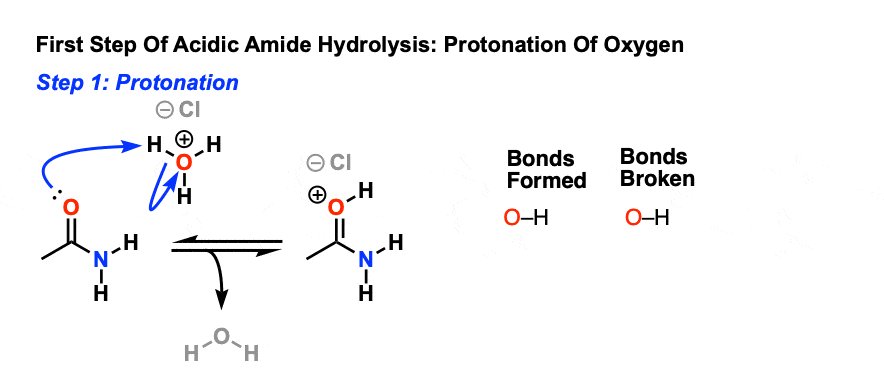
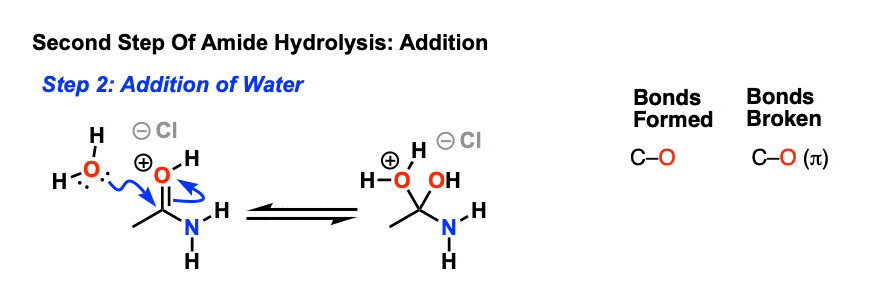
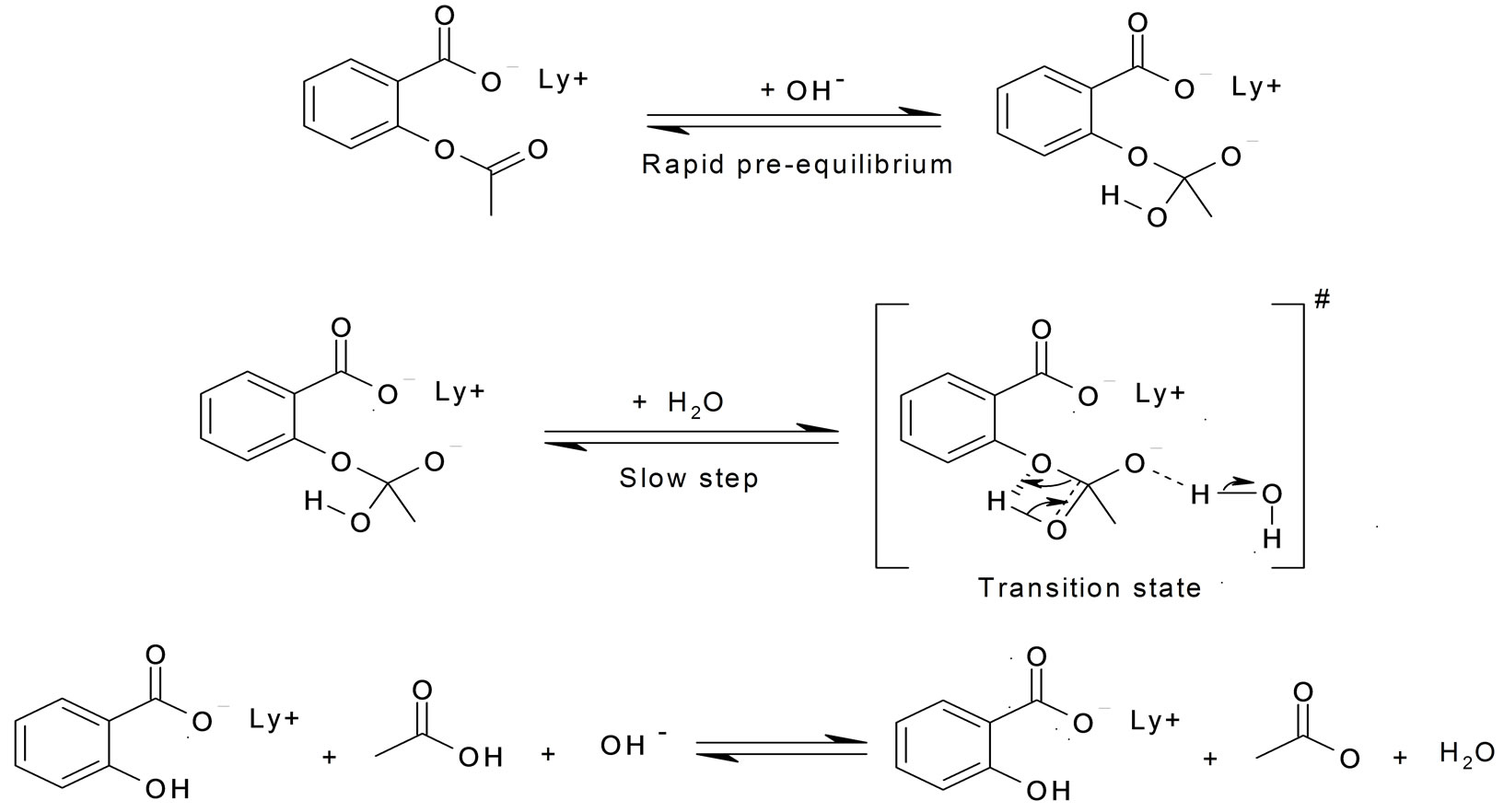
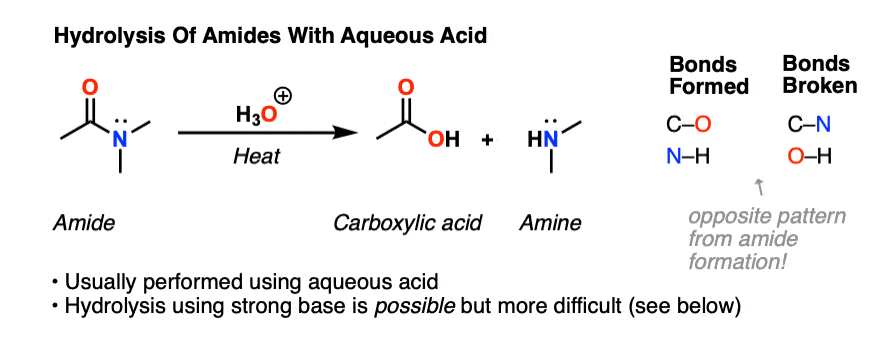
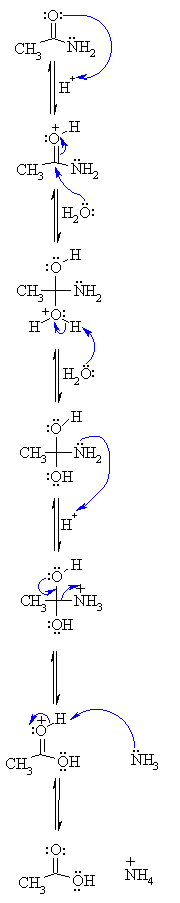
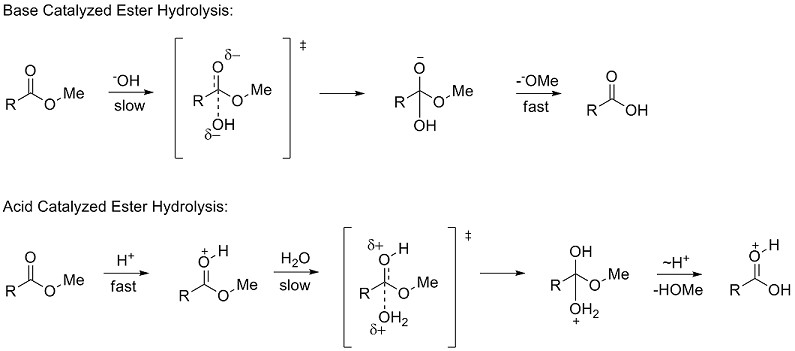
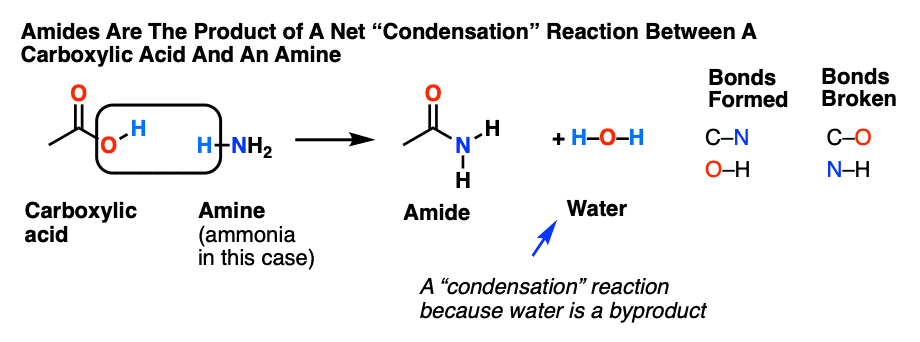
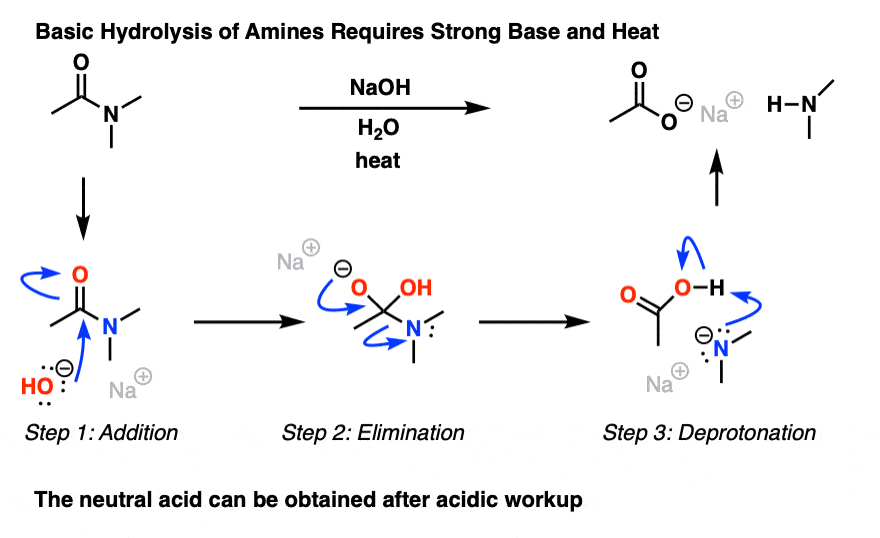
acid hydrolysis mechanism in water
|
HYDROLYSIS
Hydrolysis reactions are generally enhanced by both acids and bases and three independent reaction mechanisms account for neutral acid and base hydrolysis |
Hydrolysis of water is decomposition reaction as water decompose into oxygen and hydrogen due to electric current being passed through water.
How does acid hydrolysis work?
In organic chemistry , acid hydrolysis is a process in which a protic acid is used to catalyze the cleavage of a chemical bond via a nucleophilic substitution reaction, with the addition of the elements of water (H2O).
For example, in the conversion of cellulose or starch to glucose .
What is the mechanism of acidic hydrolysis?
Acidic hydrolysis is simply the reverse of esterification.
The ester is heated with a large excess of water containing a strong-acid catalyst.
Like esterification, the reaction is reversible and does not go to completion.
As a specific example, butyl acetate and water react to form acetic acid and 1-butanol.
What happens to water during hydrolysis?
In a hydrolysis reaction, a larger molecule forms two (or more) smaller molecules and water is consumed as a reactant.
Hydrolysis ("hydro" = water and "lysis" = break) involves adding water to one large molecule to break it into multiple smaller molecules.5 août 2021
|
The Mechanism of the Acid Hydrolysis of Sodium Aryl Sulfates1
constant) and the effect on the rate of changing per cent dioxane in dioxane-water mixtures have been determined for the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of |
|
HYDROLYSIS 2016.pdf
mechanisms account for neutral acid and base hydrolysis. Therefore |
|
The kinetics and mechanism of acid catalysed hydrolysis of lactams
Except for the (3-lactam all substrates show a strongpos~tiverate dependence on water activity |
|
The Acid Hydrolysis Mechanism of Acetals Catalyzed by a
2728. Although 1 is water-soluble it maintains a hydrophobic interior cavity able to isolate encapsulated guests from bulk solution.28 |
|
Kinetics of Alkoxysilanes and Organoalkoxysilanes Polymerization
21-Mar-2019 proton hydroxide |
|
Mechanisms of Acid Hydrolysis of Carboxylic Acid Esters and Amides
Reasons forpreferring a symmetric mechanism of ester hydrolysis and formation are of the activity of water to the Hammett acidity functionfor HC1 ... |
|
Alkaline and acidic hydrolysis of the ?-lactam ring
hydrolysis has been studied through a BAC2 mechanism characterized by a nucleophilic attack ring the H3O+ ion and a water molecule has been considered. |
|
PRESSURE EFFECT AND MECHANISM IN ACID CATALYSIS: VII
The effect of pressure on the rate of hydrolysis in water has been measured to test this mccha- nism. 'The methyl and ethyl acetates used were of analytical |
|
Towards Controlled Degradation of Poly(lactic) Acid in Technical
30-Apr-2021 The mechanism of PLA hydrolytic degradation and biodegradation will be ... Hydrolysis can take place not only in water but also in alcohol ... |
|
The Mechanism of Lactone Hydrolysis
be found on the ß-carbon atom. Fortunately the saltof ß-hydroxybutyric acid decomposes at moderate temperatures to form water and presumably a crotonate e |
|
Mechanisms of Lactone Hydrolysis in Acidic Conditions
3 jui 2013 · complexity in acid-catalyzed hydrolysis mechanisms At acidic pH the activity of water is very low, and carbon−oxygen bond cleavage occurs |
|
HYDROLYSIS
Hydrolysis reactions are generally enhanced by both acids and bases and three independent reaction mechanisms account for neutral, acid and base |
|
On the hydrolysis mechanisms of amides and peptides
15 mai 2018 · amide, formamide, hydrolysis rate law, mechanism, peptide, square root which kineticists apply a rate law with base-, water-, and acid- |
|
Mechanism of the hydrolysis of ethyl acetate in aqueous solutions of
undissociated acids, and ion pairs); the HaO + ion is added to the ester oxygen atom The kinetic equation for the reaction in which water participates as a |
|
Hydrolysis of Acetic Anhydride with Heavy Water - Thermo Fisher
In water, hydrolysis converts acetic anhydride to acetic acid, a carboxylic acid Lowry, T H ; Richardson, K S Mechanism and Theory in Organic Chemistry, 3rd |