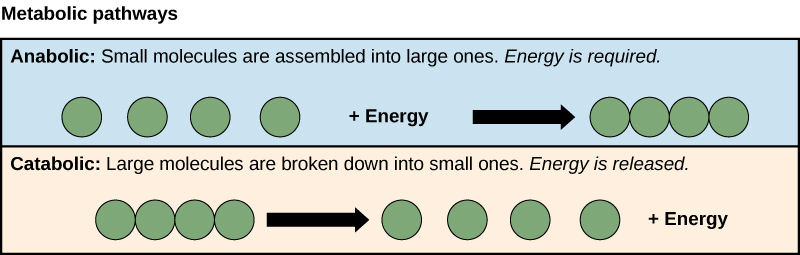
Anabolic and catabolic pathways
The processes of making and breaking down glucose molecules are both examples of metabolic pathways. A metabolic pathway is a series of connected chemical reactions that feed one another. The pathway takes in one or more starting molecules and, through a series of intermediates, converts them into products. Metabolic pathways can be broadly divided into two categories based on their effects. Photosynthesis, which builds sugars out of smaller molecules, is a "building up," or anabolic, pathway. In contrast, cellular respiration breaks sugar down into smaller molecules and is a "breaking down," or catabolic, pathway. Anabolic pathways build complex molecules from simpler ones and typically need an input of energy. Building glucose from carbon dioxide is one example. Other examples include the synthesis of proteins from amino acids, or of DNA strands from nucleic acid building blocks (nucleotides). These biosynthetic processes are critical to the life of the cell, take place constantly, and use energy carried by ATP and other short-term energy storage molecules. Catabolic pathways involve the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones and typically release energy. Energy stored in the bonds of complex molecules, such as glucose and fats, is released in catabolic pathways. It's then harvested in forms that can power the work of the cell (for instance, through the synthesis of ATP). [Need a mnemonic for anabolic and catabolic?] One final but important note: the chemical reactions in metabolic pathways don’t take place automatically, without guidance. Instead, each reaction step in a pathway is facilitated, or catalyzed, by a protein called an enzyme. You can learn more about enzymes and how they control biochemical reactions in the enzymes topic. khanacademy.org
Want to join the conversation?
Log in khanacademy.org

Purine and Pyrimidine Catabolism Pathway

Introduction to Metabolism Catabolism Vs Anabolism Biochemistry

Heme Catabolism and Degradation Pathway
|
Using the Biochemical Pathway Model to Teach the Concepts of
biochemical pathways the end products of which affect a single phe- notypic characteristic-plumage color. Another example of simple gene interaction is eye |
|
A general definition of metabolic pathways useful for systematic
a biochemical pathway with a running example taken from monosac- charide metabolism and discussing other biotechnologically and medically important examples. |
|
Biochemistry Metabolic pathways
Nov 7 2017 Is the activity of some enzymes controlled by both allosteric regulation and covalent modification? • Special focus: is there an example in ... |
|
Small molecules as products of evoluton 1/12
become possible to perform evolutonary analysis of biochemical pathways to reconstruct ancient pathways of metabolic pathways |
|
Modelling compartmentalization towards elucidation and
also examine sample problems in the engineering of these pathways. evolution and a very promising tool for engineering biochemical pathways in cells and cell ... |
|
AP Biology Sample Student Responses and Scoring Commentary
Other types of bacteria (Streptococcus sanguinis) compete with S. mutans but are unable to thrive in acidic environments. (a) Identify the biochemical pathway S |
|
Finding metabolic pathways in large networks through atom
Nov 26 2020 The weighted reactant-product pairs of an example network and the corresponding graph search algorithm are available online. The proposed method ... |
|
Article - Inferring Biochemical Reactions and Metabolite Structures
An example of this reasoning is given in Figure 3. Application of Pathmodel to the MAA Synthesis Pathway. We first used Pathmodel to compute the synthesis |
|
Prediction and Identification of Biochemical Pathway of Acteoside
distichum cultivar Ok Hwang 1ho can be used for finding enzymes involved in biochemical pathways of secondary metabolites. One of typical examples is Coffea |
|
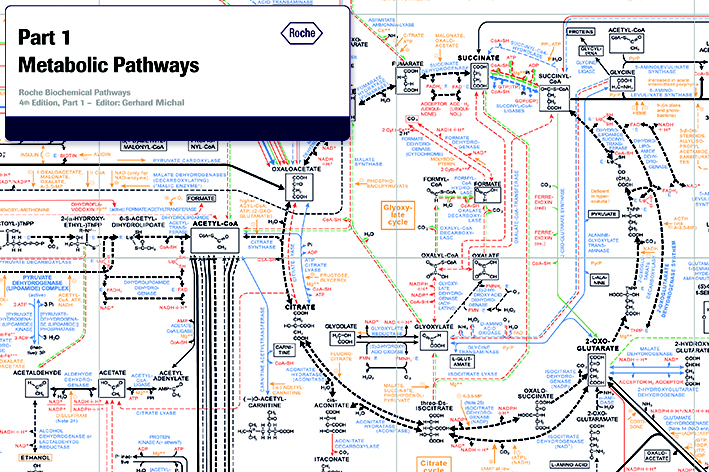
Prediction of Dynamical Properties of Biochemical Pathways with
Figure 1: Example of biochemical pathway: list of reactions with information on modifiers and kinetic formulas (as they can be obtained from a SBML model) |
|
Using the Biochemical Pathway Model to Teach the Concepts of
interaction is to give examples where the genes involved affect various steps in biochemical pathways. A biochemi- cal (metabolic) pathway is a sequential. |
|
Analysis and comparison of metabolic pathway databases
For example protein sequence information is listed in genome databases and functional data of corresponding enzymes can be found in protein and pathway |
|
Prediction of Dynamical Properties of Biochemical Pathways with
We assess the performances of this model on out-of-sample (unseen during training) data showing that we are indeed able to predict robustness with reasonable |
|
Prediction of Dynamical Properties of Biochemical Pathways with
We assess the performances of this model on out-of-sample (unseen during training) data showing that we are indeed able to predict robustness with reasonable |
|
WinBEST-KIT: Biochemical Reaction Simulator for Analyzing Multi
Aug 11 2021 metabolic pathways depicted in biochemical textbooks; (2) to create ... of a metabolic pathway |
|
Articles Databases of Metabolic Pathways
Jul 19 2006 metabolic pathways in biochemistry and molecular biology. This study reviews two such ... For example |
|
The underlying pathway structure of biochemical reaction networks
functional definition of biochemical pathways and their role in the context of the whole An example of a chemical reaction scheme is illustrated in Fig. |
|
Finding metabolic pathways in large networks through atom
Nov 26 2020 algorithms that improve navigation and pathway identification in big metabolic networks. The weighted reactant-product pairs of an example ... |
|
Retrosynthetic design of metabolic pathways to chemicals not found
However there are stunningly few examples where enzymes are artificially combined to make a chemical that is not found somewhere in nature. Here |
|
AP Biology 2017 FRQ 7 Student Samples
Sample Student Responses and Scoring Commentary (a) Identify the biochemical pathway S. mutans uses for metabolizing sugar and describe how the. |
|
Enzymes and Metabolic Pathways - De Anza
Example: phenylalanine metabolism Energy transfer from one metabolic pathway to another by means of ATP Catabolic pathway (catabolism): breaking down of macromolecules Releases energy which may be used to produce ATP Anabolic pathway (anabolism): building up of macromolecules |
|
Analysis and comparison of metabolic pathway databases
A pathway database is an effort to handle the current knowledge of biochemical pathways and in addition can be used for interpretation of sequence data Some of |
|
The underlying pathway structure of biochemical reaction - PNAS
(null space/stoichiometric matrix/bioinformatics/metabolic pathways/genome annotation) functional definition of biochemical pathways and their role in |
|
Biochemical Pathways— Photosynthesis - Esalq
23 sept 2010 · 7 3 The Metabolic Pathways of Photosynthesis 139 For example, the cyanobacteria Photosynthesis is a biochemical pathway that in- |
|
Metabolic Pathways
A metabolic pathway (network of biochemical reactions) begins with a specific molecule, which is altered in a series of defined steps, resulting in a certain product |
|
A theory of biochemical organization, metabolic pathways, and
The unique Simplified Molecular Input Line Entry System is a chemical language that represents any molecule by a linear sequence of sym- bols [2] For example, |