calculate the molarity of 1.60 l of a solution
How do you find the molarity of a solution?
Find the molarity and volume of your solution. Make sure that the units for the volume are the same as for the volume part of the molarity (e.g., mL and mol/mL). Multiply the volume by the molarity. This is the number of moles present. Is molarity the same as concentration? Molarity is not the same as concentration, although they are very similar.
How do you abbreviate molarity?
Molarity has units of mol liter , which can be abbreviated as molar or M (pronounced "molar" ). The molar concentration of the solute is sometimes abbreviated by putting square brackets around the chemical formula of the solute. For example, the concentration of chloride ions in a solution can be written as [ Cl −] .
What is molarity vs molality?
molarity = (molality × solution mass density) / (1 + (molality × solute molar mass)) In this molarity vs molality table, you can find all main differences between these two terms: Amount of substance (in moles) divided by the volume (in litres) of the solution. Amount of substance (in moles) divided by the mass (in kg) of the solvent.
How do you calculate molarity of KMNO 4?
Calculate the molarity of a solution prepared by dissolving 23.7 grams of KMnO 4 into enough water to make 750 mL of solution. This example has neither the moles nor liters needed to find molarity, so you must find the number of moles of the solute first.
Overview
Definitions of solution, solute, and solvent. How molarity is used to quantify the concentration of solute, and how to calculate molarity. khanacademy.org
Key points
•Mixtures with uniform composition are called homogeneous mixtures or solutions. •Mixtures with non-uniform composition are heterogeneous mixtures. •The chemical in the mixture that is present in the largest amount is called the solvent, and the other components are called solutes. •Molarity or molar concentration is the number of moles of solute per liter of solution, which can be calculated using the following equation: Molarity=mol soluteL of solution •Molar concentration can be used to convert between the mass or moles of solute and the volume of the solution. khanacademy.org
Introduction: Mixtures and solutions
In real life, we often encounter substances that are mixtures of different elements and compounds. One example of a mixture is the human body. Did you know that the human body is approximately 57% water by mass? We are basically an assortment of biological molecules, gases, and inorganic ions dissolved in water. I don't know about you, but I find that pretty mind-boggling If substances are mixed together in such a way that the composition is the same throughout the sample, they are called homogeneous mixtures. In contrast, a mixture that does not have a uniform composition throughout the sample is called heterogeneous. khanacademy.org
Molar concentration
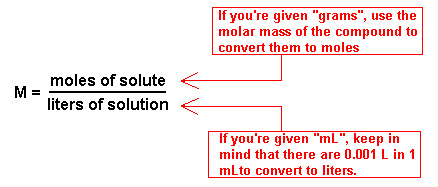
[Is molar concentration the same as molality?] The component of a solution that is present in the largest amount is known as the solvent. Any chemical species mixed in the solvent is called a solute, and solutes can be gases, liquids, or solids. For example, Earth's atmosphere is a mixture of 78% nitrogen gas, 21% oxygen gas, and 1% argon, carbon dioxide, and other gases. We can think of the atmosphere as a solution where nitrogen gas is the solvent, and the solutes are oxygen, argon and carbon dioxide. The molarity or molar concentration of a solute is defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution (not per liter of solvent): [What is a mole?] Molarity=mol soluteL of solution [Why is the volume of the solution different from the volume of the solvent?] khanacademy.org
Example 1: Calculating the molar concentration of a solute
Let's consider a solution made by dissolving 2.355g of sulfuric acid, H2SO4 , in water. The total volume of the solution is 50.0mL . What is the molar concentration of sulfuric acid, [H2SO4] ? To find [H2SO4] we need to find out how many moles of sulfuric acid are in solution. We can convert the mass of the solute to moles using the molecular weight of sulfuric acid, 98.08gmol : mol H2SO4=2.355g H2SO4×1mol98.08g=0.02401mol H2SO4 We can now plug in the moles of sulfuric acid and total volume of solution in the molarity equation to calculate the molar concentration of sulfuric acid: [H2SO4]=mol soluteL of solution=0.02401mol0.050L=0.48M Concept check: What is the molar concentration of H+ ions in a 4.8M H2SO4 solution? khanacademy.org
Example 2: Making a solution with a specific concentration
Sometimes we have a desired concentration and volume of solution, and we want to know how much solute we need to make the solution. In that case, we can rearrange the molarity equation to solve for the moles of solute. mol solute=Molarity×L of solution For example, let's say we want to make 0.250L of an aqueous solution with [NaCl]=0.800M . What mass of the solute, NaCl , would we need to make this solution? We can use the rearranged molarity equation to calculate the moles of NaCl needed for the specified concentration and volume: mol NaCl=[NaCl]×L of solution=0.800molL×0.250L=0.200mol NaCl We can then use the molecular weight of sodium chloride, 58.44gmol , to convert from moles to grams of NaCl : khanacademy.org
Summary
•Mixtures with uniform composition are called homogeneous solutions. •Mixtures with non-uniform composition are heterogeneous mixtures. •The chemical in the mixture that is present in the largest amount is called the solvent, and the other components are called solutes. •Molarity or molar concentration is the number of moles of solute per liter of solution, which can be calculated using the following equation: Molarity=mol soluteL of solution •Molar concentration can be used to convert between the mass or moles of solute and the volume of the solution. khanacademy.org
Try it: The stoichiometry of a precipitation reaction
Molarity is a useful concept for stoichiometric calculations involving reactions in solution, such precipitation and neutralization reactions. For example, consider the precipitation reaction that occurs between Pb(NO3)2(aq) and KI(aq) . When these two solutions are combined, bright yellow PbI2(s) precipitates out of solution. The balanced equation for this reaction is: Pb(NO3)2(aq)+2KI(aq)→PbI2(s)+2KNO3(aq) If we have 0.1L of 0.10M Pb(NO3)2 , what volume of 0.10M KI(aq) should we add to react with all the Pb(NO3)2(aq) ? Choose 1 answer: Choose 1 answer: •(Choice A) khanacademy.org
Want to join the conversation?
Log in khanacademy.org

Molarity Practice Problems

Molarity Made Easy: How to Calculate Molarity and Make Solutions

Molarity
|
Untitled
Calculate the molarity of 1.60 L of a solution containing 1.55 g of dissolved KBr. 1.559x. IMOL. 119.019. = 0.008/4M. 1.602. |
|
CHEMISTRY CP Name:_____ KEY Period:_____ TEST DATE: Unit
Define the following terms: solution solvent |
|
WS Solution Concentration
Calculate the molarity of a solution made by dissolving 2.00 moles of Calculate the molarity of 1.60 L of a solution containing 1.55 g of dissolved KBr. |
|
Untitled
Calculate the molarity of a solution which contains 0.40 mol of a substance dissolved in 1.6 L of a solution. 0.40 mol. 1.6L. |
|
1. CONCENTRATION UNITS A solution is a homogeneous mixture
The equation can also be used to find n (the number of moles of solute) if M (the molarity) and. V (the volume in litres) are known and V if n and M are known. |
|
Solutions are homogeneous mixtures containing two or more
See the equation below. Molarity (M) = moles of solute. Liters of solution. Sample Problem: Calculate the molarity of 1.60 L of a solution containing |
|
Tutorial 4
Solution stoichiometry calculations involve chemical reactions taking To find molarity we must convert grams KCl to moles KCl and mL solution to L:. |
|
Exercise 11.1a
4 mars 2019 Calculate the molarity of 1.60 L of a solution containing 1.55 g of dissolved KBr. 4. Calculate the molality of 4.00 mol of NaCl dissolved. |
|
Chem. 1C Midterm 2 - Practice Test 2
Calculate the molarity and molality of the student's solution. 1) 14 pts A 1.60 g sample of a mixture of naphthalene (C10H8) and anthracene. |
|
Making Dilutions Worksheet Key.pdf
You can determine the amount of a solution needed to dilute by using the following: M? x V? = M2 x V2. Where M = molarity and V = volume. and V? are the |
|
Calculations involving concentrations, stoichiometry Metric System
Conversion from mass to molar Example: Calculate molar concentration of Na2HPO4 solution c = 21 g /l (AW of Na: 23, P: 31, O: 16, H: 1) FW of Na2HPO4 |
|
Molar Concentration of Solutions
Hint: First calculate moles required, second convert moles to grams a) 600 0 mL of 0 150 M NaF b) 4 0 0 liters of 8 00 M NH4NO3 moles of solute |
|
Concentration of Solutions and Molarity - Denton ISD
dissolved in one liter of solution • To calculate the molarity of a solution, divide the moles of solute by the volume of the solution Remember that volume |
|
How to calculate Molarity
How to calculate Molarity • Molarity is a 1 Molar solution or 1M What is the molarity? • I add 37 3g of KCl to 500mL of water, what is the molarity? |
|
1 CONCENTRATION UNITS A solution is a homogeneous mixture
Solution: molarity = = 0 050 M 0 25 mole 5 0 L (b) Calculate the molarity of a solution of 4 8 mole of HCl in 600 mL of solution (N B : Convert volume to litres) |
|
How to make solutions and calculate molarity - VCU
The usual situation is that you're following a recipe that specifies, for example, a 0 5 molar solution of NaOH You know that “0 5 M” literally means 0 5 moles per |
|
TOPIC 10 CHEMICAL CALCULATIONS IV - solution stoichiometry
Molar mass = (24 31 + 2 × 35 45) = 95 21 g mol–1 i e 95 21 g of MgCl2 is exactly 1 mole Then calculate how many moles are in 45 2 g of MgCl2 Moles of MgCl2 |
|
Calculations for Solutions Worksheet and Key
2) 12 5g of glucose (C6H12O6) is dissolved in enough water to make 750 0 mL of solution a) What is the molarity (M) of the solution? b) How many moles |
|
Solutions - UTC
Note: In very dilute aqueous solution the molarity ~ molality Calculate Cgas( mol/L) as 0 16 and 1 2 x10-5 for above pressures using Cgas = kH Pgas |

/606823-calculate-molarity-of-a-solution-FINAL-5b7d7e15c9e77c0050355d4e.png)