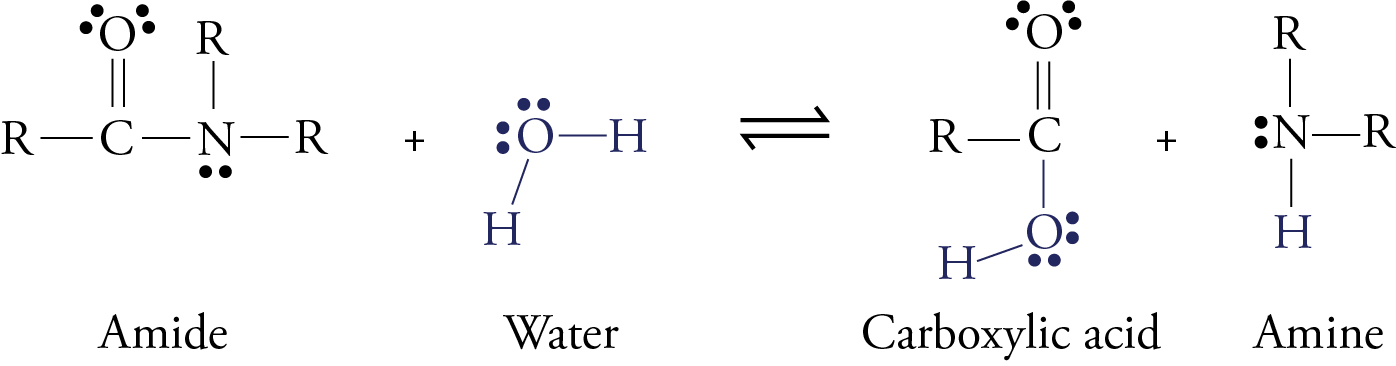acid hydrolysis of amides mechanism
What is hydrolysis of amines?
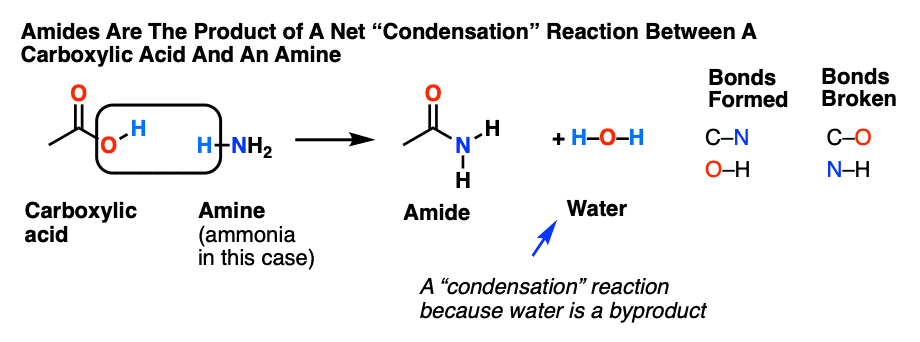
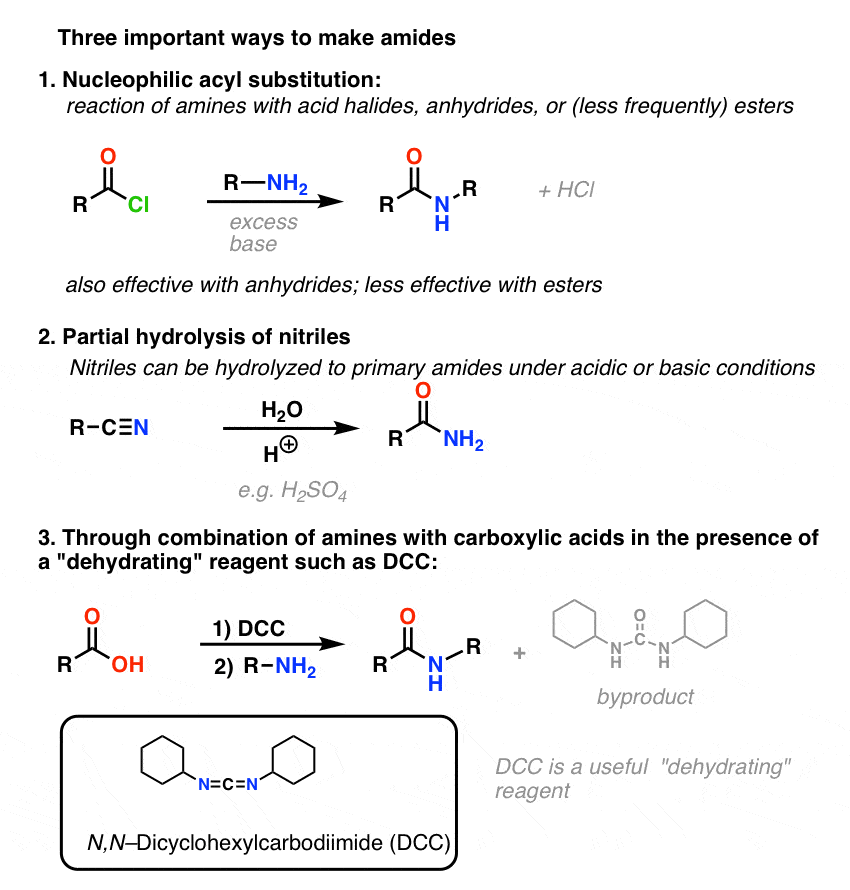
Hydrolysis of Amides Amides are carboxylic acid derivatives where the –OH of the carboxylic acid has been replaced by –NH 2, –NHR, or –NR 2 of an amine. Since the reaction between a carboxylic acid and an amine to give an amide also liberates water, this is an example of a “condensation reaction”.
What happens when amides are hydrolyzed?
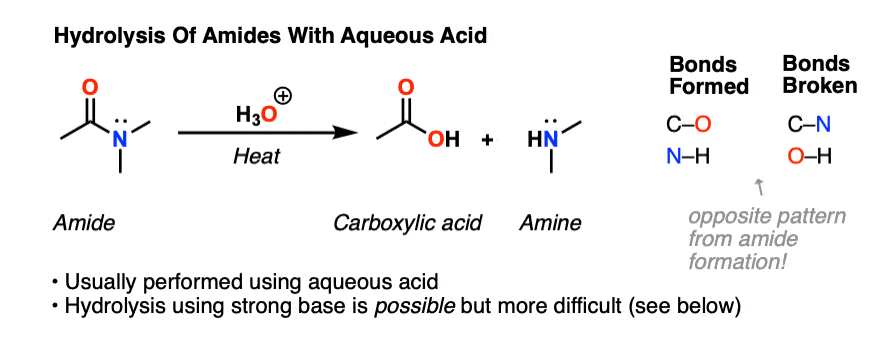
That is exactly what happens when amides are hydrolyzed in the presence of dilute acids such as dilute hydrochloric acid. The acid acts as a catalyst for the reaction between the amide and water. The alkaline hydrolysis of amides actually involves reaction with hydroxide ions, but the result is similar enough that it is still classed as hydrolysis.
What is base-promoted hydrolysis of an amide?
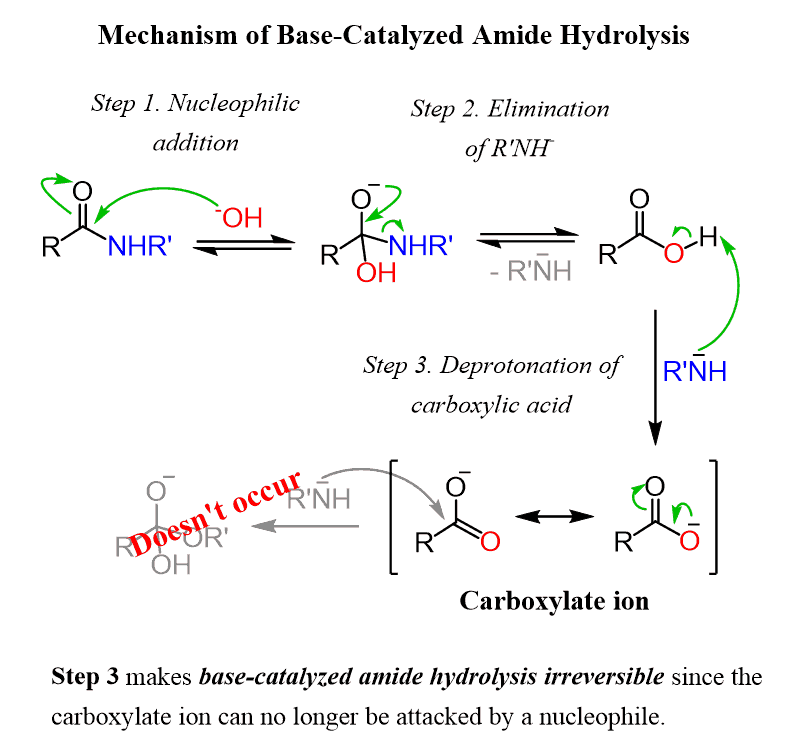
The base-promoted hydrolysis of an amide follows the typical nucleophilic acyl substitution mechanism. A full equivalent of hydroxide anion is used, so the reaction is called base-promoted and not base catalyzed.
What is an example of acidic amide hydrolysis?
For an example of acidic amide hydrolysis, this procedure in Organic Syntheses is fairly typical. A primary amide is refluxed in concentrated HCl for 2.5 hours to obtain the carboxylic acid. Catalytic Efficiencies in Amide Hydrolysis.
Hydrolysis of Amides
Amides are carboxylic acid derivatives where the –OH of the carboxylic acid has been replaced by –NH2, –NHR, or –NR2 of an amine. Since the reaction between a carboxylic acid and an amine to give an amide also liberates water, this is an example of a “condensation reaction”. [We discuss the nomenclature and synthesis of amides here]. When two amino
Hydrolysis of Amides Using Aqueous Acid: Mechanism
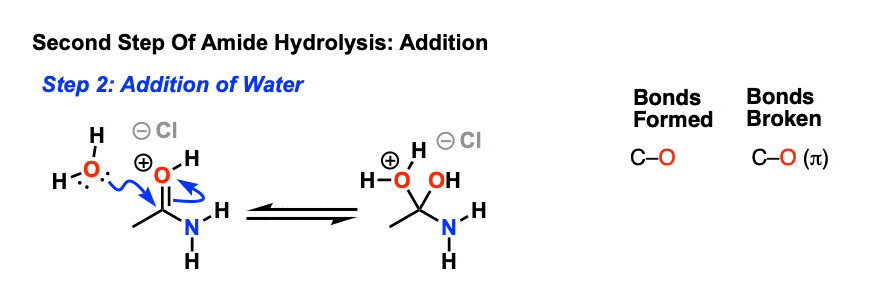
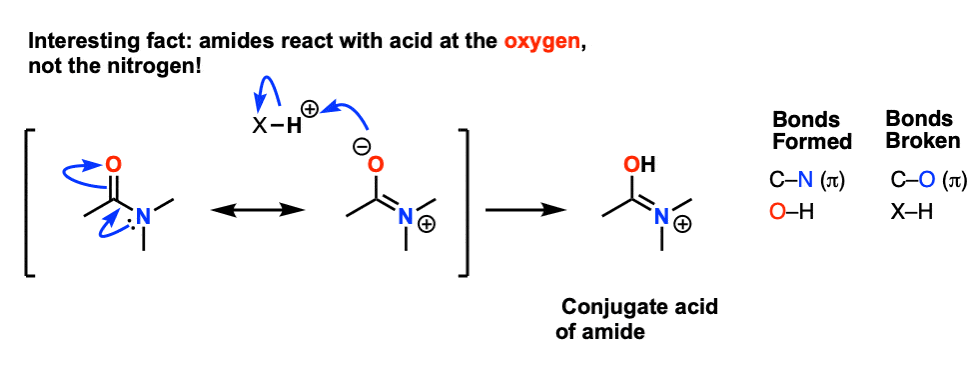
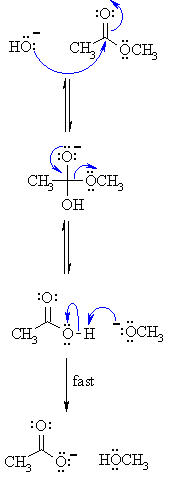
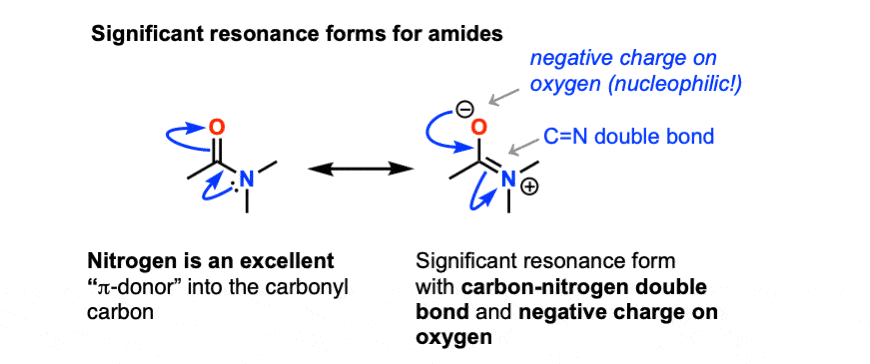
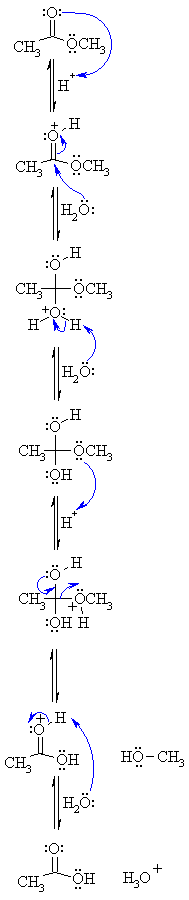
All this is to say that performing the hydrolysis of an amide is not nearly so easy as cleaving an acid halide. The mechanism is also not as simple. So how does the reaction work? As we noted, the first step is the reversible protonation of the amide on oxygen to give the conjugate acid. Protonation of the carbonyl oxygen makes the carbonyl carbon
What About Basic Hydrolysis of Amides?
So that’s acidic hydrolysis. What about basic hydrolysis? It can be done, but it’s typically not easy. If brute force is insisted upon, it’s possible. Hydrolysis of amides with base requires prolonged heating. The whole problem is that in order for a substitution reaction to occur (whether it be SN2 or acyl substitution) you need a decent leaving g
Summary: Hydrolyzing Amides to Carboxylic Acids with Acid Or Base
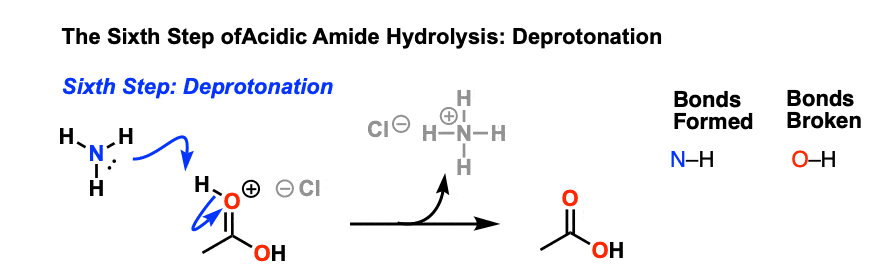
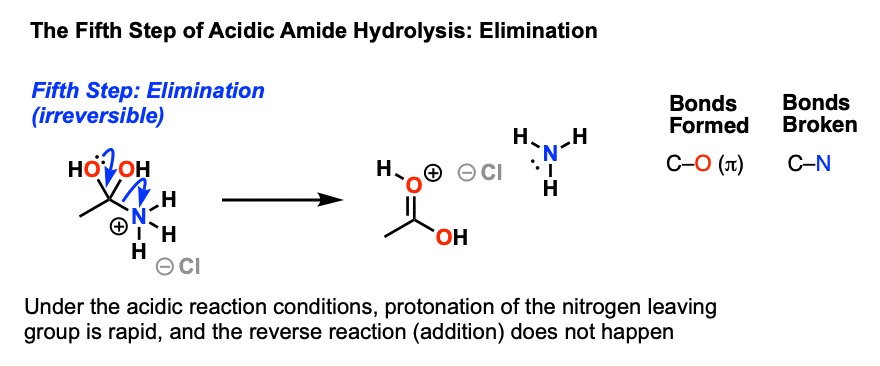
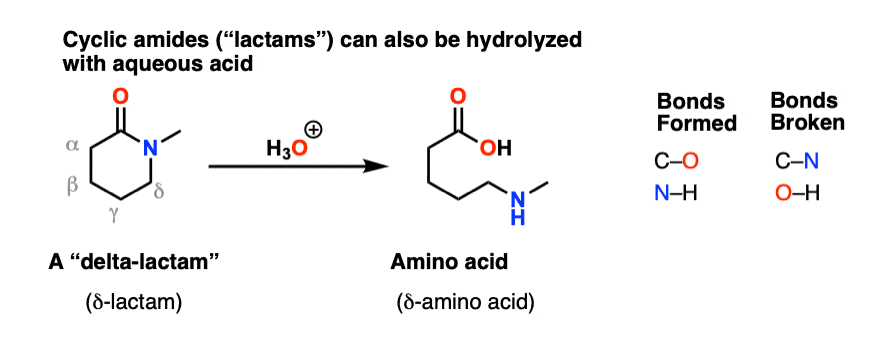
Acidic hydrolysis of amides is one of those “meat and potatoes” reactions of chemistry that are essential to know and understand. One key to thoroughly understanding the mechanism is to break the reaction down to its six steps (PADPED) and compare it to reactions that share this core mechanistic pathway (e.g. the Fischer Esterification, hydrolysis
Notes
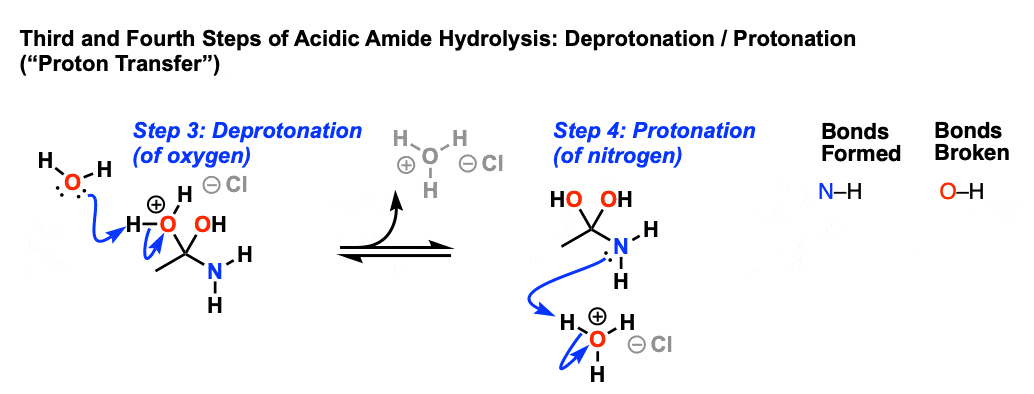
Note 1. Some studies suggest that breakage of the C-N bond does not occur until the secondOH group is deprotonated. masterorganicchemistry.com
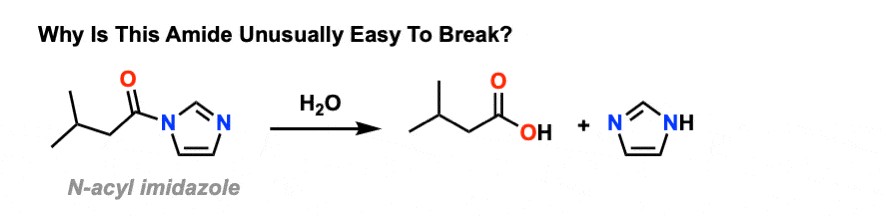
Supplemental: 3 Amides That Are Unusually Easy to Break
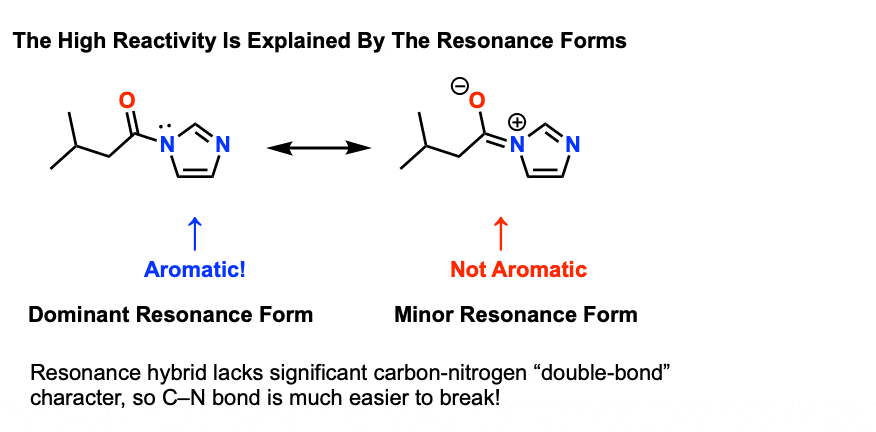
Amides That Are Unusually Easy To Break (1) – Acylimidazole As we said, amides tend to be difficult to cleave. However it’s worth looking at some exceptions that help to illustrate the key points here. One particularly easy amide to break is acyl imidazole. There’s still a C-N bond, and there’s still a lone pair on nitrogen. So why is it so easy to

Acid and base-catalyzed hydrolysis of amides Organic chemistry Khan Academy

mechanism of amide hydrolysis

Chemistry Vignettes: Amide hydrolysis
|
Acidic and Basic Amide Hydrolysis //
1 Acid Hydrolysis. A. Substituent Effects.-The mechanism generally accepted (Scheme 1) for the hydrolysis of amides in dilute acid solutions involves attack |
|
Mechanisms of Acid Hydrolysis of Carboxylic Acid Esters and Amides
Mechanisms of Acid Hydrolysis of Carboxylic Acid Esters and Amides Reasons forpreferring a symmetric mechanism of ester hydrolysis and formation are ... |
|
Hydrolysis of amides: a kinetic study of substituent effects on the
The mechanism generally accepted Tor the hydrolysis of amides in alkaline and dilute acid solution indicates that the reaction is first order with respect |
|
Observation of large amounts of carbonyl-18O exchange concurrent
A generalized mechanism of acid-catalyzed hydrolysis for the above amides is presented. Introduction. Scheme I. The generally accepted mechanism for |
|
The kinetics and mechanism of acid catalysed hydrolysis of lactams
The acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of amides has lactam hydrolysis. Three of these (A-2 types) in- been extensively investigated and the subject volve |
|
Dilute acid-catalyzed amide hydrolysis: efficiency of the N
hydrolysis of protonated amide are essentially thesame pro- viding both a necessary and sufficient criterion for the O- protonation mechanism. |
|
Hydrolysis of Amides to Carboxylic Acids Catalyzed by Nb2O5
25 déc. 2020 KEYWORDS: Nb2O5 Catalyst Amide hydrolysis |
|
Kinetics and mechanism of amide acetal hydrolysis. Carbon-oxygen
Hydrolysis. Carbon-Oxygen vs. Carbon-Nitrogen Bond Cleavage in Acid Solutions. Robert A. McClelland. |
|
Transition state activity coefficients in the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis
type of ester hydrolysis. This is interpreted in terms of an AoT2 mechanism of amide hydrolysis that is the rate-determining formation of the oxonium-type |
|
Catalyzed Hydrolysis of Amides
which contradict the acylenzyme mechanism of hydrolysis of the amide bond can be readily pf -guanidine benzoic acid [ 161. N-Benzoyl-L-arginine. |
|
On the hydrolysis mechanisms of amides and peptides
15 mai 2018 · amide, formamide, hydrolysis rate law, mechanism, peptide, square root which kineticists apply a rate law with base-, water-, and acid- |
|
Lecture 6: Hydrolysis Reactions of Esters and Amides
draw the mechanism of ester hydrolysis under acidic and basic reaction conditions; • account for the irreversibility of the hydrolysis reaction under basic |
|
THE HYDROLYSIS OF AMIDES IN THE ANIMAL BODY
TO THE MECHANISM evident that amide hydrolysis, being a relatively simple reaction, creased; the velocity of amide hydrolysis by acid, on the other hand |
|
HYDROLYSIS
mechanisms account for neutral, acid and base hydrolysis Therefore, the overall Hydrolysis generally involves conversion of phosphate tri-esters to the |