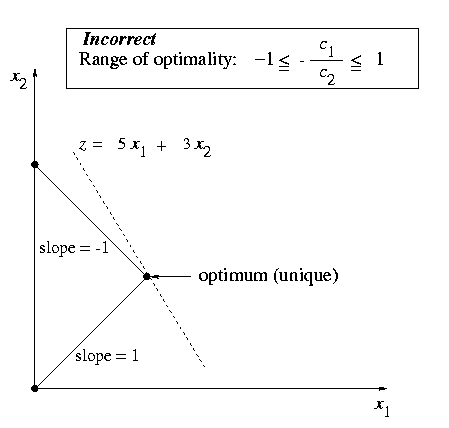
duality and post optimal analysis
|
Chapter 4 Duality
Suppose we wish to increase profit by expanding manufacturing capacities In such a situation it is useful to think of profit as a function of a vector ∆ ∈ |
|
Lecture 10: Duality and Post-Optimal Analysis
Duality and Post-Optimal Analysis September 21 2009 Overview Dual of an LP Problem (4 1) Primal-Dual Relationship (4 2 1) Simplex Table Computations (4 2 2–4 2 4) GE 330/IE 310 1 LP Dual The original LP is referred to as primal The dual is another LP associated with the given LP It is defined systematically An LP and its dual are closely related: |
|
Play:block;margin-top:24px;margin-bottom:2px;\ class=\tit wwwifpillinoiseduLecture 11: Post-Optimal Analysis
•Using dual simplex method we can determine an optimal so-lution for the perturbed problem from the optimal table of the original problem •Using the dual problem/duality we can analyze additional changes •Introducing new operations (resources) LP Model: New constraints in the original (primal) problem •Introducing new products (activities) |
Is there a finite optimal solution for both primal and dual problems?
If a finite feasible solution exists for both the primal and dual problems, then there exists a finite optimal solution for both problems where In other words, the maximum feasible value of the primal objective function equals the minimum feasible value of the dual objective function. Note then for any feasible solution,
Which theorem states One immediate implication of weak duality?
The following theorem states one immediate implication of weak duality. Theorem 4.2.2. (Certificate of Optimality) If x and y are feasible so-lutions of the primal and dual and cT x = bT y, then x and y must be optimal solutions to the primal and dual.
Does duality theory apply to linear programs?
Duality theory applies to general linear programs, that can involve greater-than, less-than, and equality constraints. However, to keep things simple, we will only study in this section linear programs that are in symmetric form. Such linear programs take the form: x ≥ 0. for some matrix A ∈
How do you find a dual objective?
Consider the following linear program (LP). Plot the feasible region of the primal and show that the primal objec-tive value goes to infinity. Formulate the dual, plot the feasible region of the dual, and show that it is empty. Convert the following optimization problem into a symmetric form linear program, and then find the dual.
4.1.1 Sensitivity Analysis
Suppose we wish to increase profit by expanding manufacturing capacities. In such a situation, it is useful to think of profit as a function of a vector ∆ ∈ <4 of changes to capacity. We denote this profit by z(∆), defined to be the maximal objective value associated with the linear program maximize cT x subject to web.stanford.edu
4.1.3 The Dual Linear Program
Shadow prices solve another linear program, called the dual. In order to distinguish it from the dual, the original linear program of interest – in this case, the one involving decisions on quantities of cars and trucks to build in order to maximize profit – is called the primal. We now formulate the dual. To understand the dual, consider a situati
4.2 Duality Theory
In this section, we develop weak and strong duality in general mathematical terms. This development involves intriguing geometric arguments. Devel-oping intuition about the geometry of duality is often helpful in generating useful insights about optimization problem. Duality theory applies to general linear programs, that can involve greater-than,
4.2.3 First Order Necessary Conditions
It is possible to establish the Strong Duality Theorem directly, but the KKT conditions (given later in this section) are useful in their own right, and strong duality is an immediate consequence. Before given the KKT conditions, we digress still more, and talk about convex sets and hyperplanes. Given two sets, U and V , we say that a hyper-plane H
4.3 Duals of General Linear Programs
For a linear program that isn’t in the symmetric form we can still construct the dual problem. To do this, you can transform the linear program to sym-metric form, and then construct the dual from that. Alternatively, you can apply the KKT conditions directly. Either approach results in an equivalent problem. For example, suppose the linear program
4.4 Two-Player Zero-Sum Games
In this section, we consider games in which each of two opponents selects a strategy and receives a payoff contingent on both his own and his opponent’s selection. We restrict attention here to zero-sum games – those in which a payoff to one player is a loss to his opponent. Let us recall our example from Chapter ?? that illustrates the nature of s
4.5 Allocation of a Labor Force
Our economy presents a network of interdependent industries. Each both produces and consumes goods. For example, the steel industry consumes coal to manufacture steel. Reciprocally, the coal industry requires steel to support its own production processes. Further, each industry may be served by multiple manufacturing technologies, each of which req
M technologies.
In the remainder of this section, we will leverage linear algebra and duality theory to prove the substitution theorem. web.stanford.edu
4.5.1 Labor Minimization
Consider a related problem with an objective of minimizing the labor required to generate a particular “bill of goods” b ∈ web.stanford.edu
4.5.2 Productivity Implies Flexibility
Consider M technologies, each of which produces one of the M goods. To-gether they can be described by an M × M production matrix A. Inter-estingly, if A is productive then any bill of goods can be met exactly by appropriate application of these technologies. This represents a sort of flexi-bility – any demands for goods can be met without any exce
Aˆx < αAx + Aˆx = A(αx + ˆx),
contradicting the fact that at least one component of A(αx+ˆx) is nonpositive. web.stanford.edu
Question 6
Consider a symmetric form primal linear program: maximize cT x subject to Ax ≤ b ≥ 0. Find the dual of this problem. Noting that max f(x) = min −f(x) rearrange the dual into symmetric form. Take the dual of you answer, and rearrange again to get into symmetric form. Explain why the sensitivities of the optimal dual objective to the dual constraints
M = , q = , z = . −AT 0 −b y
Derive the dual Show that the optimal solution to the dual is given by that of the primal and vice-versa. Show that the primal problem has an optimal solution if and only if it is feasible. web.stanford.edu
Question 10
Why is it that, if the primal has unique optimal solution x∗, there is a sufficiently small amount by which c can be altered without changing the optimal solution? web.stanford.edu
Question 13 - Elementary Asset Pricing and Arbitrage
You are examining a market to see if you can find arbitrage opportunities. For the same of simplicity, imagine that there are M states that the market could be in next year, and you are only considering buying a portfolio now, and selling it in a years time. There are also N assets in the market, with price vector ρ ∈ web.stanford.edu
|
Lecture 10: Duality and Post-Optimal Analysis
Lecture 10: Duality and Post-Optimal Analysis. September 21 2009 of a dual constraint |
|
Ch.4 Duality and Post Optimal Analysis
provides the optimal solution to the other. • The primal problem represents a resource allocation case where the dual problem. |
|
Linear Programming with Post-Optimality Analyses
The original maximization equation/problem is known as the Primal. To calculate the Dual problem the number of variables is calculated by looking at the number |
|
Lecture 11: Post-Optimal Analysis
Sep 23 2009 Dual Simplex Method. • The dual simplex method will be crucial in the post-optimal analysis. • It used when at the current basic solution |
|
LECTURE 5: DUALITY AND SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS
Sensitivity is a post-optimality analysis of a linear program in which some components of (A |
|
1 Post-optimal analysis
This set of notes discusses post-optimal analysis or how to draw conclusions However LINDO also lists values for so-called reduced costs" and dual. |
|
Lecture 12: Post-Optimal Analysis
Sep 25 2009 Then a dual simplex method can be used to determine a new feasible solution. We want x7 to leave (since it is not feasible). Which variable will ... |
|
Duality in Linear Programming
In the preceding chapter on sensitivity analysis we saw that the shadow-price interpretation of the optimal simplex multipliers is a very useful concept. |
|
Duality in Linear Programming
Furthermore an optimal dual variable is nonzero only if its associated constraint In Chapter 3 |
|
Lecture 10: Duality and Post-Optimal Analysis
Duality and Post-Optimal Analysis September 21, 2009 The original LP is referred to as primal • The dual is another LP associated with the given LP |
|
5 DUAL LP, SOLUTION INTERPRETATION, AND POST-OPTIMALITY
POST-OPTIMALITY 5 1 DUALITY Associated with every linear programming problem (the primal) is Various types of sensitivity analysis can answer such |
|
Linear Programming with Post-Optimality Analyses
This is what essentially all LP packages do in a more efficient way call the Simplex Method Dual Problem and Its Meaning The Dual Analysis involves looking at |
|
LECTURE 5: DUALITY AND SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS - NC State ISE
Sensitivity analysis 4 Dual simplex If x is a primal feasible solution to (P) and w is a dual feasible Sensitivity is a post-optimality analysis of a linear program |
|
Lesson 5 Slides-Revised Simplex Method, Duality and - NPTEL
Primal-Dual relationship is also helpful in sensitivity or post optimality analysis of decision variables Page 3 D Nagesh Kumar, IISc Optimization Methods: M3L5 |
|
Chapter 4 Duality
analysis Consider a situation where the metal stamping and engine assembly ca - pacity constraints are binding at the optimal solution to the linear program |
|
1 Post-optimal analysis
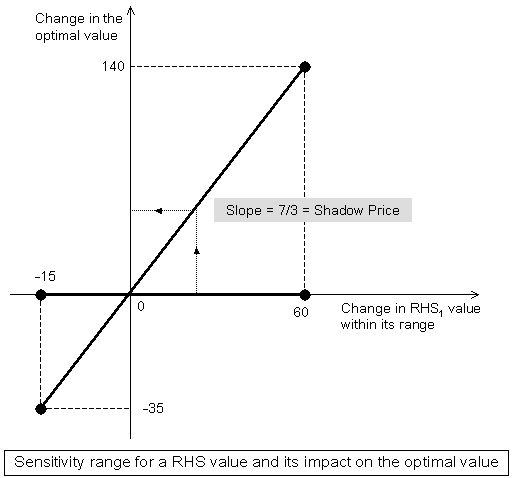
A constraint's dual price is also a measure of the decrease in the optimal solution value for each allowable unit of decrease in the RHS value of that constraint |
|
SENSITIVITY AND DUALITY ANALYSES OF AN OPTIMAL WATER
one Operations Researcher to assist them in some of these post-optimality analyses KEYWORDS: Sensitivity Analysis, Duality Analysis, Linear Programming, |
![Post-optimal analysis of LPP - [PDF Document] Post-optimal analysis of LPP - [PDF Document]](https://i1.rgstatic.net/publication/255639274_Post-optimality_Analysis_in_Bounded_Variables_Problem/links/53ef186e0cf26b9b7dcde89e/largepreview.png)


![Post-optimal analysis of LPP - [PDF Document] Post-optimal analysis of LPP - [PDF Document]](https://www.coursehero.com/thumb/b2/d0/b2d05659e09e2f2ea56fb8d61508e3dbe2ae8674_180.jpg)






![Post-optimal analysis of LPP - [PDF Document] Post-optimal analysis of LPP - [PDF Document]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/169662952/original/6ba6248bbb/1610936232?v\u003d1)