antibodies produced by b cells mark pathogens for destruction by macrophages
Why do phagocytic cells have antibodies?
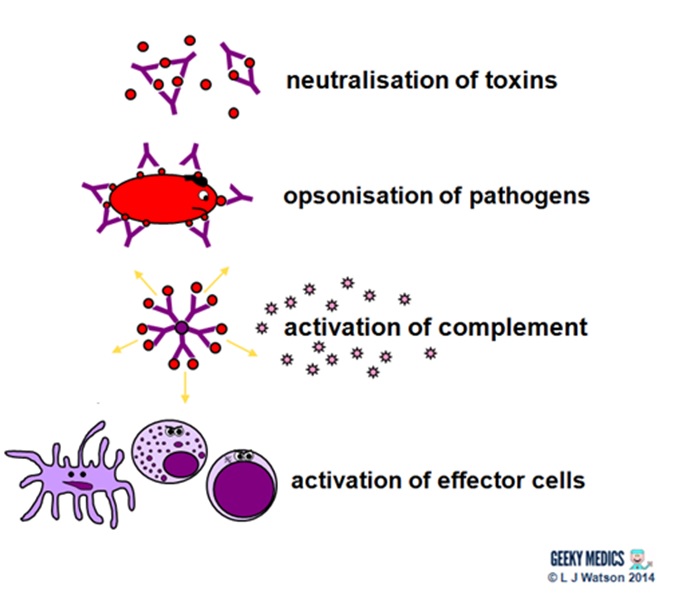
Antibodies also mark pathogens for destruction by phagocytic cells, such as macrophages or neutrophils, because phagocytic cells are highly attracted to macromolecules complexed with antibodies. Phagocytic enhancement by antibodies is called opsonization.
Why are macrophages important?
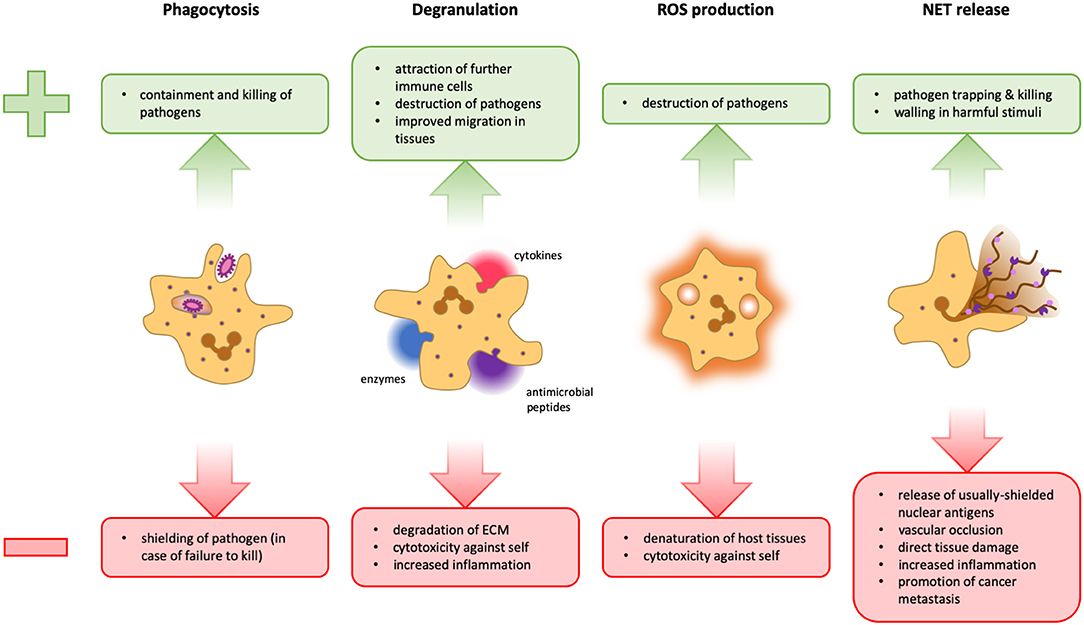
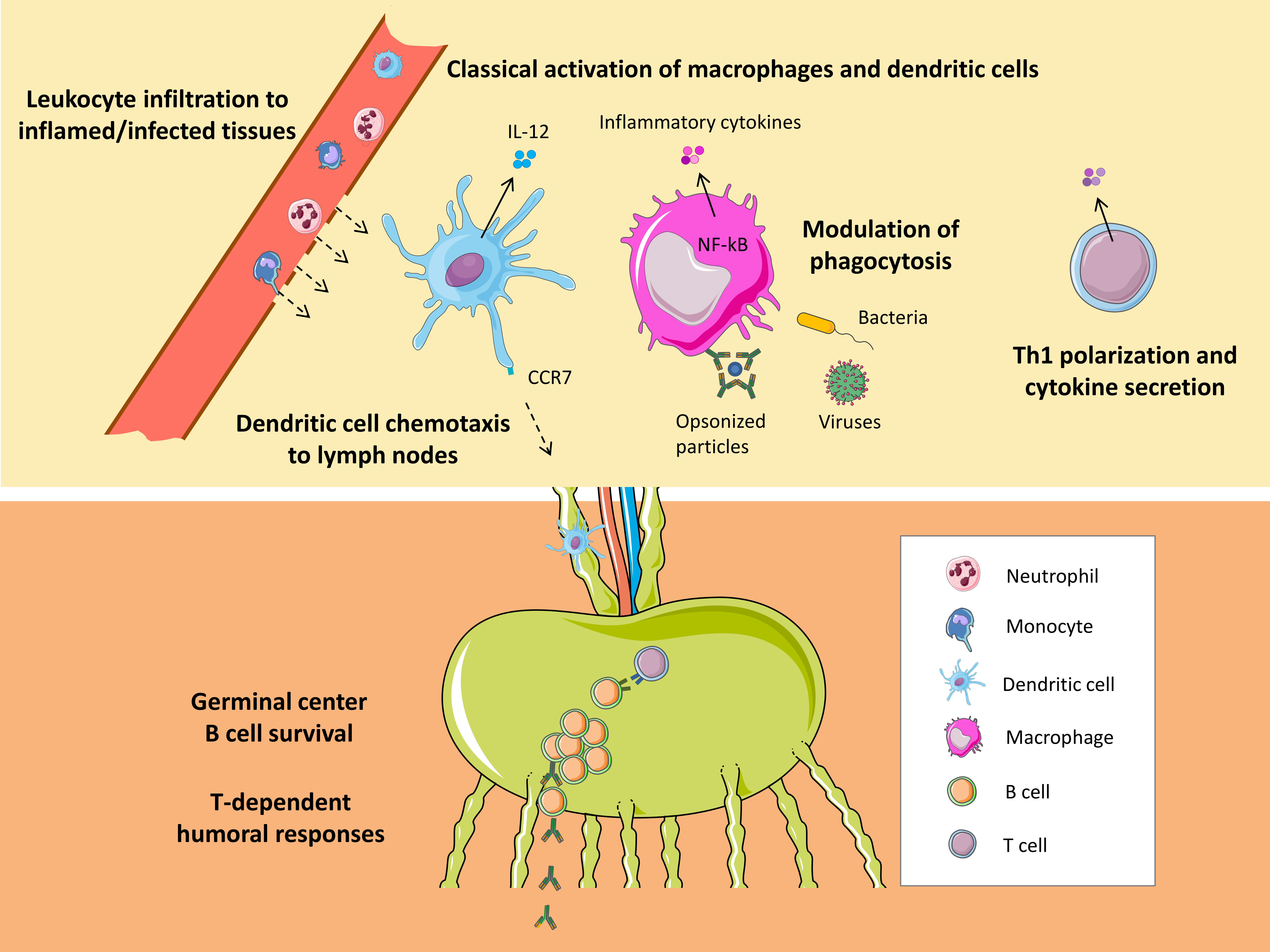
The evolution of macrophages has made them primordial for both development and immunity. Their functions range from the shaping of body plans to the ingestion and elimination of apoptotic cells and pathogens. Cytokines are small soluble proteins that confer instructions and mediate communication among immune and non-immune cells.
What cytokines and chemokines do macrophages release?
Macrophage subtypes release a vastly different array of cytokines and chemokines that can either promote inflammation and sometimes tissue destruction, or wound healing and tissue repair. M1 macrophages are known to be tumor suppressive whereas M2 macrophages generally promote tumorigenesis.
Which cells ingest antibodycoated bacteria and kill them?
Accessory cells include the phagocytic cells (macrophages and neutrophils), which ingest antibodycoated bacteria and kill them, and other cells—natural killer (NK) cells, eosinophils, basophils, and mast cells (see Fig. 1.4 )—which are triggered to secrete stored mediators when their Fc receptors are engaged.
What Are Macrophages?
Macrophages are a type of white blood cell that play an important role in the human immune system and carry out various functions including engulfing and digesting microorganisms; clearing out debris and dead cells; and stimulating other cells involved in immune function. Macrophages confer innate immunity, which is typically the first line of defe
What Are The Types of Macrophages?
Macrophages can largely be categorized into two main types: M1 and M2 macrophages. The M1 type, referred to as classically-activated macrophages, are activated by pathogen invasion and play a large role in the immune response to foreign pathogens such as bacteria. The M2 type, referred to as alternatively-activated macrophages, play a role in wound
What Is The Function of Macrophages?
Generally, macrophages play a role in destroying infectious organisms that enter the body, clearing cellular debris, and wound healing. They also play an important role in forming granulomas, which are aggregations of macrophages that function in walling off an infection. The specific function of M1 macrophages is to detect, engulf and destroy bact
Are Macrophages Good Or Bad?
Overall, macrophages are good and play a critical role in the human body. They protect our body from bacterial and viral infections by secreting antimicrobial mediators and pro-inflammatory cytokines, while also mediating repair through an anti-inflammatory response. They also allow for protection from neuronal damage in the brain, and regulate iro
What Are The Most Important Facts to Know About Macrophages?
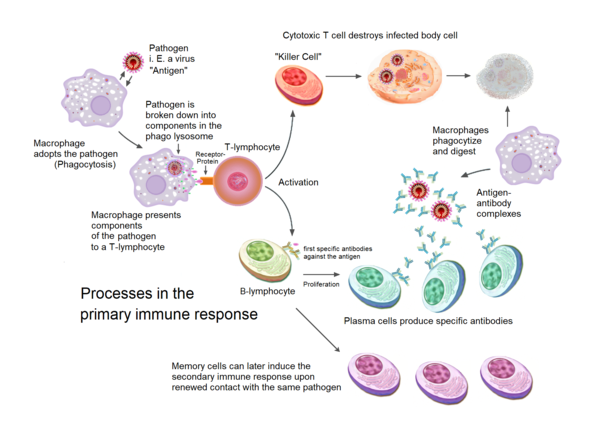
Macrophages are a type of white blood cell that play an integral part in the immune system with the role of phagocytosing foreign antigens, such as bacteria. They are able to present these antigens to other immune cells, such as T-cells, for further destruction. Macrophages also play a role in wound healing and tissue repair. They attract anti-infl

Macrophage in action vs E. coli: MOA Animation of Phagocytosis a fundamental immunological process

Macrophages: The Destroyers

Antibody Immune Response #shorts
|
Questions on Disease and Immunity
B. Viruses have developed resistance to antibiotics. Plasma (B) cells. III. Macrophages. A. II only ... D. They produce antibodies to destroy pathogens. |
|
Acting Out the Immune Response
attacked so that the antibody can mark the pathogen for T cell recognition and destruction. B lymphocytes mainly produce large amounts of antibody |
|
Innate Immunity Inflammation and Toll-like Receptors Overview
Nov 2 2010 neutrophils monocytes. B cell. T cell. Adaptive Immune Response ... Strep throat is caused by group A Streptococcus bacteria which can ... |
|
Innate Immune Response
pathogen to phagocytic cells such as macrophages and B cells |
|
A Malignant FLA
tralize pathogens or mark them for destruction B CELL. Antigens stimulate this cell to divide and produce antibodies that neutralize invaders. |
|
Mock-Patient Interviews
Infectious diseases are caused by pathogenic microbes pathogenic microbes for destruction by ... White blood cells (B cells) make antibodies against. |
|
Immune Response to Borrelia: Lessons from Lyme Disease
cells to recognize and respond to B. burgdorferi production of antibodies are critical for controlling pathogen burden after B. burgdorferi infection in. |
|
A Review of Micronutrients and the Immune System–Working in
Jan 16 2020 Calcitriol suppresses antibody production by B cells [7] ... in the blood and fluids to mark pathogens for destruction by phagocytes. |
|
Destructive Periodontitis Lesions are Determined by the Nature of
ence of bacteria the formation of an inflammatory infiltrate in B-cell/plasma cell differentiation and antibody production. |
|
Immune Mechanisms against Pathogens
the destruction of intracellular bacteria by activated macrophages additional B cells that produce anti-bacterial IgM and IgG antibodies. |
|
Biology 251 Fall 2015 1 TOPIC 24: THE IMMUNE SYSTEM I
bacteria, which are single celled organisms b) viruses, which are defense by resident macrophages b) localized vasodilation to increase blood flow c) increased produce antibodies that mark unwanted cells for destruction by other kinds of |
|
Acting Out the Immune Response - The American Association of
cell production, and T killer cell destruction of the antigen The goal of this attacked so that the antibody can mark the pathogen for T cell recognition and the body has including: the skin, macrophages, T cells, B cells, antibodies, and the |
|
Questions on Disease and Immunity
pathogens The acidity of mucus kills harmful bacteria (Total 1 mark) Plasma ( B) cells III Macrophages D They produce antibodies to destroy pathogens B Each type can recognize one specific antigen and produces a specific antibody Which sequence of events correctly describes the destruction of pathogens in |
|
Teacher Lesson Plan - The Vaccine Makers Project
detected by antigen presenting cells (APCs), such as macrophages and dendritic cells These APCs Activated B cells produce antibodies, which either neutralize the pathogen by preventing it from entering cells or flagging it for destruction Some B cells Antibodies • Mark pathogens for destruction by phagocytes and |
|
IMMUNE SYSTEM
specific cells - lymphocytes, macrophages, etc , originate from precursor cells Cell mediated immune response – defends against intracellular pathogens and cancer by binding to and lyzing the B cells - are produced and mature in the bone marrow – they Antibodies can clump microbes for destruction, mark microbes |
|
The Immune System
Activated macrophages and neutrophils release cytokines some pathogens that enable them to avoid destruction by phagocytic cells Secreted antibodies are similar to B cell receptors Antibodies do not kill pathogens; instead, they mark |
|
Common Concepts of Immune Defense - Springer
factors called chemokines and cytokines 3 Activate the complement system to mark, e g , bacteria and promote clearance of dead cells or antibody complexes |
|
The Immune System
o Innate immune cells produce a small, preset group of receptor proteins that accomplish this Some pathogens can avoid destruction by phagocytic cells o Dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells, known as antigen-presenting cells, display and exposing it to circulating antibodies, which mark it for disposal |
|
Alcohols Contribution to Compromised Immunity - Pubsniaaa
increased susceptibility to diseases caused by bacterial infections, such as tuberculosis and infected cell) and thus mark them for destruction and induces macrophages to produce IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α that eventually lead to the destruction of the bacteria bacteria Thus, antibodies on the B-cell surface recog- |