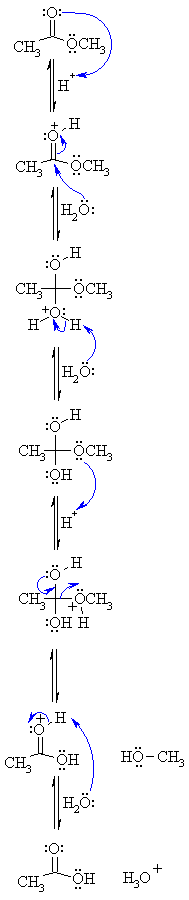
aac2 mechanism full form
|
Ravi Divakaran 1 Mechanisms of Ester hydrolysis [Ref
Secondary and benzylic acetates hydrolyse by the AAC2 mechanism in dilute sulfuric acid but the mechanism is AAL1 in concentrated acid AAL2 : This mechanism |
|
Mechanisms of a Cyclobutane-Fused Lactone Hydrolysis in Alkaline
9 jui 2021 · The AAC2 mechanism is generally considered to be the most favorable mechanism in acidic conditions: the carbonyl oxygen is protonated one water |
|
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
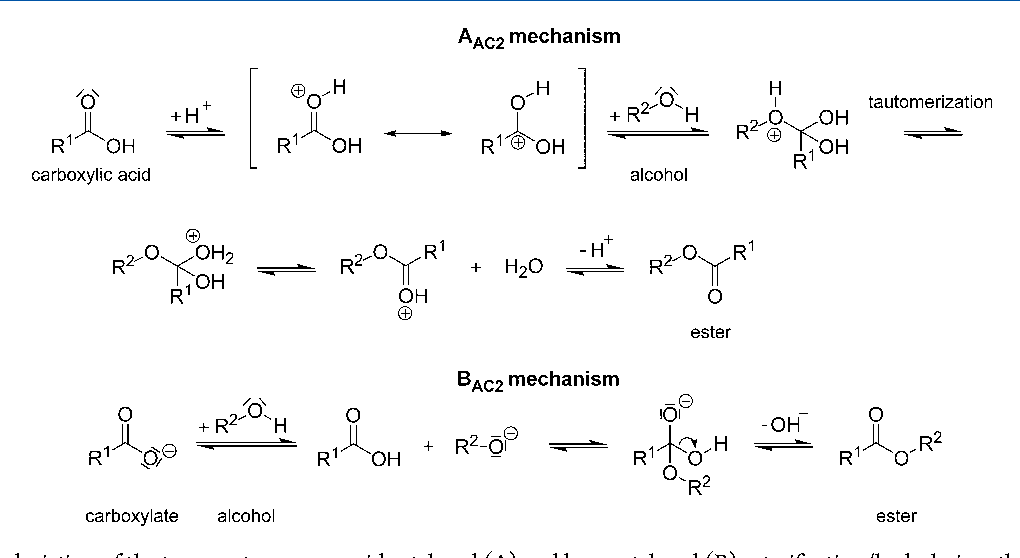
A generalized reaction mechanism under acidic conditions AAC2 (acidic acyl bimolecular) looks like this: Sodium soap is a surfactant; it disperses into |
Mechanism of Base Hydrolysis of Esters
The electrophilic reagent that is present is attacked by hydroxide nucleotides at C=0; thus creating the tetrahedral intermediate.
When the intermediate collapses, C=O will result in the loss of leaving the group alkoxide.
What is the AAC1 mechanism?
Heterolysis (AAC1 Mechanism)
This mechanism is commonly known as Acid-catalyzed, acyl-oxygen cleavage, unimolecular.
It occurs only in powerful ionizing solvents.
Exactly the same considerations apply to the esterification of hindered acids (C; Figure 1) in the reverse direction.
What is the AAL2 mechanism?
shown in Scheme 3 and Figure 7, the AAL2 mechanism is a single-step hydrolysis reaction in which a water molecule attacks the alkyl-carbon and the alkoxy bond breaks.
The bond lengths of C-Onuc and C-Olg were found to be 2.14 and 2.01 Å, respectively.
What is the mechanism of the AAC2 reaction?
The AAC2 mechanism is generally considered to be the most favorable mechanism in acidic conditions: the carbonyl oxygen is protonated, one water molecule acts as a nucleophile to attack the acyl–carbon, and finally the acyl–oxygen bond is broken to form a product.9 jui. 2021
|
Mechanisms of a Cyclobutane-Fused Lactone Hydrolysis in Alkaline
09-Jun-2021 We manually placed the water molecules to make the system form as many ... The AAC2 mechanism is similar to BAC2 both of which are two-step ... |
|
Ravi Divakaran 1 Mechanisms of Ester hydrolysis [Ref: Jerry March
Secondary and benzylic acetates hydrolyse by the AAC2 mechanism in dilute sulfuric acid but the mechanism is AAL1 in concentrated acid. AAL2 : This mechanism |
|
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
A generalized reaction mechanism under acidic conditions AAC2 (acidic |
|
Mechanistic Interpretation of the Simultaneous Hydrolysis and
with increased methanol content and in methanol the reaction takes place solely by the AAc2 mechanism. The hydrolyses of chloromethyl mono- di- |
|
AAC No. 2 of 2018
25-Jan-2018 1 The applicant shall apply to the DGCA Headquarters (Directorate of. Airworthiness) on CAR Form 12a along with Maintenance Training ... |
|
Mechanisms of ester hydrolysis in aqueous sulfuric acids
AAc2 type of mechanism in which a protonated ester molecule is attacked in This is reasonable since cleavage to form acyl- ium ion would be assisted more. |
|
Mitochondrial protein import clogging as a mechanism of disease
21-Sept-2022 ... AAC2 and aac2∆ strains in the W303-1B background. We chose this ... form when mtDNA is depleted (43). We found that growth of cells co ... |
|
Ethyl trichloroacetate hydrolysis. I. Kinetic evidence for a common
talysis instead of the AAc2 mechanism commonly observed for unsubstituted carboxylic esters. and the Aac2 path would have the form of eq 11. The k¿. £i + ti ... |
|
Application of the Hammett equation in the esterification of
In a previous study (4) we have shown that the esterification of substituted benzoic acids on AlPO in the gas phase is carried out by a typical AAc2 mechanism |
|
Electrolyte effects upon acid-catalyzed ester hydrolyses
AAc2 mechanism added sodium chloride increased the hydrolysis rate and In its original form |
|
Mechanisms of a Cyclobutane-Fused Lactone Hydrolysis in Alkaline
09-Jun-2021 favors the BAC2 and AAC2 mechanisms in alkaline and acidic conditions ... water molecules could form hydrogen bonds with each other to ... |
|
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
A generalized reaction mechanism under acidic conditions AAC2 (acidic |
|
Mechanisms of Lactone Hydrolysis in Acidic Conditions
03-Jun-2013 At acidic pH nonactivated esters usually favor the AAC2 mechanism |
|
Lecture 6: Hydrolysis Reactions of Esters and Amides - Objectives
form new esters by base- or acid-catalysed transesterification mechanisms; reaction mechanism that is described as an AAC2 reaction: the reaction is ... |
|
Mechanistic Modeling of Hydrolysis and Esterification for Biofuel
12-Oct-2011 acid esters. Krammer and Vogel23 proposed a modified form of the. Aac2 mechanism for hydrolysis of ethyl acetate in neutral HTW. |
|
An SN2 deprotection of synthetic peptides with a low concentration
by an SN2 mechanism (Aal2 and Aac2) in which carbocations are not generated |
|
Mechanisms of ester hydrolysis in aqueous sulfuric acids
they occur. Of the four mechanisms possible for acid catalysis namely the AAc1 |
|
Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of diethyl. alpha.-arylvinyl phosphates
catalyzed hydrolysis of a series of -arylvinyl phos- phates (I).6·7. 0P03Et2. Chart I. Possible Hydrolysis Mechanisms of Diethyl Vinyl. Phosphates. Aac2. |
|
Ethyl trichloroacetate hydrolysis. I. Kinetic evidence for a common
talysis instead of the AAc2 mechanism commonly observed for unsubstituted carboxylic esters. significant step is indicated by the algebraic form of the. |
|
Amino Acid Nanofibers Improve Glycemia and Confer Cognitive
29-Dec-2021 AAC2 or AAC6 was dissolved in PBS to form a 20 mM solution and left for 12 h. ... dependent mechanisms that increase glucose uptake under ... |
|
Mechanisms of Lactone Hydrolysis in Acidic Conditions
3 jui 2013 · AAC2 to AAC1 hydrolysis takes place as acidity increases A parallel work correct systematic errors by means of a homodesmic reaction The |
|
Lecture 6: Hydrolysis Reactions of Esters and Amides
form new esters by base- or acid-catalysed transesterification mechanisms; reaction mechanism that is described as an AAC2 reaction: the reaction is |
|
HYDROLYSIS
mechanisms account for neutral, acid and base hydrolysis elimination to form alkene products, which can be more environmentally persistent and hazardous In conditions and either acid or base catalysis is required (AAC2 or BAC2) N |
|
Mechanisms of Lactone Hydrolysis in Neutral and Alkaline Conditions
11 jui 2013 · AAC2) are the usual mechanisms of catalyzed hydrolysis (see below) Thus connected to each transition state by means of IRC calculations |
|
Reactions involving carbonyl compounds - NPTEL
Mechanism is similar to typical nucleophilic addition Glucose and ribose mainly exists in cyclic hemiacetal form OH OH O HO HO HO AAC2 mechanism : |
|
Reactions of Carbonyl Compounds
The mechanism of this hydrolysis reaction has been studied in great detail 4 The It is possible to shift ester hydrolyses away from the normal AAc2 or B Ac2 Protonation on nitrogen means that neutral ammonia rather than the amide ion |







![acid base catalysed Ester hydrolysis - [PDF Document] acid base catalysed Ester hydrolysis - [PDF Document]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esterhydrolysis-130213014134-phpapp02/95/acid-base-catalysed-ester-hydrolysis-6-638.jpg?cb\u003d1360719744)

![acid base catalysed Ester hydrolysis - [PDF Document] acid base catalysed Ester hydrolysis - [PDF Document]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esterhydrolysis-130213014134-phpapp02/95/acid-base-catalysed-ester-hydrolysis-4-638.jpg?cb\u003d1360719744)