composition of seawater ppt
What is the salinity of seawater?
The salinity of seawater is typically about 35‰, about 220 times saltier than freshwater. • Based on total salt content the water classify into: - Fresh water ( less than 1,000 ppm) - Slightly saline water (1,000 ppm to 3,000 ppm) - Moderately saline water ( 3,000 ppm to 10,000 ppm) - Highly saline water (10,000 ppm to 35,000 ppm)
What is the density of 35 ppt saline seawater?
• The density of 35ppt saline seawater at 15ºC is about 1.0255, or s (sigma)= 25.5. • Cold sea water is denser than warm sea water. • At 4°C and with the salinity of 35, the density σ of sea water is 1.02781 gram per cubic centimeter. 39. Depth –temp- density 40. Density v/s NaCl 41. Sea surface density 42.
What is the density of water at the sea surface?
• Density of ocean water at the sea surface is about 1027 kg/m3. • The density of fresh water is 1.00 (gram/ml or kg/liter) but added salts can increase this. • The saltier the water, the higher its density. 38. Density v/s temperature • When water warms, it expands and becomes less dense. • The colder the water, the denser it becomes.
Overview
seawater, water that makes up the oceans and seas, covering more than 70 percent of Earth’s surface. Seawater is a complex mixture of 96.5 percent water, 2.5 percent salts, and smaller amounts of other substances, including dissolved inorganic and organic materials, particulates, and a few atmospheric gases. Seawater constitutes a rich source of various commercially important chemical elements. Much of the world’s magnesium is recovered from seawater, as are large quantities of bromine. In certain parts of the world, sodium chloride (table salt) is still obtained by evaporating seawater. In addition, water from the sea, when desalted, can furnish a limitless supply of drinking water. Many large desalination plants have been built in dry areas along seacoasts in the Middle East and elsewhere to relieve shortages of fresh water. britannica.com
Chemical and physical properties of seawater
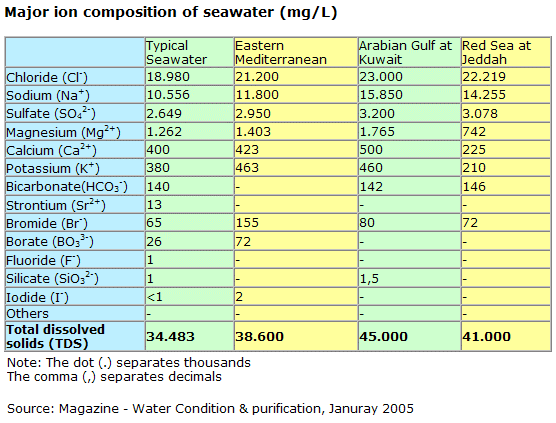
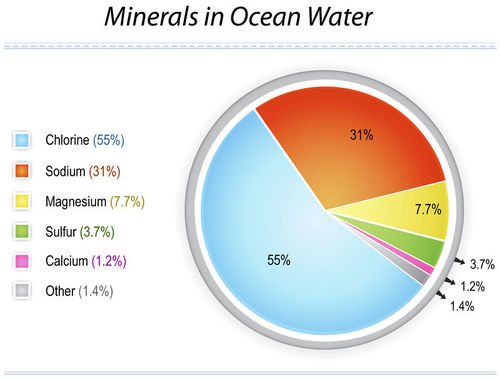
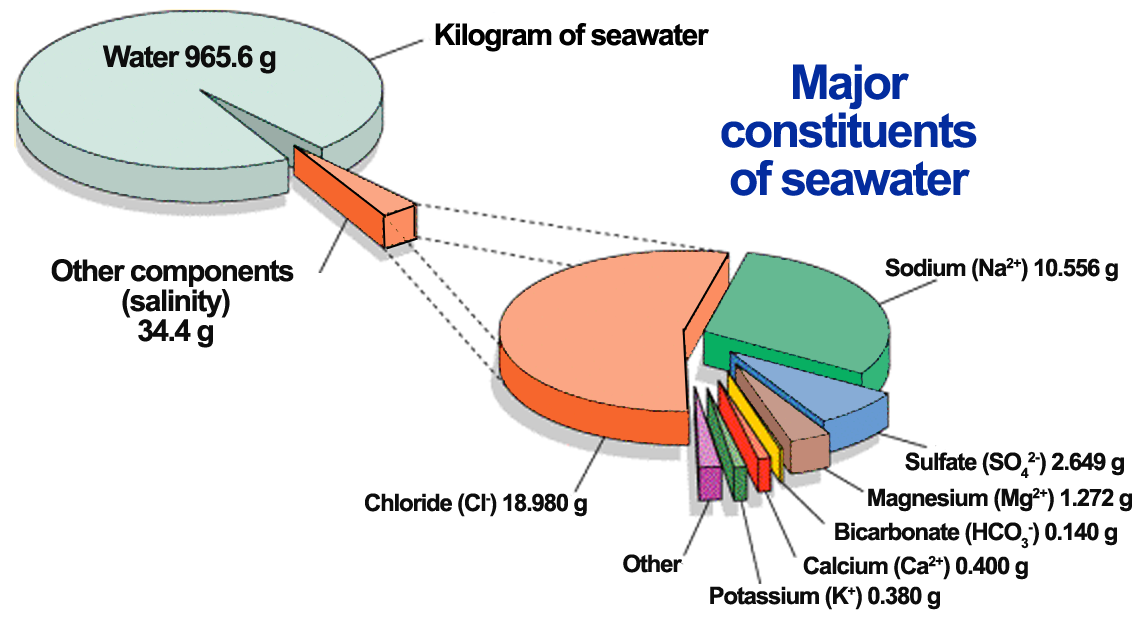
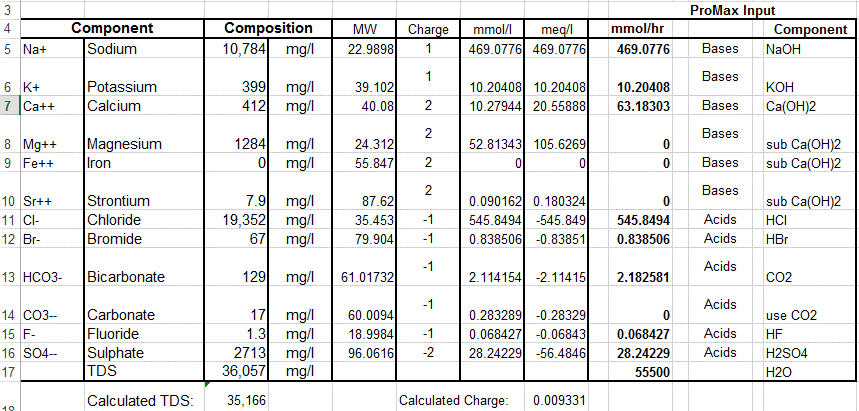
The six most abundant ions of seawater are chloride (Cl−), sodium (Na+), sulfate (SO24−), magnesium (Mg2+), calcium (Ca2+), and potassium (K+). By weight these ions make up about 99 percent of all sea salts. The amount of these salts in a volume of seawater varies because of the addition or removal of water locally (e.g., through precipitation and evaporation). The salt content in seawater is indicated by salinity (S), which is defined as the amount of salt in grams dissolved in one kilogram of seawater and expressed in parts per thousand. Salinities in the open ocean have been observed to range from about 34 to 37 parts per thousand (0/00 or ppt), which may also be expressed as 34 to 37 practical salinity units (psu). See also salinity. Inorganic carbon, bromide, boron, strontium, and fluoride constitute the other major dissolved substances of seawater. Of the many minor dissolved chemical constituents, inorganic phosphorus and inorganic nitrogen are among the most notable, since they are important for the growth of organisms that inhabit the oceans and seas. Seawater also contains various dissolved atmospheric gases, chiefly nitrogen, oxygen, argon, and carbon dioxide. Some other components of seawater are dissolved organic substances, such as carbohydrates and amino acids, and organic-rich particulates. These materials originate primarily in the upper 100 metres (330 feet) of the ocean, where dissolved inorganic carbon is transformed by photosynthesis into organic matter. Britannica Quiz Water and its Varying Forms britannica.com
Chemical composition
The chemical composition of seawater is influenced by a wide variety of chemical transport mechanisms. Rivers add dissolved and particulate chemicals to the oceanic margins. Wind-borne particulates are carried to mid-ocean regions thousands of kilometres from their continental source areas. Hydrothermal solutions that have circulated through crustal materials beneath the seafloor add both dissolved and particulate materials to the deep ocean. Organisms in the upper ocean convert dissolved materials to solids, which eventually settle to greater oceanic depths. Particulates in transit to the seafloor, as well as materials both on and within the seafloor, undergo chemical exchange with surrounding solutions. Through these local and regional chemical input and removal mechanisms, each element in the oceans tends to exhibit spatial and temporal concentration variations. Physical mixing in the oceans (thermohaline and wind-driven circulation) tends to homogenize the chemical composition of seawater. The opposing influences of physical mixing and of biogeochemical input and removal mechanisms result in a substantial variety of chemical distributions in the oceans. Special offer for students Check out our special academic rate and excel this spring semester britannica.com
|
Chemical composition of seawater; Salinity and the major constituents
Note: practical salinity is unit-less and is not a SI quantity! Salinity Measurement – The Past. Standard Mean Ocean Water (SMOW): S ≈ 35 |
|
Density Temperature Salinity Pressure Why seawater composition
and is usually expressed as parts per thousand (ppt). • 75% of seawater has a salinity ranging between 34-35 ppt. The average salinity in the oceans is 34.7 |
|
Residence time of osmium in the oceans
20 Jun 2001 composition of seawater. For elements that have residence times ... ppt [Levasseur et al. 1999]. [Os]sw |
|
CAJUN PostScript prologue for automating pdfmarks (PPT extended
composition of seawater: stratigraphic and biogeochemical implications. The Sulfur Isotopic Composition of Seawater as deduced From Trace. Sulfates in ... |
|
Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 58(6) 1095-1102 (1992) Free Amino Acid
seawater around 30 ppt because they did not need to exert excess effort for composition. Mar. Biol. |
|
Ocean water is a combination of freshwater and a variety of
Salinity is a measure of the amount of dissolved salts in seawater measured in parts per thousand (ppt). Composition of Seawater 8. Salinity (parts per ... |
|
The effect of salinity on the body chemical composition and RNA
30 Jun 2018 The water used was sea water of 34 ppt and fresh water. Seawater was taken from the beach next to the BADC while fresh water was from an ... |
|
RetroLinkTM
Zinc anodes are recommended if water is less than. 12% full strength seawater (4.2 ppt Cl). Anode composition / electrical properties - aluminium. Description. |
|
Seawater Concentrate Management
The purpose of this white paper is to discuss the composition of seawater desalination byproducts; provide an sea water discharge (55.37 ppt end- of-pipe) is ... |
|
Typical chemical characteristics of full- strength seawater
20 Apr 2020 The average value most commonly reported is 35 ppt but some authors use 34.5 ppt. ... Many authors have reported the major ion composition of ... |
|
Chemical composition of seawater; Salinity and the major constituents
Salt dissolved in ocean water alters the properties of water. Freezing point of seawater is ~ -1.8?C. Density continually increases to freezing point |
|
Chemical composition of seawater; Major constituents
Jan 28 2014 parts per thousand (ppt) ... the overall salt content of seawater ... accounts for the variation of seawater composition from. |
|
Chemical composition of seawater; Salinity and the major constituents
Salt dissolved in ocean water alters the properties of water. Freezing point of seawater is ~ -1.8?C. Density continually increases to freezing point |
|
Physical Properties of Seawater
The physical properties of seawater–temperature salinity |
|
Marine Environment and Seawater Properties.pdf
and physical activity. CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF SEAWATER 19ppt Chlorinity. Salinity (ppt) = 0.03 + 1.805 Cl-. Anions g/kg of water Cation g/kg of water. |
|
Seawater Concentrate Management
white paper is to discuss the composition of seawater desalination byproducts; concentrate salinity is usually in a range of 52 ppt to 70 ppt. |
|
Physical Properties of Seawater
For example the average salinity of ocean water is about 35 grams of salts per kilogram of seawater (g/kg) |
|
Chloride and Salinity.pdf
Sep 8 2011 Seawater has a chloride ion concentration of about 19 |
|
Indexed in Scopus Can intraspecific variations be exploited to
Apr 25 2018 chemical body composition showed increasing in dry matter |
|
Chemical composition of seawater; Major constituents
28 jan 2014 · parts per thousand (ppt) = g/kg for liquids and accounts for the variation of seawater composition from The salinity of surface sea water: |
|
Chemical composition of seawater; Salinity and the - SOEST Hawaii
Chemical composition of seawater; Salinity and the major constituents OCN 623 – Chemical Oceanography Salt dissolved in ocean water alters the properties |
|
The salinity of seawater is usually 35 parts per thousand (also
The salinity of seawater is usually 35 parts per thousand (also written as o/oo) in most marine areas This salinity measurement is a total of all the salts that are |
|
The Composition of Seawater
typically express salinity in parts per thousands • Most of the salt in seawater is sodium chloride, common table salt • Salt concentration is 3 5 salt (35 ppt) |
|
Compositions of Oceans PPT
composition of the Earth's oceans and Standard: S6E3c Describe the composition, location, and ocean floor from which sea water that has seeped into the |
|
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 14 Earth Science, 12e - NJIT
Composition of seawater ❖Seawater consists of about 3 5 (by weight) dissolved minerals ❖Salinity • Total amount of solid material dissolved in water |
|
Seawater Salinity - INSTAAR
Seawater Salinity AdOc 4060 / 5060 http://www gi alaska edu/~eicken/ he_teach/ppt/G615_Petrich pdf change the total salinity but not the composition |
|
Red Sea - AWS
elemental composition around the thriving natural reefs vary slightly to the open Parameter Artificial salt water NSW Salinity 33-36 ppt Variable pH 8 2-8 4 |