d=v*t physique
|
EXERCICES SUR LA VITESSE LA DISTANCE ET LE TEMPS NIVEAU
– soit on utilise une des trois formules : v = d t t= d v ou d=t×v NIVEAU DEBUTANT NIVEAU CONFIRME 1) Temps (en s) 20 1 Distance (en m) 50? C'est un tableau de proportionnalité :? = 50×1 20 = 25 m Donc la vitesse moyenne est 25 m/s 2) Temps (en s) 1? Distance (en cm) 2 16 C'est un tableau de proportionnalité :? = 16×1 2 = 8 s |
|
Mathematical Physics 2: Dynamics
v(t) = vT + (v0 − vT ) exp(−kt) where vT = −g/k is the terminal velocity of the particle Hence find x(t) By using the second form for the acceleration find a solution for v = v(x) Show the equivalence of the two solutions obtained Solution Since dx d ̇x dv |
|
Physics Intro & Kinematics
a = Dv/Dt (by definition) a = (v f – v 0)/t v f = v 0 + at v avg = (v 0 + v f)/2 will be proven when we do graphing Dx = vt = ½ (v 0 + v f)t = ½ (v 0 + v 0 + at)t Dx = v 0 t+ at2 2 1 (cont ) Kinematics Derivations (cont ) 2 1 v f = v 0 + at t = (v f – v 0)/a Dx = v 0t + at2 Dx =v 0 [(v f – v 0)/a] + a[(v f – v 0)/a]2 v f 2 – v 0 2 |
|
Play:block;margin-top:24px;margin-bottom:2px;\ class=\tit le-castillon-le-pieuxcollegeac-normandiefrVitesse
1 Distance parcourue ( en mètres ) 10 Formule la plus La formule d = v · t permettra de calculer la vitesse et la durée du parcours La formule t = d permettra de calculer la durée du parcours v parcourue et la vitesse Changement d’unités de vitesse : L’unité principale de distance étant le mètre et l’unité principale de |
|
V = d /t ou d =v x t ou t=v/d
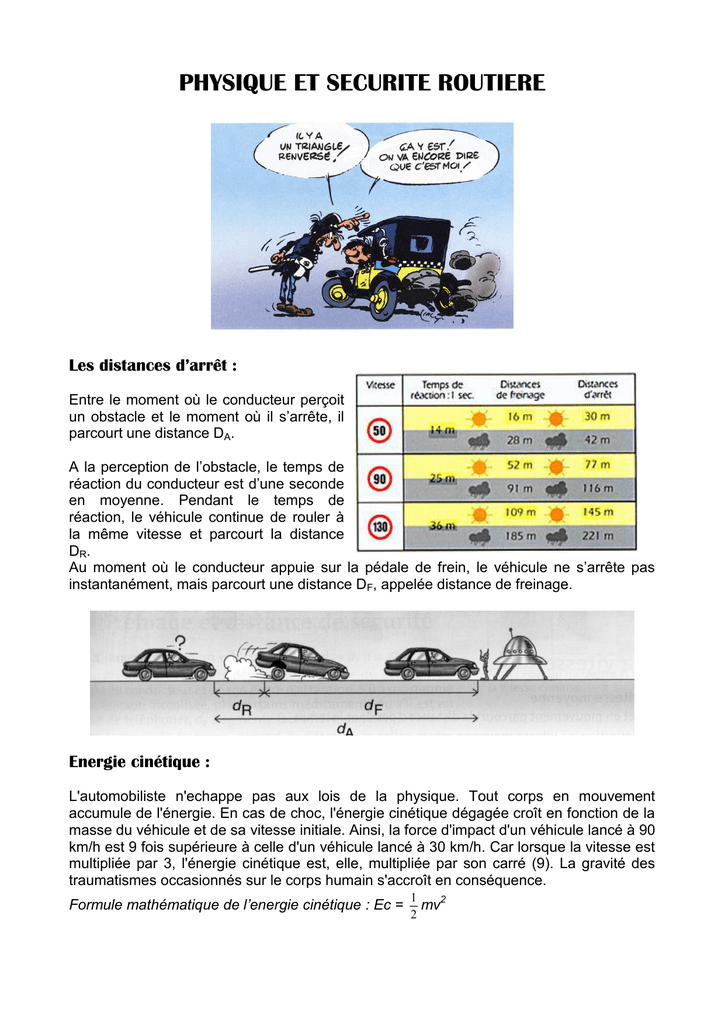
La relation entre la vitesse v d’un objet en déplacement sur une distance d pendant un temps t est : Les unités utilisées pour la vitesse sont m/s ou km/h 2- Distance de réaction Pour toute personne en bonne conditions physiques on évalue à environ 1 seconde le temps de réaction |
What is V T in physics?
Because velocity is the antiderivative of acceleration, that means that v' (t) = a (t) and v (t) = int [a (t)]. Simplifying the integral results in the equation v (t) = -9.8t + C_1, where C_1 is the initial velocity (in physics, this the initial velocity is v_0). This means that for every second, the velocity decreases by -9.8 m/s.
What is v 0 t 1 2 a T 2?
The term v 0 t represents the area of the blue rectangle since A r e c t a n g l e = h w . The term 1 2 a t 2 represents the area of the red triangle since A t r i a n g l e = 1 2 b h . [Wait, how?] That's it. The formula Δ x = v 0 t + 1 2 a t 2 has to be true since the displacement must be given by the total area under the curve.
What does v t mean in a position graph?
The areas above and below are about equal, so even though a significant distance may have been covered, the displacement is about zero, meaning the stopping point was near the starting point. The position graph shows this too. v t “forward area” “backward area”
Overview
Here are the main equations you can use to analyze situations with constant acceleration. What are the kinematic formulas? The kinematic formulas are a set of formulas that relate the five kinematic variables listed below. ΔxDisplacement tTime interval v0 Initial velocity khanacademy.org
What are the kinematic formulas?
The kinematic formulas are a set of formulas that relate the five kinematic variables listed below. ΔxDisplacement tTime interval v0 Initial velocity v Final velocity a Constant acceleration khanacademy.org
What is a freely flying object—i.e., a projectile?
It might seem like the fact that the kinematic formulas only work for time intervals of constant acceleration would severely limit the applicability of these formulas. However one of the most common forms of motion, free fall, just happens to be constant acceleration. All freely flying objects—also called projectiles—on Earth, regardless of their mass, have a constant downward acceleration due to gravity of magnitude g=9.81ms2 . g=9.81ms2(Magnitude of acceleration due to gravity) A freely flying object is defined as any object that is accelerating only due to the influence of gravity. We typically assume the effect of air resistance is small enough to ignore, which means any object that is dropped, thrown, or otherwise flying freely through the air is typically assumed to be a freely flying projectile with a constant downward acceleration of magnitude g=9.81ms2 . This is both strange and lucky if we think about it. It's strange since this means that a large boulder will accelerate downwards with the same acceleration as a small pebble, and if dropped from the same height, they would strike the ground at the same time. [How can this be so?] khanacademy.org
How do you select and use a kinematic formula?
We choose the kinematic formula that includes both the unknown variable we're looking for and three of the kinematic variables we already know. This way, we can solve for the unknown we want to find, which will be the only unknown in the formula. For instance, say we knew a book on the ground was kicked forward with an initial velocity of v0=5 m/s , after which it took a time interval t=3 s for the book to slide a displacement of Δx=8 m . We could use the kinematic formula Δx=v0t+12at2 to algebraically solve for the unknown acceleration a of the book—assuming the acceleration was constant—since we know every other variable in the formula besides a —Δx,v0,t . Problem solving tip: Note that each kinematic formula is missing one of the five kinematic variables—Δx,t,v0,v,a . 1.v=v0+at(This formula is missing Δx.) 2.Δx=(v+v02)t(This formula is missing a.) 3.Δx=v0t+12at2(This formula is missing v.) khanacademy.org
How do you derive the first kinematic formula, v=v0+at ?
This kinematic formula is probably the easiest to derive since it is really just a rearranged version of the definition of acceleration. We can start with the definition of acceleration, a=ΔvΔt [Isn't this the average acceleration?] Now we can replace Δv with the definition of change in velocity v−v0 . a=v−v0Δt Finally if we just solve for v we get khanacademy.org
How do you derive the second kinematic formula, Δx=(v+v02)t ?
A cool way to visually derive this kinematic formula is by considering the velocity graph for an object with constant acceleration—in other words, a constant slope—and starts with initial velocity v0 as seen in the graph below. The area under any velocity graph gives the displacement Δx . So, the area under this velocity graph will be the displacement Δx of the object. Δx= total area We can conveniently break this area into a blue rectangle and a red triangle as seen in the graph above. The height of the blue rectangle is v0 and the width is t , so the area of the blue rectangle is v0t . The base of the red triangle is t and the height is v−v0 , so the area of the red triangle is 12t(v−v0) . khanacademy.org
How do you derive the third kinematic formula, Δx=v0t+12at2 ?
There are a couple ways to derive the equation Δx=v0t+12at2 . There's a cool geometric derivation and a less exciting plugging-and-chugging derivation. We'll do the cool geometric derivation first. Consider an object that starts with a velocity v0 and maintains constant acceleration to a final velocity of v as seen in the graph below. Since the area under a velocity graph gives the displacement Δx , each term on the right hand side of the formula Δx=v0t+12at2 represents an area in the graph above. The term v0t represents the area of the blue rectangle since Arectangle=hw . The term 12at2 represents the area of the red triangle since Atriangle=12bh . [Wait, how?] khanacademy.org
How do you derive the fourth kinematic formula, v2=v02+2aΔx ?
To derive the fourth kinematic formula, we'll start with the second kinematic formula: Δx=(v+v02)t We want to eliminate the time t from this formula. To do this, we'll solve the first kinematic formula, v=v0+at , for time to get t=v−v0a . If we plug this expression for time t into the second kinematic formula we'll get Δx=(v+v02)(v−v0a) Multiplying the fractions on the right hand side gives Δx=(v2−v022a) khanacademy.org
What's confusing about the kinematic formulas?
People often forget that the kinematic formulas are only true assuming the acceleration is constant during the time interval considered. Sometimes a known variable will not be explicitly given in a problem, but rather implied with codewords. For instance, "starts from rest" means v0=0 , "dropped" often means v0=0 , and "comes to a stop" means v=0 . Also, the magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity on all freely flying projectiles is assumed to be g=9.81ms2 , so this acceleration will usually not be given explicitly in a problem but will just be implied for a freely flying object. People forget that all the kinematic variables—Δx,vo,v,a —except for t can be negative. A missing negative sign is a very common source of error. If upward is assumed to be positive, then the acceleration due to gravity for a freely flying object must be negative: ag=−9.81ms2 . The third kinematic formula, Δx=v0t+12at2 , might require the use of the quadratic formula, see solved example 3 below. khanacademy.org
Example 1: First kinematic formula, v=v0+at
A water balloon filled with Kool-Aid is dropped from the top of a very tall building. What is the velocity of the water balloon after falling for t=2.35 s ? Assuming upward is the positive direction, our known variables are v0=0 (Since the water balloon was dropped, it started at rest.) t=2.35 s (This is the time interval after which we want to find the velocity.) ag=−9.81ms2 (This is implied since the water balloon is a freely falling object.) khanacademy.org
|
V = d /t ou d =v x t ou t=v/d
La relation entre la vitesse v d'un objet en déplacement sur une distance d pendant un temps t est : Les unités utilisées pour la vitesse sont m/s ou km/h. |
|
Physique Chapitre 6 Terminale S
la valeur de la coordonnée vx(t) du vecteur vitesse est constante au cours du temps ; V ? x. O y. 3- D'après la modélisation = 20 m.s-1 et = 3 |
|
PROBL`EMES DE THERMODYNAMIQUE (L3) et leurs corrigés
thermodynamiques pression P volume V et température T d'un syst`eme ... comme limite l'équation d'état des gaz parfaits pour les grands volumes. |
|
5G3 – Mécanique
En physique la vitesse est une grandeur vectorielle notée v t. ?. ( ) et définie par : ( ). 0. 0 lim lim moyenne t t d. v t v t. |
|
Mécanique des fluides et transferts
?t. + V.?c = D.?2c ? k.c. Adimensionner cette équation. Mettre en évidence trois temps caractéristiques du système physique re-. |
|
Le mouvement circulaire
T = 2?r / v (T est la période) la vitesse angulaire est alors (en radians/s): ? = 2? / T = 2? v / 2?r = v / r. Accélération angulaire : ? = d? / dt. Page 6. 6. |
|
Vérifier lhomogénéité dune équation physique
déterminer la dimension d?une grandeur physique quelconque : T (temps) L (longueur) |
|
La cinématique
La mécanique est la partie de la physique qui permet de décrire et de comprendre les La distance parcourue en MRU pendant une durée est : d = V . t. |
|
Le son met un certain temps pour arriver donc il a une certaine vitesse.
m. Calculer sa vitesse moyenne : v=d/t=2m/4s=05m/s. -Rappel :. |
|
Le Bon Conseil n°6 : Extraire une grandeur dune relation littérale
Si on veut calculer d à partir des valeurs de v et t on doit d'abord extraire d |
|
Lesson 9: d-t & v-t Graphs - Studyphysics
manipulated to d = v t displacement! So if I have a v-t graph and I calculate the area under the line (which means I’m calculating velocity multiplied by time) I will know the object's displacement Homework p 15 #1 p 20 #3 6 10 p 27 # 1 2 p 45 #111617 2020-02-25 © studyphysics ca Page 5 of 5 / Section 1 2 – 1 4 |
|
Some More Practice: d-t v-t a-t - drrossymathandscience
Physics 504 Some More Practice: d-t v-t a-t 1 Consider the graph below: a What is the velocity of the object at 12 s? b What is the acceleration of the object at 5 s? |
|
V = ou t = ou d= v x t ATTENTION ! Les unités sont
Les unités sont : La tension U en Volt (V) L’intensité du courant I en Ampère (A) La résistance R en ohm (?) Formule pour calculer la puissance électrique d’un appareil : Un appareil électrique de puissance P alimenté par une tension U sera traversé par un courant d’intensité I U I = U x I ou U = ou I = ATTENTION ! |
|
V = d /t ou d =v x t ou t=v/d
La relation entre la vitesse v d’un objet en déplacement sur une distance d pendant un temps t est : v = d /t ou d =v x t ou t=v/d Les unités utilisées pour la vitesse sont m/s ou km/h 2- Distance de réaction Pour toute personne en bonne conditions physiques on évalue à environ 1 seconde le temps de réaction |
Ticker-Tape Diagrams
Constant rightward velocity
Velocity-Time Graphs
from PhysicsLab Online http://dev.physicslab.org/Document.aspx?doctype=3&filename=Kinematics_VelocityTimeGraphs.xml
What is the difference between a D-T and V-T graph?
On a d-t graph the line curves upwards, but not on a v-t graph. ?On a v-t graph the line is straight and has a positive slope. ?A straight sloped line on a v-t graph means acceleration. ?The slope of the line is equal to the acceleration; a positive slope is a positive acceleration, and a negative slope is a negative acceleration.
What is displacement - time (d-t) graph?
Displacement - Time (d-t) Graphs This type of graph is based on the most basic things we need to know about the motion of an object (position and time). ?Typically you will be given a table of values that show the displacement of the object over a particular period of time.
How to remember if it was positive or negative acceleration on D-T?
?A curved line on a d-t graph means acceleration. Here’s how you can remember if it was positive or negative acceleration on a d-t graph. ?If you see any part of the happy clown's face on a graph, it is positive acceleration. ?If you see any part of the sad clown's face, it is negative acceleration. Velocity as a function of Time Graphs
Durée : 4:09
Postée : 15 mar. 2020
Comment calculer d'avec V et T ?
Quel est la relation entre V et T ?
. Cette relation s'exprime par l'équation : V = E/T.
Comment calculer v d t ?
. Autrement dit V = D / T.
. Il est primordial de bien être attentif aux unités.
. La distance est exprimée en mètre et le temps en seconde, la vitesse sera alors exprimée en m/s (mètre par seconde).
|
Physique - Aperçu de cours du Programme du diplôme du
I Description et objectifs globaux du cours De toutes les sciences expérimentales, la physique est la plus fondamentale car elle cherche à expliquer l'univers, |
|
Document complet - Physique secondaire 3, programme détudes
et à la révision du programme d'études en physique au secondaire 3, Les sciences chimiques et physiques se préoccupent de la matière, de l'énergie |
|
Physique-chimie - AEFE Proche-Orient
Le programme de physique-chimie de la classe de première s'inscrit dans la continuité de celui de la classe de seconde, en promouvant la pratique |
|
Physique-chimie - Ministère de léducation nationale
de physique-chimie pour les classes de première et terminale Intentions majeures Compétences travaillées Quelques lignes directrices pour l' enseignement |
|
Physique côté Cours - Alienororg
Véronique Merlin-Anglade : conservateur du Musée du Périgord, Francis Gires, collectionneur et professeur de Sciences Physiques au lycée-collège Saint- |
|
Programme de physique-chimie de la voie MP - cachemedia
Le programme de physique-chimie de la classe de MP s'inscrit dans la continuité du programme de MPSI La formation scientifique de la filière MP s'appuie sur |
|
Modèle en physique ?
physique et la notion de modèle en classe de seconde dans le cadre du précédent l'enseignement de la physique-chimie au cycle terminal permet la |