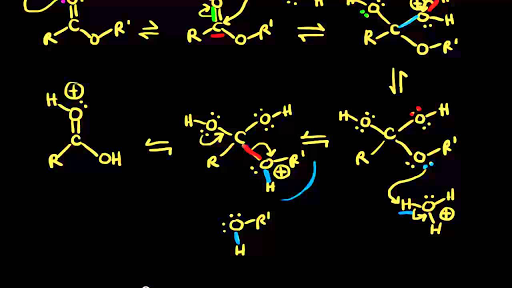
aac1 mechanism
|
THE CHEMISTRY OF THE CARBONYL GROUP
The mechanism involves base catalysed addition of hydroxide to the aldehyde; followed by hydride transfer Page 9 9 Ph O H Ph |
|
Ravi Divakaran 1 Mechanisms of Ester hydrolysis [Ref
'1' represents a 'unimolecular' mechanism and '2' represents 'bimolecular' (look at the slow step) Thus AAC1 is read as “acid-catalysed acyl cleavage |
|
Mechanisms of a Cyclobutane-Fused Lactone Hydrolysis in Alkaline
9 jui 2021 · Cyclobutane shows a perfect stability to keep the polymer's backbone when the ester groups are hydrolyzed under alkaline and acidic conditions |
What is the a Al 1 mechanism?
AAL1 : This mechanism occurs very readily when R' easily comes off as a stable carbonium ion, ie., when R' is tertiary alkyl, allyl, benzyl etc.
This is the common mechanism for acid hydrolysis of esters of tertiary alcohols.
This mechanism has been confirmed by kinetic studies, 18O labeling and isomerisation in R'.What is the mechanism of acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of ester?
The nucleophile involved in acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of the ester is H2O.
The water molecule attacks the carbonyl carbon atom by donating the oxygen's lone pair of electrons and forming a bond.
It is a nucleophilic substitution reaction as water act as a nucleophile, by attacking the carbonyl carbon of ester.Ethyl ethanoate is heated under reflux with a dilute acid such as dilute hydrochloric acid or dilute sulphuric acid.
The ester reacts with the water present to produce ethanoic acid and ethanol.
Because the reaction is reversible, an equilibrium mixture is produced containing all four of the substances in the equation.
What is AAC2 mechanism?
The AAC2 mechanism is generally considered to be the most favorable mechanism in acidic conditions: the carbonyl oxygen is protonated, one water molecule acts as a nucleophile to attack the acyl–carbon, and finally the acyl–oxygen bond is broken to form a product.9 jui. 2021
|
Substitution at sp2 Carbon (C=O System) (Part II) CONTENTS 1
Unimolecular Acid-catalyzed Hydrolysis and Esterification with Acyl-Oxygen. Heterolysis (AAC1 Mechanism). When the acid alkyl group R1 in R1CO2R2 |
|
Ravi Divakaran 1 Mechanisms of Ester hydrolysis [Ref: Jerry March
(4) Neopentyl R' does not undergo rearrangement on hydrolysis. Page 2. © Ravi Divakaran. 2. Discussion: AAC1 : This mechanism for acid-catalysed ester |
|
Mechanisms of ester hydrolysis in aqueous sulfuric acids
they occur. Of the four mechanisms possible for acid catalysis namely the AAc1 |
|
Electrolyte effects upon acid-catalyzed ester hydrolyses
AAc1 mechanism) and /-butyl acetate and benzoate. (following the AaJ mechanism) the catalytic order of strong acids is HC104 > H2S04 > HC1 |
|
The SLC25 Mitochondrial Carrier Family: Structure and Mechanism
Here we use new insights into the transport mechanism of the mitochondrial ADP There are four different isoforms in humans |
|
Mitochondrial uncouplers induce proton leak by activating AAC and
25 мая 2022 г. We also develop a mathematical model that proposes a mechanism of uncoupler-dependent IH through AAC. ... of AAC1 in the c-state and 4 in the m- ... |
|
Transcription of the AAC1 Gene Encoding an Isoform of
AAc1-4. ACT+. W.T. had. Fig. 2. Levels of AACl transcript in the wild-type and aac2 the mechanisms by which AACl is regulated by oxygen a pre- liminary ... |
|
THE CHEMISTRY OF THE CARBONYL GROUP
different catagories (AAC1 AAC2 |
|
ADIKAVI NANNAYA UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY
Ac2AAC1 |
|
The Molecular Mechanism of Transport by the Mitochondrial ADP
27 дек. 2018 г. ade2-1 trp1-1 ura3-1 can1-100 aac1::LEU2 aac2::HIS3) and grown in YEPG at 30 C. Mutant ADP/ATP carriers for biophysical studies were ... |
|
Mechanisms of ester hydrolysis in aqueous sulfuric acids
which are explicable in terms of a change in mechanism at some intermediate acidity for each believed to hydrolyze by the AA[1 and AAc1 mechanisms. |
|
Mechanisms of Lactone Hydrolysis in Acidic Conditions
03-Jun-2013 carbocations such as tertiary alkyl esters |
|
Electrolyte effects upon acid-catalyzed ester hydrolyses
Abstract: For the hydrolysis of methyl mesitoate (following the AAc1 mechanism) and /-butyl acetate and benzoate. (following the AaJ mechanism) |
|
Electrolyte effects upon acid-catalyzed ester hydrolyses
Abstract: For the hydrolysis of methyl mesitoate (following the AAc1 mechanism) and /-butyl acetate and benzoate. (following the AaJ mechanism) |
|
Ravi Divakaran 1 Mechanisms of Ester hydrolysis [Ref: Jerry March
[Ref: Jerry March “Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reactions |
|
Mechanisms of monofunctional and bifunctional catalysis of an ester
to an AAc1 mechanism here. Hydroxide Ion Reaction. The base hydrolysis of the doubly ionized ester observed in solutions above pH 10. |
|
The Molecular Mechanism of Transport by the Mitochondrial ADP
27-Dec-2018 mechanism by which mitochondrial carriers transport has not ... ade2-1 trp1-1 ura3-1 can1-100 aac1::LEU2 aac2::HIS3) and grown in YEPG at ... |
|
Kinetics and Mechanism of the Reactions of ?-Isovalerolactone in
cleave by the Aac1 mechanism to yield V.In the case of ?-propiolactone the coun- terparts of the intermediates IV and V are. |
|
THE CHEMISTRY OF THE CARBONYL GROUP
Organic Chemistry Clayden |
|
Transcription of the AAC1 Gene Encoding an Isoform of
tylate it has been shown [5] |
|
Mechanisms of Lactone Hydrolysis in Acidic Conditions
3 jui 2013 · low acid concentrations through the AAL1 mechanism AAC1 is rare and is observed mostly for esters of very bulky acids or in strongly acidic |
|
© Ravi Divakaran, 1 Mechanisms of Ester hydrolysis [Ref: Jerry
'1' represents a 'unimolecular' mechanism and '2' represents 'bimolecular' (look at the slow step) Thus AAC1 is read as “acid-catalysed acyl cleavage unimolecular”, and BAL2 as “base-catalysed alkyl cleavage bimolecular” etc |
|
Reactions involving carbonyl compounds - NPTEL
Mechanism of nucleophilic addition Orbital considerations Mechanism is similar to typical nucleophilic addition reaction AAC1 mechanism : Hydrolysis of |
|
Chapter 7 REACTIONS OF CARBONYL COMPOUNDS - at NTNU
31 mai 2009 · AAC1 MECHANISM (IN VERY STRONG ACIDIC SOLUTION) This is a useful method of hydrolyzing esters that are very severely sterically |
|
Kinetics and Mechanism of Methylthiomethyl Acetate Conversion
This mechanism apparently rules out any significant The mechanism of the acid-catalyzed conver- steps of the mechanisms AAl1 and AAC1, respectively |
|
Unit -4
Hydrolysis: Introduction, hydrolyzing agents and different mechanism of The mechanism may be written two ways, BAL2, AAC1, AAC2, AAL1 and AAL2 |
|
Lecture 6: Hydrolysis Reactions of Esters and Amides
draw the mechanism of ester hydrolysis under acidic and basic reaction conditions form new esters by base- or acid-catalysed transesterification mechanisms; |





![acid base catalysed Ester hydrolysis - [PDF Document] acid base catalysed Ester hydrolysis - [PDF Document]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esterhydrolysis-130213014134-phpapp02/95/acid-base-catalysed-ester-hydrolysis-10-638.jpg?cb\u003d1360719744)







![PDF] Theoretical Studies on Mechanism of Inactivation of Kanamycin PDF] Theoretical Studies on Mechanism of Inactivation of Kanamycin](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/l_WuC4vpTsY/sddefault.jpg)