computer networking and internet pdf
|
CS144 – Introduction to Computer Networking
Homework ∼ 5 lab assignments implemented in C Possibly a problem set or other kind of lab Grading “Max” policy (sort of) Topics Network programming (sockets RPC) Network (esp Internet) architecture Switching Routing Congestion control TCP/IP Wireless networks Using the network |
|
Introduction to Networking and the Internet
Function calls system calls threads and processes |
|
Computer Networking and Management Lesson 1 Computer Networks
overview of the Internet and of networking protocols introducing several key terms and concepts We examine the \'edge\' of a computer network looking at the end systems and applications and at the transport service provided to applications running of the end systems |
What does a computer network study?
We also examine the 'core' of a computer network, examining the links and switches that transport data. We then take a broader view of networking. From a performance standpoint, we study the causes of packet delay and loss in computer network. We identify key architectural principles in networking, including layering and service models.
What is the purpose of a network?
The basic purpose of the various networks is to share software and other information between two or more computers. Over networks, there is the sharing of files, and in this process, there is the possibility of viruses being shared with the files. In recent times, the common cyber-attacks have been targeted towards big tech companies.
Where are we?
Function calls, system calls, threads and processes courses.engr.illinois.edu
What’s next?
Networked communication and distributed applications courses.engr.illinois.edu
Introduction
What is the Internet? Network edge What is a protocol? Protocol layers, service models courses.engr.illinois.edu
What is the Internet?
Communication infrastructure Enables distributed applications Web, VoIP, email, games, e-commerce, file sharing Communication services Provided to applications Reliable data delivery from source to destination “best effort” (unreliable) data delivery Mobile network Global ISP Home network Regional ISP Institutional network courses.engr.illinois.edu
Network Service
Goal Transfer data between end systems Support For Common Services Simplify the role of applications Hide the complexity of the network Semantics and interface depend on applications Example: Sending a Letter courses.engr.illinois.edu
Channels
Channel The abstraction for application-level communication Idea Turn host-to-host connectivity into process-to-process communication courses.engr.illinois.edu
Networked Communication Challenges
Networked communication ≠ IPC Problems typically masked by communication channel abstractions Bit errors (electrical interference) Packet errors (congestion) Link/node failures Message delays Out-of-order delivery Eavesdropping Goal Fill the gap between what applications expect and what the underlying technology provides courses.engr.illinois.edu
Network Architecture
Networks are complex Many “pieces” Hosts Routers Links of various media Applications Protocols Hardware, software Question Is there any hope of organizing structure of network? courses.engr.illinois.edu
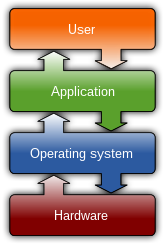
Abstraction through Layering
Abstract system into layers: Decompose the problem of building a network into manageable components Each layer provides some functionality Modular design provides flexibility Modify layer independently Allows alternative abstractions Application programs Unconfirmed service Acknowledged service Host-to-host connectivity Hardware courses.engr.illinois.edu
Layering Example: Air Travel
Layers Each layer implements a service Via its own internal-layer actions Relying on services provided by layer below courses.engr.illinois.edu
Why layering?
Complexity Explicit structure allows identification, relationship of complex system’s pieces Modularity Eases maintenance, updating of system Change of implementation of layer’s service transparent to rest of system e.g., change in gate procedure doesn’t affect rest of system courses.engr.illinois.edu
Protocol: Language of communication across hosts
Defines structure of communication between two instances of a layer (on two hosts) Protocols are defined by Specific msgs sent Specific actions taken when msgs received, or other events Protocols define Format Order of msgs sent and received among network entities Actions taken on msg transmission, receipt courses.engr.illinois.edu
Network Protocols
A protocol implements a communication service that higher-layer objects use to exchange messages Service interface To objects on the same computer that want to use its communication services Peer interface To its counterpart on a different machine Peers communicate using the services of lower-level protocols courses.engr.illinois.edu
Peer-to-peer interface
Service interface Peer-to-peer interface Higher-level protocol (TCP) Lower-level Protocol (IP) Lower-level Protocol (IP) courses.engr.illinois.edu
Layering Concepts
Encapsulation Higher layer protocols create messages and send them via the lower layer protocols These messages are treated as data by the lower-level protocol Higher-layer protocol adds its own control information in the form of headers or trailers Multiplexing and Demultiplexing Use protocol keys in the header to determine correct upper-layer pro
Encapsulation
Application Application program DATA program UNC HDR DATA Best effort Reliable Service Service Application Application program DATA program UNC HDR DATA Best effort Reliable Service Service Host-to-Host Host-to-Host HHP HDR UNC HDR DATA HHP HDR UNC HDR DATA courses.engr.illinois.edu
Internet Protocol Stack
Application Transport Network Data Link Physical Application: courses.engr.illinois.edu
Application specific protocols
Transport: Process-to-process channel Network: Host-to-host packet delivery Data Link: Physical: Framing of data bits Transmission of raw bits courses.engr.illinois.edu
Transport Layer
Provide logical communication between application processes running on different hosts Transport protocols run in end systems Send side Break application messages into segments Pass to network layer Receive side Reassemble segments into messages Pass to application layer More than one transport protocol available to applications Internet: TC
Transport vs. Network Layer
Transport layer Logical communication Bob Logical flow of information between Alice processes Relies on, enhances, network layer services Network layer Logical communication between hosts courses.engr.illinois.edu
Internet Architecture
Features No strict layering Application TCP UDP IP Network Internet Architecture – Network courses.engr.illinois.edu
Applications Creating a Network Application
Write programs that Run on (different) end systems Communicate over network e.g., web server software communicates with browser software No need to write software for network-core devices Network-core devices do not run user applications courses.engr.illinois.edu
Client-server Architecture
Server Always-on host Well-known IP address Clients Communicate with server May be intermittently connected May have dynamic IP client/server addresses Do not communicate directly with each other courses.engr.illinois.edu
P2P Architecture
No always-on server Arbitrary end systems directly communicate peer-peer Peers are intermittently connected and change IP addresses Highly scalable but difficult to manage courses.engr.illinois.edu
Sockets
Process sends/receives messages to/from its socket Analogous to a door host or host or server server Sending process shoves messages out the door courses.engr.illinois.edu
Transport infrastructure on other side of door brings message to socket at receiving process
process process socket socket TCP with buffers, variables Internet TCP with buffers, variables Sockets API Choice of transport protocol Ability to set a few parameters host or host or server server process socket TCP with buffers, variables Internet process socket TCP with buffers, variables courses.engr.illinois.edu
TCP
Unreliable data transfer Does not provide Connection setup, reliability, flow control, congestion control, timing, throughput guarantee, or security Question Why bother? Why is there a UDP? courses.engr.illinois.edu Unreliable data transfer Does not provide Connection setup, reliability, flow control, congestion control, timing, throughput guarantee, or security Question Why bother? Why is there a UDP? courses.engr.illinois.edu

1.7 History of Computer Networking and Chapter 1 (Introduction to Networking) wrap-up.

Introduction to Networking Network Fundamentals Part 1

How does the internet work? (Full Course)
|
Lesson 1 - Computer Networks and Internet - Overview
Here we use the public Internet a specific computer network |
|
Computer Networks
COMPUTER SCIENCE - CLASS XII. 186 but it is considerably less as compared to LAN. Cable TV network or cable based broadband internet services are. |
|
Computer networking & internet
EVOLUTION OF COMPUTER NETWORKS The Internet is a computer network made up of thousands of ... Files in proprietary formats (.pdf .doc). |
|
Computer Networking A Top-Down Approach 6th Edition
aspects of this book: its top-down approach its focus on the Internet and a modern treatment of computer networking |
|
Basic Networking Concepts
-A network can be defined as a group of computers and other devices -An IP address identifies a host machine on the Internet. |
|
Networking and the Internet
a human protocol and a computer network protocol: resulting in a network of networks called an internet ... The Internet: An internet that spans the. |
|
Computer-networking-and-the-internet-halsall-fred.pdf
A OneKey product is available for Computer Networking and the Internet dominant computer network as people at home and at work started to use the Web. |
|
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach 7th Edition
%207th |
|
Computer Networking and Internet Protocols: A Comprehensive
Computer Networking and Internet Protocols: Professor of Computer Science and Engineering ... http://ieee802.org/16/tgm/docs/80216m-07_002r2.pdf ... |
|
COMPUTER NETWORKS [R15A0513] LECTURE NOTES MALLA
Understanding communications and Networks 3rd Edition |
|
Computer networking & internet
EVOLUTION OF COMPUTER NETWORKS Apart form The Internet is a computer network made up of thousands of Files in proprietary formats ( pdf doc) |
|
Computer Networks and the Internet - Washington University in St
Computer Networks and the Internet Raj Jain Internet = Inter-Network = Network connecting networks http://www cse wustl edu/~jain/cse473-16/ftp/ i_0int pdf |
|
Computer Networking and Internet Protocols - Computer Science
Computer Networking and Internet Protocols: Professor of Computer Science and Engineering http://ieee802 org/16/tgm/docs/80216m-07_002r2 pdf |
|
An Introduction to Computer Networks (pdf)
3 jan 2021 · in computer networks, carefully researched, with consistent notation and in later chapters we will look at how the IP (or Internet Protocol) layer |
|
Introduction to Computer Networking - doc-developpement-durable
Fig 1 gives an example of a network in a school comprising of a local area network or LAN connecting computers with each other, the internet, and various servers |
|
Data Communication and Computer Network - Tutorialspoint
The internet hugely connects all WANs and it can have connection to LANs and Home networks Internet uses TCP/IP protocol suite and uses IP as its addressing |
|
Basic Networking Concepts
1 Introduction -A network can be defined as a group of computers and other devices -An IP address identifies a host machine on the Internet -An IP port will |
|
Introduction to Networking and the Internet
What is the Internet? Hide the complexity of the network ○ Semantics and interface depend To objects on the same computer that want to use its |
|
Networking and the Internet
Star (Wireless networks with central Access Point) a human protocol and a computer network protocol: The Internet: An internet that spans the world |

![PDF~] Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach Featuring the Intern PDF~] Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach Featuring the Intern](https://i.gr-assets.com/images/S/compressed.photo.goodreads.com/books/1458497004l/28636644.jpg)






![PDF] Basic Networking free tutorial for Beginners PDF] Basic Networking free tutorial for Beginners](https://image.isu.pub/180804090438-4c05d1a90dac2e06434117ce0231b45b/jpg/page_1.jpg)












![BOOK] Computer Networking for Beginners A Complete Guide to BOOK] Computer Networking for Beginners A Complete Guide to](https://cheqtester.com/pictures/how-to-setup-internet-cafe-network-pdf-2.jpg)