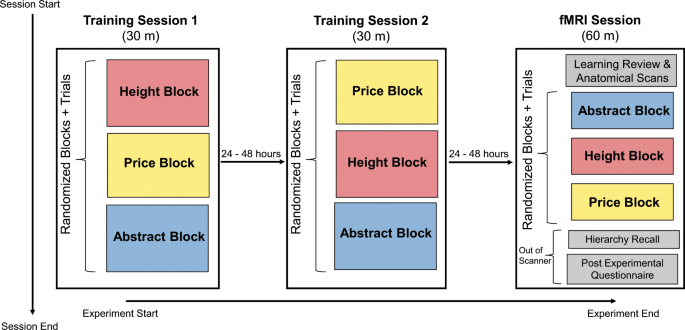
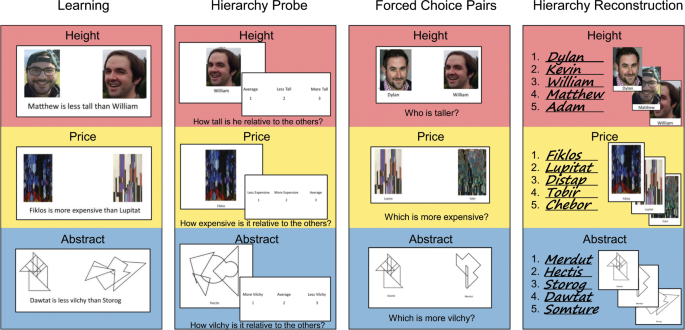
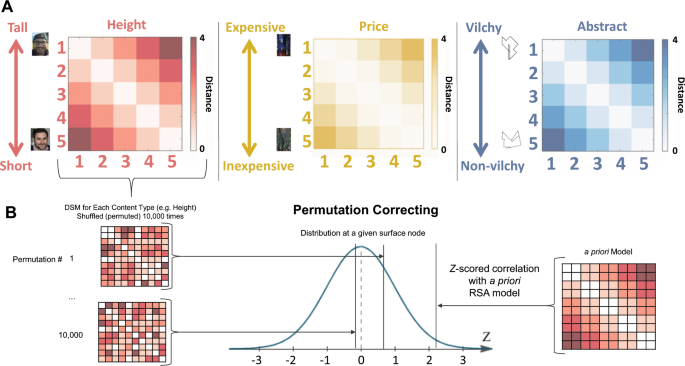
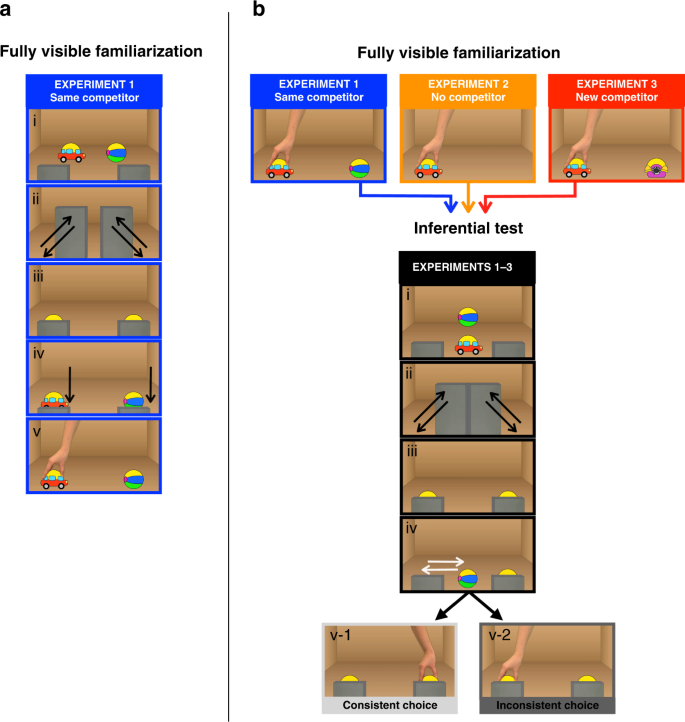
Transitive and pseudo-transitive inferences - Mental Models and
|
A Process Model of Human Transitive Inference
Developing abut rocess model of transitive inference is further complicated by on limited-capacity working memory make For transitive inferences to capacity limitations appear (Halford to1984) be and subject transi ive inference can be greatly impaired by damage to for the form of working memory required for appears that transitive inference |
|
Geoffrey P Goodwin
‘‘pseudo-transitive” fallacies Experiment 1 established that individuals’ diagrams of certain non-transitive relations yield transitive conclusions Experiment 2 showed that these premises also give rise to fallacious transitive inferences Experiment 3 established that when the context |
Are 'pseudo-transitive' fallacies a consequence of the model theory?
An unexpected consequence of the model theory is that if adult reasoners construct simple models of typical situations, then they should infer transitive relations where, in certain cases, none exists. We report four studies corroborating the occurrence of these “pseudo-transitive” fallacies.
Do individuals make invalid transitive inferences from pseudo-transitive premises?
If individuals draw such diagrams, they are likely to have envisaged corresponding mental models representing the same sort of situations. We then showed that individuals do make invalid transitive inferences from pseudo-transitive premises (Experiment 2). For example, given the problem: Fred is a blood relative of Bob’s.
Do spontaneous or preferred mental models of pseudo-transitive relations yield transitive conclusions?
Together, the two tasks aimed to show that individuals’ spontaneous or preferred mental models of the pseudo-transitive relations yielded transitive conclusions, even though they judged diagrams in which the transitive conclusions did not hold as consistent with the premises.
Is there a difference between pseudo-transitive and transitive relations?
However, a moment’s reflection should convince readers that, in contrast to the pseudo-transitive relations, there is little likelihood of constructing transitive models for such relations. The difference in the models that these relations elicit should lead to different inferences being drawn from them.
|
Transitive and pseudo-transitive inferences
axioms (''meaning postulates”) to capture such transitive inferences. An alternative theory pro- poses instead that reasoners construct mental models of the |
|
AGAINST LOGICAL FORM P.N. JohNSoN-LAirD Princeton
An alternative theory is that reasoning depends on mental models and should then be more likely to refrain from pseudo-transitive inferences. For. |
|
Mental models and human reasoning
26 oct. 2010 descriptions can avoid the need for an initial transitive inference and so mental logic fails to make the correct prediction. Anal-. |
|
Relational knowledge: the foundation of higher cognition
transitive inference based on construction of a mental model in working memory as in Figure 2a |
|
Reasoning About Relations
The Theory of Mental Operations. The first brief conjecture about transitive inferences is due to. William James and he referred to it as the fundamental |
|
Mental models and human reasoning
Now the transitive inference is no longer necessary: you have only to make the 2D inference. So |
|
Mental models and human reasoning
26 oct. 2010 descriptions can avoid the need for an initial transitive inference and so mental logic fails to make the correct prediction. Anal-. |
|
Reasoning skills and Reading (Habilidades de razonamiento y
inference making and the use of mental models in transitive reasoning the relationship of reasoning and reading comprehension and strategies in reasoning |
|
Relational knowledge: the foundation of higher cognition
Explicit transitive inference based on construction of a mental model in working memory as in Figure 2a |
|
Transitive and pseudo-transitive inferences
axioms (''meaning postulates”) to capture such transitive inferences An alternative theory pro- poses instead that reasoners construct mental models of the |
|
Mental models and human reasoning - PNAS
26 oct 2010 · When humans perceive the world, vision yields a mental model instead that E is in front of B Now, the transitive inference is no Goodwin GP, Johnson-Laird PN (2008) Transitive and pseudo-transitive inferences |
|
Reasoning from connectives and relations between entities - CORE
15 oct 2011 · They made more valid transitive inferences from a biconditional when knowledge to construct mental models of premises, and depending on |
|
Preferred mental models in reasoning about spatial relations
This diagram denotes a mental model of the layout, but The theory of mental models postulates that individuals infer that a spatial Transitive and pseudo- |