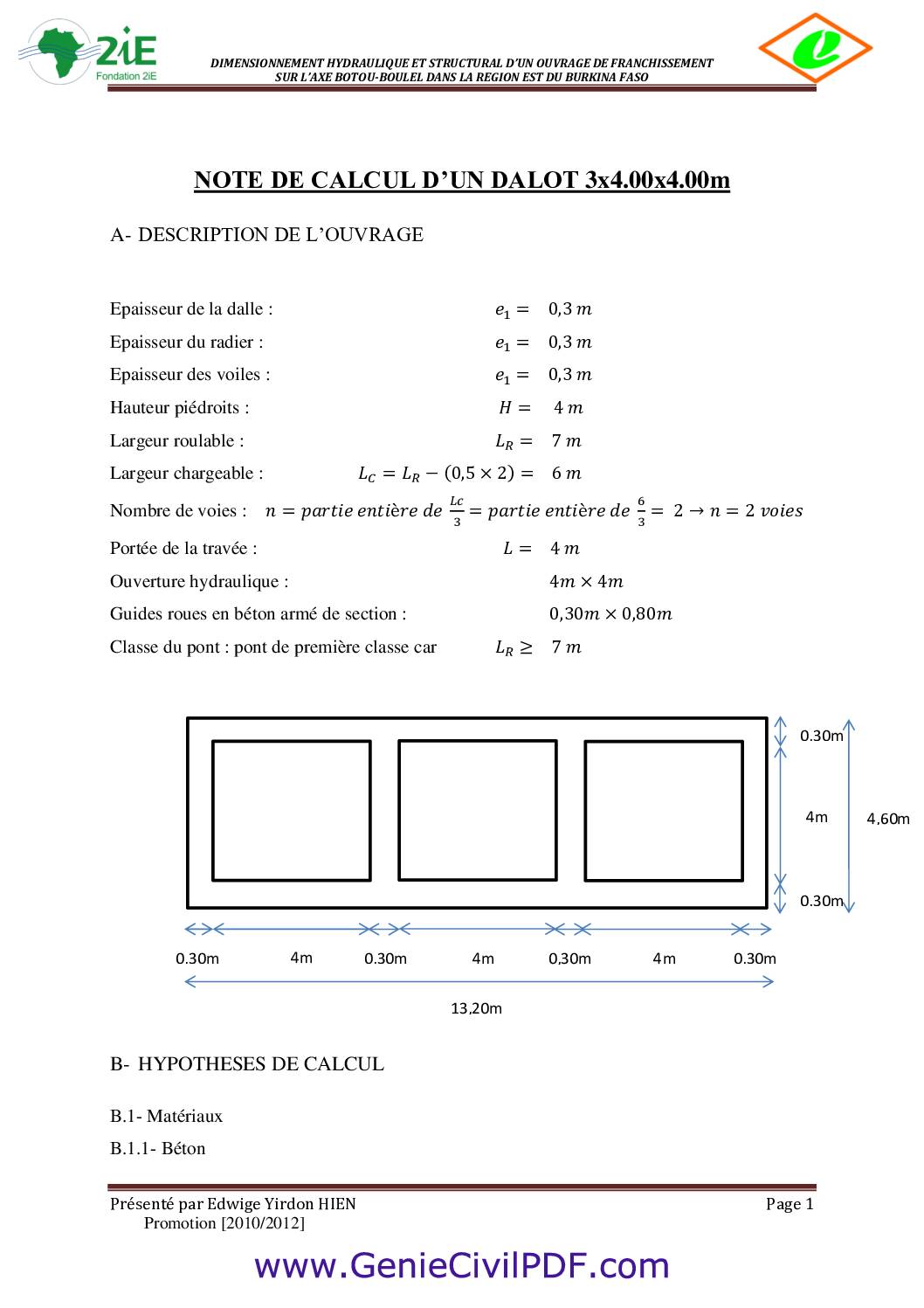
v=d/t calcul
|
1802A Topic 22 Read: TB: 174 17
r(t) = position s = arclength speed = v = ds dt v(t) = r0(t) = ds dt T = tangent vector velocity a(t) = dv dt = d2r dt2 = acceleration T = unit tangent vector N = unit normal vector κ = curvature R = 1/κ = radius of curvature ϕ = tangent angle C = Center of curvature = center of best fitting circle (has radius = radius of curva |
|
Introduction to Calculus
The number v(t) is the value of the function t at the time t The time t is the input to the function The velocity v(t) at that time is the output Most people say \"v oft\" when they read v(t) The number \"v of 2\" is the velocity when t = 2 The forward-back example has v(2) = + V and v(4) = -V The function |
|
MAT 136 Calculus I Lecture Notes
d= v t= f(t) t: (2 1 6) Now suppose that f(t) is variable If it is continuous then its value varies slightly if tchanges by a small amount Hence we may approximate the distance traveled by dividing the time interval [a;b] into small segments [t 0;t 1];[t 1;t 2]; ;[t n 1;t n] (2 1 7) of width t= b a n On each time segment [t i 1;t i] the |
|
MIT OpenCourseWare Free Online Course Materials
Calculus by Gilbert Strang is a free online textbook that covers both single and multivariable calculus in depth with applications and exercises It is based on the |
|
Vector Calculus
In reality the velocity field is V(x y z) with three components M N P Those are the velocities v v2 v in the x y z directions The speed (VI is the length: IVI2 = v: + v: -t v: In a \"plane flow\" the k component is zero and the velocity field is vi+v2j= Mi+ Nj gravity F = -R// \" |
|
VECTOR CALCULUS
v(t) = dr dt = 4ti +3j +6tk a(t) = dv dt = 4i +6k The speed of the particle at t = 1 is jv(1)j = p 42 +32 +62 = p 61 The acceleration of the particle is constant (independent of t) and its component in the direction s is a ¢ ^s = (4i +6k) ¢ (i +2j + k) p 12 +22 +12 = 5 p 6 3 3 |
How do you calculate V from F?
The velocity v is measured in km/hr or miles per hour. A unit of time enters the velocity but not the distance. Every formula to compute v from f will have f divided by time. The central question of calculus is the relation between v and f. and vice versa, and how?
How do you find V(10) in differential calculus?
Divide the change in distance by the change in time: f (10.5) -f (10.0) That average of 20.5 is closer to the speed at t = 10. It is still not exact. The way to find v(10) is to keep reducing the time interval. This is the basis for Chapter 2, and the key to differential calculus.
How f(t) is produced from the number T?
The number f (t) is produced from the number t. We read a graph, plug into a formula, solve an equation, run a computer program. The input t is "mapped" to the output f(t), which changes as t changes. Calculus is about the rate of change. This rate is our other function v. Subtracting 2 from f affects the range.
What quantities are used in the application of derivatives?
Below are some quantities that are used with the application of derivatives: 1. is the shortest distance between two positions and has a direction. Examples: - The park is 5 kilometers north of here 2. refers to the speed and direction of an object. Examples: - Object moving 5 m/s backwards 3. is the rate of change of velocity per unit time.
|
Useful Pharmacokinetic Equations
Vd = volume of distribution ke = elimination rate constant ka = absorption rate constant. F = fraction absorbed (bioavailability). K0 = infusion rate. T |
|
Chapter 15 - The Hamiltonian method
For example consider a particle undergoing 1-D motion under the influence of a potential V (x) |
|
Power MOSFET Basics
Gate Charge Test (a) Circuit (b) Resulting Gate and Drain Waveforms. V. I R. R C dv dt. GS. G. G GD. |
|
Chapter 1 - The Hodgkin–Huxley Equations
The electric field E ? @V =@x |
|
Basic Pharmacokinetics Sample Chapter
bution (V or Vd) and fraction of drug absorbed where dX/dt is the rate (mg h?1) of change of amount of drug in the blood; X is the mass or amount of. |
|
Calculation of turn-off power losses generated by an ultrafast diode
03-Oct-2017 In most ST ultrafast diode datasheets the curves of IRM |
|
Inductor Calculation for Buck Converter IC
The relation between current IL and voltage VL of coil L which has self-inductance |
|
IGBT datasheet tutorial - STMicroelectronics
Turn-on current (di/dt(on)) and voltage slope (dv/dt(on)) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27 VCES maximum ratings showed in absolute maximum ratings . |
|
De l(in)utilité du temps-réel pour le calcul ditinéraire dans les
02-May-2019 t we compute the edge euv where the vehicle is currently located and issue a new query q = (v |
|
Power MOSFET Electrical Characteristics
26-Jul-2018 dv/dt. V/ns. The maximum drain-source voltage ramp allowed at the turn-off of a MOSFET. 1.2.1. Capacitance characteristics. |
|
VECTOR CALCULUS - National University of Singapore
v(t) = dr dt = 4ti +3j +6tk a(t) = dv dt = 4i +6k The speed of the particle at t = 1 is jv(1)j = p 42 +32 +62 = p 61 The acceleration of the particle is constant (independent of t) and its component in the direction s is a ¢ ^s = (4i +6k) ¢ (i +2j + k) p 12 +22 +12 = 5 p 6 3 3 |
|
Kinematics in 1-D - Harvard University
In calculus terms v is the derivative ofx andais the derivative of v Equivalently v is theslope of thexvs tcurve andais the slope of thevvs tcurve In the case of the velocityvyou can see how this slope arises by taking the limit of v=?x/?t as?tbecomes very small;see Fig 2 1 |
|
Speed Velocity and Acceleration Calculations Worksheet s
a = (Final Velocity – Initial Velocity) / Time = (v f – v o) / t 11 A driver starts his parked car and within 5 seconds reaches a speed of 60 km/h as he travels east What is his acceleration? Equation: Plug numbers into the equation Final Answer w/ units 12 |
|
Vector Calculus - North Carolina State University
Vector Calculus - North Carolina State University |
| 72 Calculus of Variations - MIT Mathematics |
What does V mean in calculus?
In calculus terms, v is the derivative ofx, andais the derivative of v. Equivalently, v is theslope of thexvs.tcurve, andais the slope of thevvs.tcurve. In the case of the velocityv,you can see how this slope arises by taking the limit of v=?x/?t, as?tbecomes very small;see Fig. 2.1.
How to calculate the work done by a constant force?
•A work done by a constant force Fin moving object from point P to point Q in space is . •Unit tangent vector: •Consider now a variable force F(x,y,z) along a smooth curve C. •Divide Cinto number of a small enough sub-arcs so that the force is roughly constant on each sub-arc.
How do you find the area under AVVS T curve?
The area under avvs. t curve is the distancetraveled, so the di?erence in the distances is the area of the shaded region. The trian-gular region on the left has an area equal to half the base times the height, which givesT(aT)/2=aT2/2. And the parallelogram region has an area equal to the horizontal widthtimes the height, which givest(aT) =aTt.
Comment calculer T avec V et d ?
. Attention aux unités Par exemple, V est en km/h, D en km et t en h.
Quel est la relation entre V et T ?
. Cette relation s'exprime par l'équation : V = E/T.
Quelle est la formule de la vitesse V ?
|
Calcul mental - Mathématiques pré-calcul
Le calcul mental fait appel aux connaissances des nombres et des opérations Les exercices de calcul mental devraient être fréquents et courts Ils devraient |
|
REGLES DE CALCUL, ENSEMBLES DE NOMBRE, ORDRE
1/ Les calculs entre parenthèses 2/ Les puissances 3/ La multiplication et la division 4/ L'addition et la soustraction 5/ En cas d'opérations de mêmes priorités, |
|
MATHÉMATIQUES - mediaeduscoleducationfr - Ministère de l
Aux cycles 2 et 3, les calculs sont menés sous différentes formes (calcul mental, calcul en ligne, calcul posé, calcul instrumenté) souvent utilisées en interaction |
|
Le calcul en ligne au cycle 2 - mediaeduscoleducationfr - Ministère
La ressource « le calcul aux cycles 2 et 3 » (à venir), explicite de façon synthétique les objectifs et stratégies d'enseignement des différentes formes de calcul |
|
Chapitre I : Rappel sur le calcul vectoriel
Chapitre I : Rappel sur le calcul vectoriel I 1 Introduction I 2 Scalaire et vecteur I 3 Opérations sur les vecteurs I 3 1 Somme et multiplication par un scalaire |
|
Histoire du calcul
Pour simplifier leurs calculs et éviter les erreurs les hommes se sont aidés de leurs doigts puis on développer des méthodes de calculs plus efficaces pour calculer |
|
Les différentes techniques de calcul
Calcul qui se fait par décomposition des nombres et propriétés des opérations - Soit parce que l'élève ne connaît pas encore la technique de l'opération posée |
|
Thème 1: Calcul numérique
CALCUL NUMERIQUE 1 1C– JtJ 2020 Thème 1: Calcul numérique 1 1 Calculs avec des nombres entiers Notations : ensemble des nombres naturels |
|
Calcul - concours Passerelle Grande École
10 oct 2019 · Dans cette épreuve, trois compétences sont évaluées : contextualiser, calculer et raisonner Partie 1 : Calcul Cette partie propose aux candidats |
![Calcul matriciel [pdf] Calcul matriciel [pdf]](https://1.bp.blogspot.com/-ocfwSaW9GYg/XXLoKbPfCcI/AAAAAAAAHkI/vqASucEzLHkFTPqJM2wokzB2q_BFwpFTQCLcBGAs/s1600/Formation%2BSAP2000%2Ben%2Bpdf.jpg)